Read The Article Here https://time.com/6208174/maybe-the-universe-thinks/The concept that the Universe resembles a brain, a neural network, or a self-organizi…
Category: space – Page 272
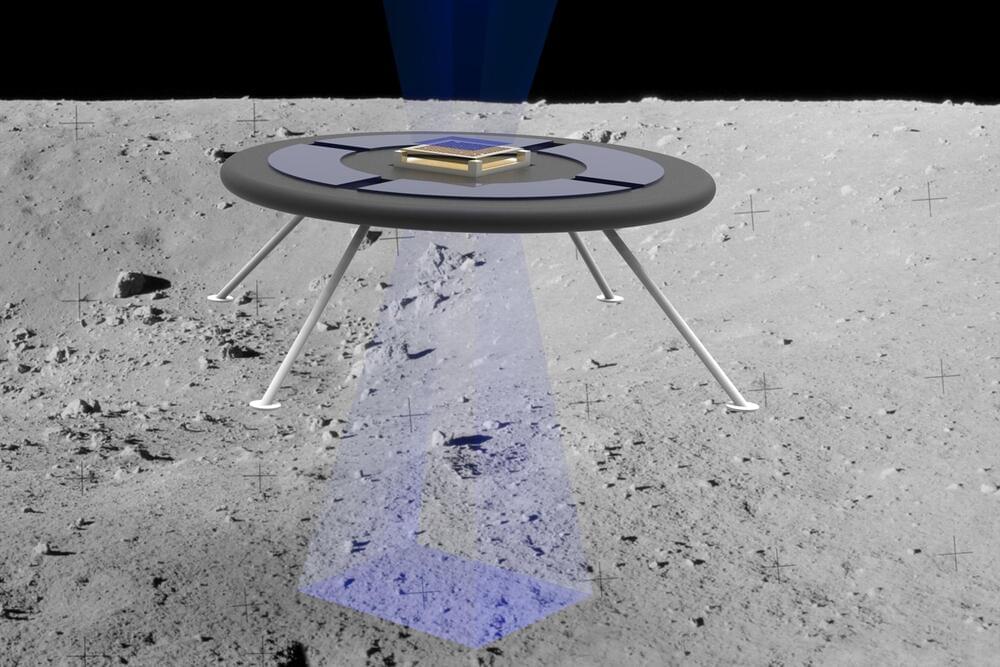

MIT engineers test an idea for a new hovering rover
Year 2021 face_with_colon_three
Because they lack an atmosphere, the moon and other airless bodies such as asteroids can build up an electric field through direct exposure to the sun and surrounding plasma. On the moon, this surface charge is strong enough to levitate dust more than 1 meter above the ground, much the way static electricity can cause a person’s hair to stand on end.
Engineers at NASA and elsewhere have recently proposed harnessing this natural surface charge to levitate a glider with wings made of Mylar, a material that naturally holds the same charge as surfaces on airless bodies. They reasoned that the similarly charged surfaces should repel each other, with a force that lofts the glider off the ground. But such a design would likely be limited to small asteroids, as larger planetary bodies would have a stronger, counteracting gravitational pull.
The MIT team’s levitating rover could potentially get around this size limitation. The concept, which resembles a retro-style, disc-shaped flying saucer, uses tiny ion beams to both charge up the vehicle and boost the surface’s natural charge. The overall effect is designed to generate a relatively large repulsive force between the vehicle and the ground, in a way that requires very little power. In an initial feasibility study, the researchers show that such an ion boost should be strong enough to levitate a small, 2-pound vehicle on the moon and large asteroids like Psyche.
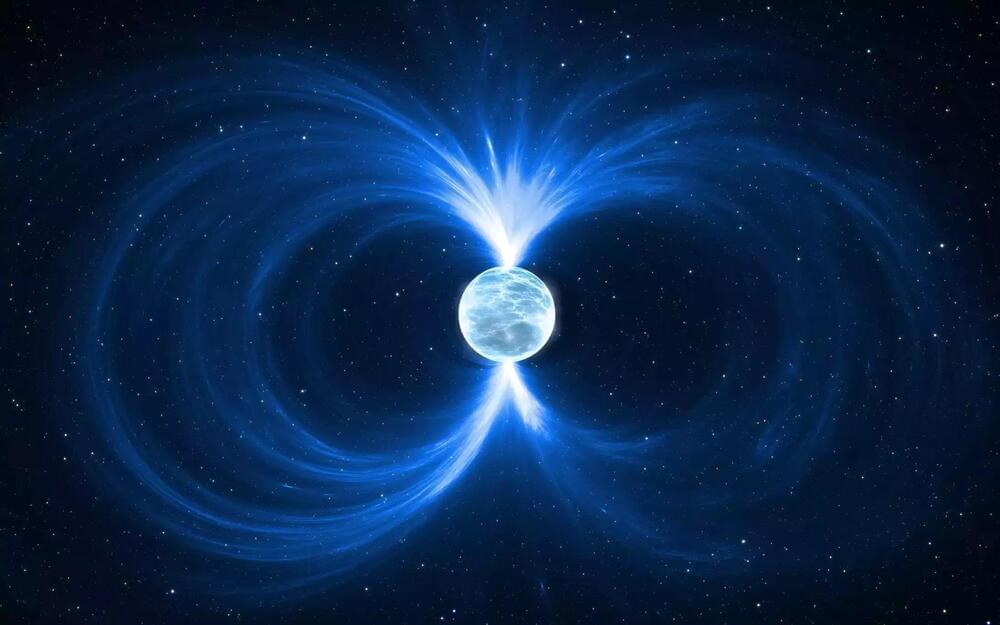
Astronomers used JWST to finally solve a 37-year mystery over one of the brightest cosmic explosions ever seen in modern history
Hunting for a neutron star
To discover what lies at the center of SN 1987A, astronomers needed a telescope big enough and advanced enough to detect evidence of radiation from a hidden neutron star.
Enter the James Webb Space Telescope: the largest, most powerful telescope ever launched into space that is already revolutionizing our understanding of the universe within its first two years of operation.
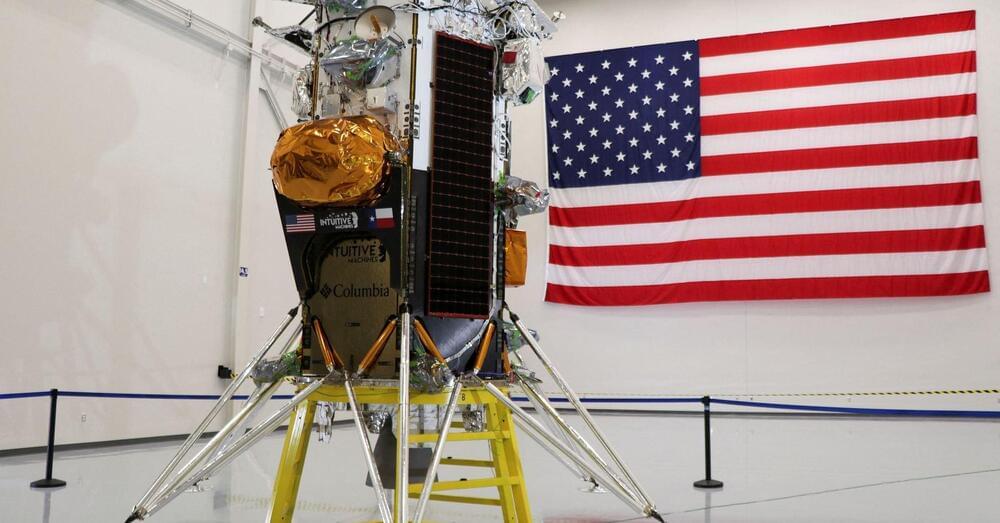

Intuitive Machines shares jump after successful moon landing
Shares of Intuitive Machines, which fell for two straight sessions before the landing, were among the top trending stocks on retail trader platform Stocktwits on Friday.
More shares traded in February — exceeding 200 million — than in the previous two years combined, according to LSEG data.
Ghaffarian, who is also the co-founder of Axiom Space, is on the board of other space organizations and has held numerous technical and management positions at Lockheed Martin, Ford Aerospace and Loral.

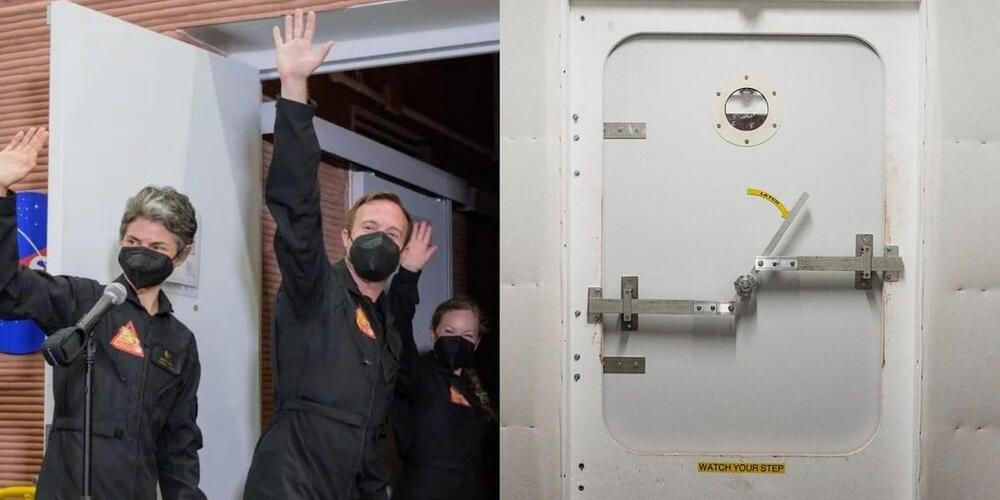
NASA seeks volunteers for a paid, yearlong simulated Mars mission
The agency says applicants must have a master’s degree with STEM qualifications and experience in the field, or a minimum of 1,000 hours piloting an aircraft or the requisite military experience. A bachelor of science degree in a STEM field also may be considered, NASA said.
“What we are looking for in this call is everyday civilians who are very astronaut-like to be research participants for us,” Bell said.
Compensation for participating in the mission is available, according to NASA, but an exact salary will be provided during the candidate screening process.


Experiment paves the way for new set of antimatter studies by laser-cooling positronium
AEgIS is one of several experiments at CERN’s Antimatter Factory producing and studying antihydrogen atoms with the goal of testing with high precision whether antimatter and matter fall to Earth in the same way.
In a paper published today in Physical Review Letters, the AEgIS collaboration reports an experimental feat that will not only help it achieve this goal but also pave the way for a whole new set of antimatter studies, including the prospect to produce a gamma-ray laser that would allow researchers to look inside the atomic nucleus and have applications beyond physics.
To create antihydrogen (a positron orbiting an antiproton), AEgIS directs a beam of positronium (an electron orbiting a positron) into a cloud of antiprotons produced and slowed down in the Antimatter Factory. When an antiproton and positronium meet in the antiproton cloud, the positronium gives up its position to the antiproton, forming an antihydrogen.

What determines greatness?/¿Qué es lo que determina la grandeza?
What would I have told my past self, back when my days started to get painful, confusing, and suffocating?
It is not yet possible to travel in time, but if you need the answer, I will tell you.
I would have said: You share the same nature as the cosmos. You are part of it, and therefore, it is likely that you are governed by the same principles. So trust that you will grow. Soon, the pressure of tragic experiences that now seem like grotesque monsters will be nothing more than proof that you can continue growing. Soon, you will look at these facts as you look at a small, lost asteroid — once it has fulfilled its task of making you grow, it will slowly be lost in infinity. But you will have expanded.
Solar Storm Alert — Live
Breaking X6.3 Solar flare erupted from the sun! What caused the cell phone communications to go down on the morning of the 22 of Feb 24? Timing was in line with X1.9 and X1.7 solar storms, but where they really strong enough or did something else occur? Either way this is a call to prepare!
See the Special Deals at My Patriot Supply: www.PrepWithGreg.com.
True Leaf Market brings you a great selection of Non GMO heirloom seed: http://www.pntrac.com/t/TUJGRklGSkJGT…
Eden Brothers’ seeds are non-GMO.
https://www.pntra.com/t/SENJRklJS0ZDR…
GoldBacks from Green Greg’s affiliate link:
https://www.defythegrid.com/goldbacks…
Use coupon code GreenGregs for 1% off.
Check out my Green Gregs Channel previous videos: