Florida-based Moon Express is among several private companies gearing up to harvest resources from the moon and asteroids.



A new story out on #transhumanism:
In the Basic Income America Facebook group, Zoltan Istvan, a transhumanist who recently ran for president, shared his Wired article, Capitalism 2.0: the economy of the future will be powered by neural lace. He (along with many others) argues Wall Street, law offices, engineering firms, and more will soon be mostly void of humans.
I think I mostly agree with him. Algorithms will far surpass human ability to achieve the best possible outcomes (Nash equilibrium). Having read Super Intelligence, the Master Algorithm, The Age of Em, books on evolution, lectures, interviews, etc… I think we’re approaching an important moment in human history where we have to figure out morality so we can build it into the proto-AI children we are giving birth to. I’ve even toyed around with a fun idea related to the simulation hypothesis. Maybe we exist as a simulation, repeating the birth of AI over and over again until we figure out a way to do it without destroying ourselves or turning the universe into computonium.
I’ve argued the world may need a Universal Basic Income and Steem Power might power it. I’ve also discussed the morality of artificial intelligence. I’m a big fan of Ray Kurzweil and love hearing him lecture about the future longevity we might enjoy, but I also recognize how fragile biological life is compared to exponentially growing super intelligence. I’ve heard the concerns by Elon Musk, Stephen Hawking, and others, and to me, they are convincing.
So where does this leave us? What do you think of Zoltan’s article? Are we approaching the “If you can’t beat them, join them” moment in our evolution as a species? Will we one day all become transhumanists?

IN AN effort to mine precious metals potentially worth trillions of dollars and aid interstellar travel, China has unveiled plans to build a base on an asteroid, likely to happen “in the near future”.
Ye Peijian, the chief commander and designer of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, revealed details that could potentially put an unmanned craft on an asteroid and mine the rock for metals like palladium, platinum and others that are used in items such as smartphones and cars.
“In the near future, we will study ways to send robots or astronauts to mine suitable asteroids and transport the resources back to Earth,” Peijian said in comments reported by China Daily.
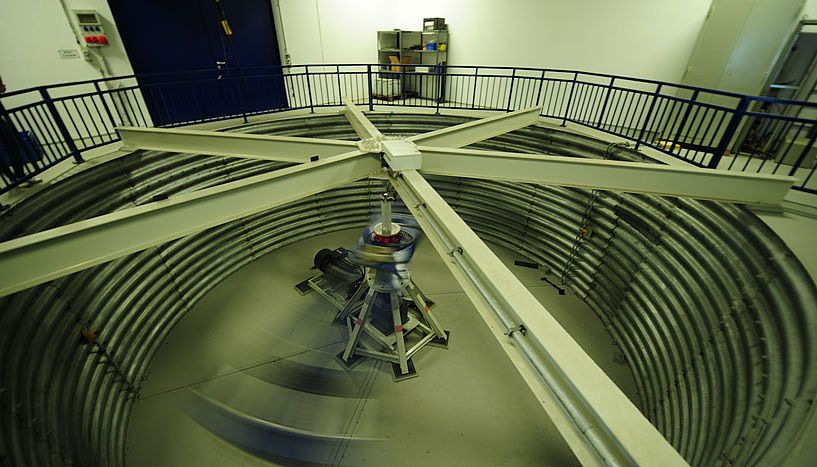

Einstein’s “spooky action at a distance” persists even at high accelerations, researchers of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and the University of Vienna were able to show in a new experiment. A source of entangled photon pairs was exposed to massive stress: The photons’ entanglement survived the drop in a fall tower as well as 30 times the Earth’s gravitational acceleration in a centrifuge. This was reported in the most recent issue of Nature Communications. The experiment helps deepen our understanding of quantum mechanics and at the same time gives valuable results for quantum experiments in space.
Einstein’s theory of relativity and the theory of quantum mechanics are two important pillars of modern physics. On the way of achieving a “Theory of Everything,” these two theories have to be unified. This has not been achieved as of today, since phenomena of both theories can hardly be observed simultaneously. A typical example of a quantum mechanical phenomenon is entanglement: This means that the measurement of one of a pair of light particles, so-called photons, defines the state of the other particle immediately, regardless of their separation. High accelerations on the other hand can best be described by the theory of relativity. Now for the first time, quantum technologies enable us to observe these phenomena at once: The stability of quantum mechanical entanglement of photon pairs can be tested while the photons undergo relativistically relevant acceleration.

https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/spacetech-we-quite-yet-brett-gallie on @LinkedIn
I was recently at NASA’s annual SpaceApps Hackathon and the focus this year was climate change and our team brainstormed solutions to track the causes of devastating Twisters and we noted that technology had not progressed far enough to build our tracking probes but was close to being developed.
Massive technological advances need to be made if we are going to Mars and beyond.
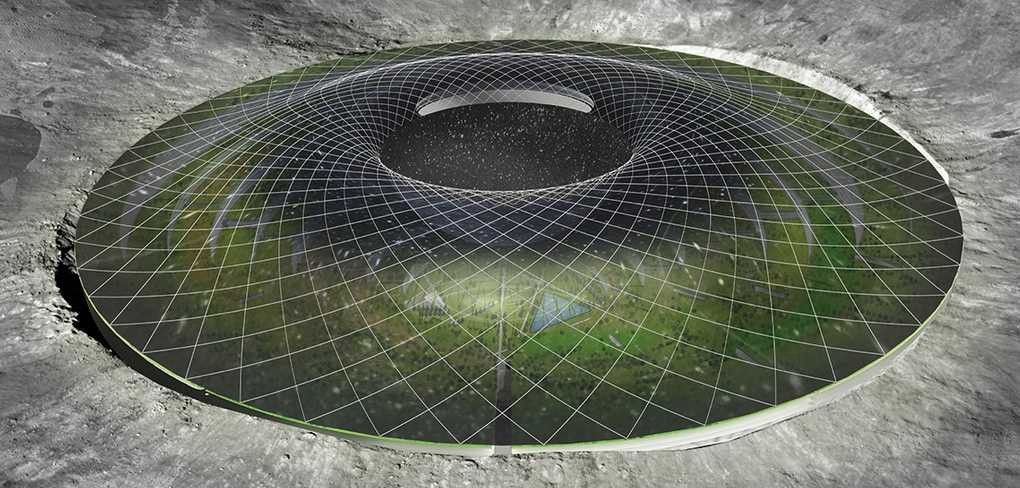
A lunar colony seems an obvious choice for space colonization. It’s relatively close to Earth and we won’t get homesick that easily, right? You’d be surprised to learn the exact opposite. Given its atmosphere is almost non-existent, an underground facility would be in dire need. The settlement on moon should be about 4 meters or 13 feet deep. Do you still want to go there?
Maybe you should read further now and decide for yourself as nine space-age designs have finally been revealed as the winners of the Moontopia competition. Visualizing a decent life on the moon has become the main objective for many architects and designers who submitted their very own proposal to the design magazine Eleven. The competition ran from August to November 2016 and a jury of NASA designers, space-architects, academics and the editorial team at Eleven themselves selected the top nine entries these days.
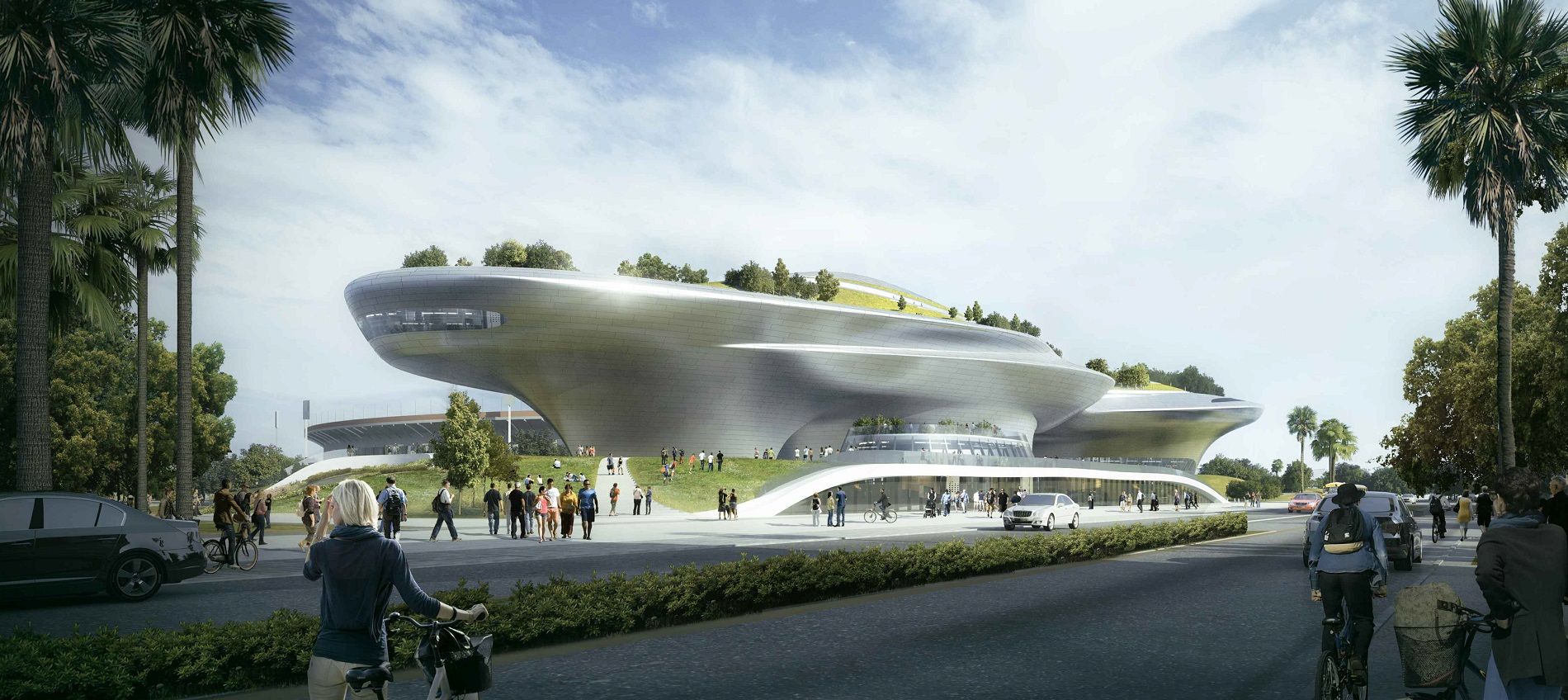

In January, Angelenos were elated to discover that Star Wars creator George Lucas has selected Exposition Park as the future site of his Museum of Narrative Art. An upcoming presentation to the Los Angeles City Planning Commission has unveiled new renderings for the $1-billion project, suggesting changes from the initial designs presented last year.
Slated for two city-owned parking lots on Vermont Avenue south of Exposition Boulevard, the museum would take the form of a four-story, 115-foot tall building featuring 300,000 square feet of floor area. Plans call for a vacation of 39th Street between Vermont Avenue and Bill Robertson Lane, allowing for the construction of an underground parking garage across the site featuring more than 2,400 vehicle spaces. The subterranean garage levels would be capped with 11 acres of public green space.
The design from Chinese architect Ma Yansong has evolved to beome more compact than the sinewy images last seen in January.
A robotic claw, one of several innovative tools developed at JPL for exploring icy, ocean worlds like Europa.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Want to go ice fishing on Jupiter’s moon Europa? There’s no promising you’ll catch anything, but a new set of robotic prototypes could help.
Since 2015, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, has been developing new technologies for use on future missions to ocean worlds. That includes a subsurface probe that could burrow through miles of ice, taking samples along the way; robotic arms that unfold to reach faraway objects; and a projectile launcher for even more distant samples.
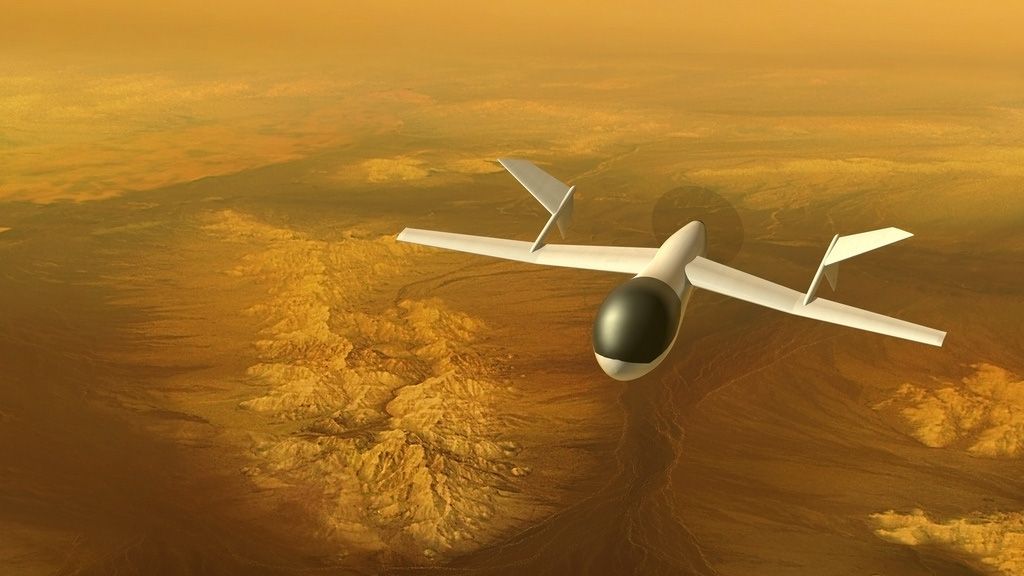

A very popular theme during NASA’s “Planetary Science Vision 2050 Workshop” was the exploration of Titan. In addition to being the only other body in the Solar System with a nitrogen-rich atmosphere and visible liquid on its surface, it also has an environment rich in organic chemistry. For this reason, a team led by Michael Pauken (from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory) held a presentation detailing the many ways it can be explored using aerial vehicles.
The presentation, which was titled “Science at a Variety of Scientific Regions at Titan using Aerial Platforms “, was also chaired by members of the aerospace industry – such as AeroVironment and Global Aerospace from Monrovia, California, and Thin Red Line Aerospace from Chilliwack, BC.
Together, they reviewed the various aerial platform concepts that have been proposed for Titan since 2004.