Jupiter and a slim crescent moon are the stand-out night sky sight in the evening sky right now.
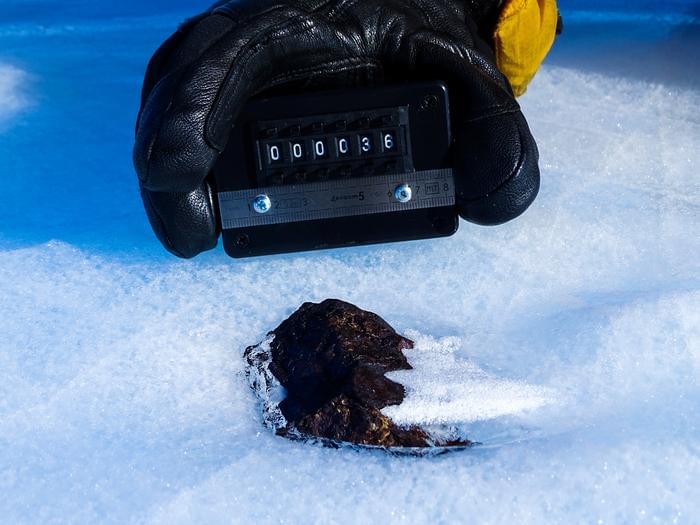




“We need to accelerate and intensify efforts to recover Antarctic meteorites,” said Dr. Harry Zekollari. “The loss of Antarctic meteorites is much like the loss of data that scientists glean from ice cores collected from vanishing glaciers – once they disappear, so do some of the secrets of the universe.”
How can climate change effect the search for meteorites in Antarctica? This is what a recent study published in Nature Climate Change hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated how melting snow and ice could prevent successful identification of meteorites, of which approximately 60 percent of all meteorites retrieved on Earth have been found in Antarctica. This study holds the potential to help scientists, climate change activists, and legislators better understand the impacts of climate change on science, as meteorites are crucial for gaining greater insight into the formation and evolution of the solar system and beyond.
With a combination of climate models, satellite observations, and artificial intelligence, the researchers estimate that at current rates, they will lose the ability to identify approximately 5,000 meteorites annually, with approximately 24 percent being lost by 2050 and potentially 76 percent by 2100.

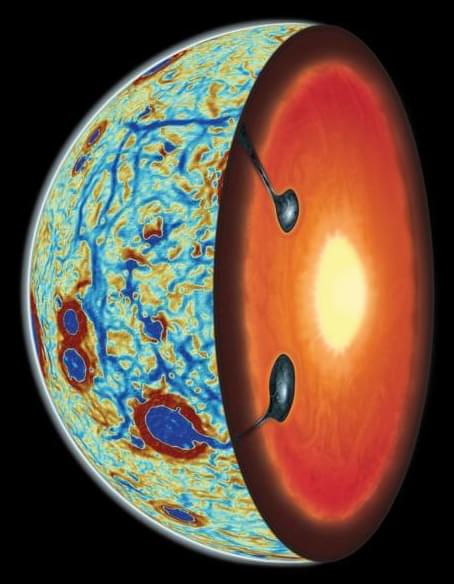
“For the first time we have physical evidence showing us what was happening in the moon’s interior during this critical stage in its evolution, and that’s really exciting,” said Dr. Jeff Andrews-Hanna.
Our Moon has long been hypothesized to have formed from a planet-sized object colliding with the Earth. But, what happened after and how can its unique geologic exterior and interior be explained? This is what a recent study published in Nature Geoscience hopes to address as an international team of researchers led by the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory (LPL) at the University of Arizona used a combination of spacecraft data and computer models to investigate the geologic processes that led to heavier elements being present on the nearside of the Moon, which is constantly facing Earth due to being tidally locked with our planet. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the geologic mechanisms behind planetary formation and could lead to gaining greater insight into how rocky planets like Earth and Mars formed.
For the study, the researchers used data from NASA’s GRAIL mission, which was used to map gravitational anomalies on the Moon, and computer models to determine the distribution of ilmenite, a combination of titanium and iron, across the Moon’s nearside and how much sunk into the Moon’s interior during the Moon’s formation and evolution. It has been previously hypothesized that while ilmenite sunk to the Moon’s interior early on, portions of it returned to the surface from volcanism, and the mechanisms behind these events have led scientists puzzled.


That is, until we drop an egg, spill our coffee, or an expensive vase falls off a shelf in our homes, reminding us that even the weakest of the four fundamental interactions known to physics, while hidden in plain sight, still exerts a significant influence on everything around us.
Some 1029 times weaker than the appropriately named weak force, which governs the radioactive decay of atoms, gravity is so subtle that it has virtually no effect at the subatomic level. Yet at the scale where interactions between objects are observable to us, gravity is the force that literally commands the motions of planets, as well as that of stars and galaxies. Even light, which universal laws govern to be the fastest thing in existence, cannot escape the influence of gravity.
Despite its ubiquity, gravity also remains one of the great mysteries of modern physics. While there remains no complete or perfect theory as to how gravity works, the best description of it remains the one Einstein gave us in 1915 with the publication of his general theory of relativity. To Einstein, gravity can be thought of not so much as a force acting on objects, but instead as a way to observe the curvature of spacetime itself that results from variances in the distribution of mass throughout the universe.
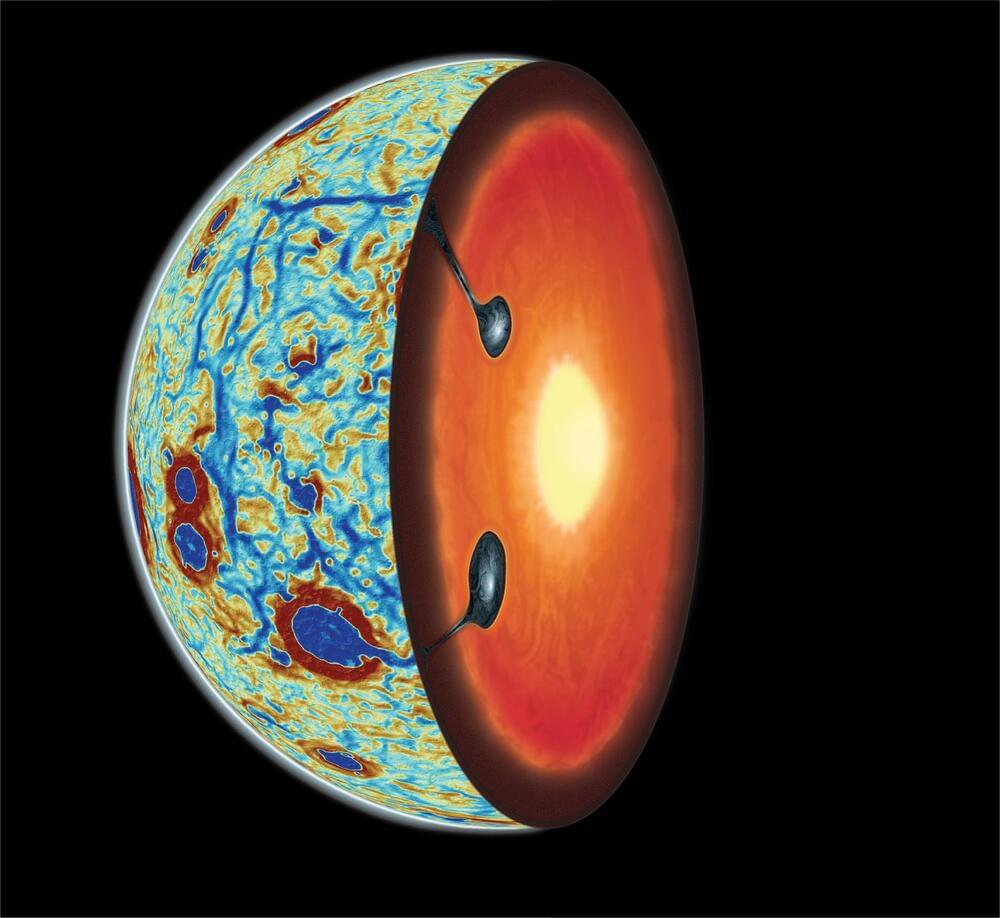
About 4.5 billion years ago, a small planet smashed into the young Earth, flinging molten rock into space. Slowly, the debris coalesced, cooled and solidified, forming our moon. This scenario of how the Earth’s moon came to be is the one largely agreed upon by most scientists. But the details of how exactly that happened are “more of a choose-your-own-adventure novel,” according to researchers in the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory who published a paper in Nature Geoscience.
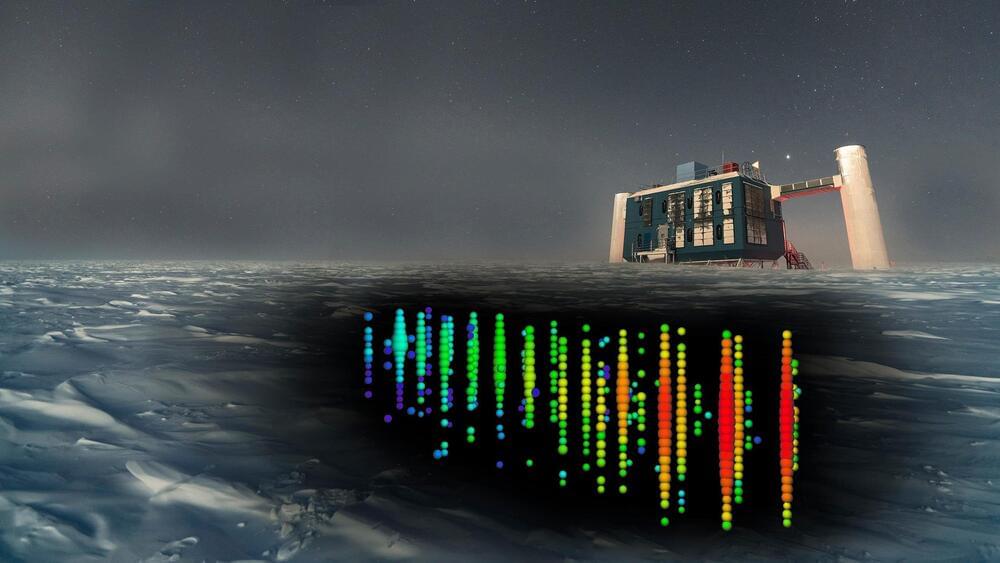

University of Copenhagen team contributes to an Antarctic large-scale experiment striving to find out if gravity also exists at the quantum level; An extraordinary particle able to travel undisturbed through space seems to hold the answer.
Several thousand sensors distributed over a square kilometer near the South Pole are tasked with answering one of the large outstanding questions in physics: does quantum gravity exist? The sensors monitor neutrinos – particles with no electrical charge and almost without mass – arriving at the Earth from outer space. A team from the Niels Bohr Institute (NBI), University of Copenhagen, has contributed to developing the method that exploits neutrino data to reveal if quantum gravity exists.
“If as we believe, quantum gravity does indeed exist, this will contribute to unite the current two worlds in physics. Today, classical physics describes the phenomena in our normal surroundings such as gravity, while the atomic world can only be described using quantum mechanics. The unification of quantum theory and gravitation remains one of the most outstanding challenges in fundamental physics. It would be very satisfying if we could contribute to that end,” says Tom Stuttard, Assistant Professor at NBI.
Researchers using Murriyang, CSIRO ’s Parkes radio telescope, have detected unusual radio pulses from a previously dormant star with a powerful magnetic field.
New results published today (April 8) in Nature Astronomy describe radio signals from magnetar XTE J1810-197 behaving in complex ways.
Magnetars are a type of neutron star and the strongest magnets in the Universe. At roughly 8,000 light years away, this magnetar is also the closest known to Earth.