Starship could host entertainment and SpaceX is worth more than you think. What happened to last week’s Falcon 9? It’s Musk Reads: SpaceX Edition #145.
A version of this article appeared in the “Musk Reads” newsletter. Sign up for free here.

Starship could host entertainment and SpaceX is worth more than you think. What happened to last week’s Falcon 9? It’s Musk Reads: SpaceX Edition #145.
A version of this article appeared in the “Musk Reads” newsletter. Sign up for free here.
Engineers at the University of Washington are working on a new type of rocket engine that holds the promise of being lighter, more efficient, and simpler to make than conventional liquid-fuel rockets. Called a Rotational Detonation Engine (RDE), one of the biggest hurdles to making it practical is to develop mathematical models that can describe how the very unpredictable engine design works in order to make it more stable.
An RDE is a rocket engine that is similar to the pulse jet engines that powered the infamous German V1 cruise missile of the Second World War, which used a simple combustion chamber with an exhaust pipe at one end and spring-mounted slats on the front face. In operation, air would come in through the slats, mix with fuel, which was then detonated, producing a pulse of thrust. An RDE takes this idea one step further.
“A rotating detonation engine takes a different approach to how it combusts propellant,” says James Koch, a UW doctoral student in aeronautics and astronautics. “It’s made of concentric cylinders. Propellant flows in the gap between the cylinders, and, after ignition, the rapid heat release forms a shock wave, a strong pulse of gas with significantly higher pressure and temperature that is moving faster than the speed of sound.

Great woman.
Her impeccable calculations had already helped plot the successful flight of Alan B. Shepard Jr., who became the first American in space when his Mercury spacecraft went aloft in 1961. • • Johnson’s work over 33 years propelled many of America’s breakthroughs in space exploration, including Neil Armstrong’s “giant leap for mankind” on the Moon. • • Rest in Peace Ma’am 😓.
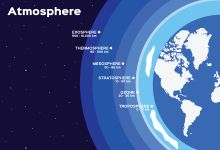
Sensors are usually thought of in terms of physical devices that receive and respond to electromagnetic signals – from everyday sensors in our smartphones and connected home appliances to more advanced sensors in buildings, cars, airplanes and spacecraft. No physical sensor or aggregation of electronic sensors, however, can continuously and globally detect disturbances that take place on or above the earth’s surface. But the physical atmosphere itself may offer such a sensing capability, if it can be understood and tapped into.
To that end, DARPA recently announced its Atmosphere as a Sensor (AtmoSense) program, whose goal is to understand the fundamentals of energy propagation from the ground to the ionosphere to determine if the atmosphere can be used as a sensor. A Proposers Day is scheduled for February 14, 2020, in Arlington, Virginia.
It’s well known that energy propagates from the Earth’s surface to the ionosphere, but the specifics of how that happens is not currently known enough to use the atmosphere as a sensor. Scientific literature has clearly documented that events like thunderstorms, tornadoes, volcanos, and tsunamis make big “three-dimensional wakes” that propagate to the upper reaches of the ionosphere and leave a mark there. Since that energy traverses several other layers of atmosphere – the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere – on its way up to the ionosphere, the idea is to try and identify the disturbances the “wake” is making along its way to see if researchers can capture information to indicate what type of event caused it.

As a teenage boy, Elon Musk felt a “personal obligation” for the fate of mankind, according to the book “Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic Future” by Ashlee Vance.
Musk’s love of books and the lessons he took from them inspired him to create “cleaner energy technology or [build] spaceships to extend the human species’s reach” in the future, according to Vance.
One set of those books Musk still recommends today: the seven-book “Foundation” science fiction series by scientist and author Isaac Asimov.
Quantum Vacuum Plasma Thruster
White shows me into the facility and ushers me past its central feature, something he calls a quantum vacuum plasma thruster (QVPT). The device looks like a large red velvet doughnut with wires tightly wound around a core, and it’s one of two initiatives Eagleworks is pursuing, along with warp drive. It’s also secret. When I ask about it, White tells me he can’t disclose anything other than that the technology is further along than warp drive … Yet when I ask how it would create the negative energy necessary to warp space-time he becomes evasive.

In some biology classes, teachers will place vials of spit into a funny looking contraption and let it spin around the samples until the stringy DNA separates from the rest of the saliva. It’s a pretty rudimentary experiment, but it quickly gets to the heart of not only your own genetic material, but also how centrifugal force works: Spinning really fast in a circle creates a force strong enough to push a moving object out and away from the center of its path.
But what happens when that moving object is a rocket that weighs thousands of pounds? We might find out as soon as this year, when a cryptic startup called SpinLaunch starts suborbital test flights of a rocket that is launched using an enormous centrifuge.
Here’s the gist: A centrifuge the size of a football field will spin a rocket around in circles for about an hour until its speed eventually exceeds 5,000 miles per hour. At that point, the rocket and its payload will feel forces 10,000 times stronger than gravity. When the centrifuge finally releases the rocket at launch speed, it should, practically speaking, fly through the stratosphere until it fires its engines at the periphery of our atmosphere.

Warning: This article presents information that sounds like it comes out of a high-tech Hollywood sci-fi production. I suggest you first view the patent filing linked here to verify its credibility before proceeding.
Because the patent was filed by the US Navy and is now under an “Active” status, this is the real deal. This is NOT a work of fiction.
The Short Story
Violent Detonations
Engineers have long suspected such a design could revolutionize the fuel efficiency of modern engines, but until now, there was one major problem.
“We have tons of data about these engines, but we don’t understand what is going on,” Koch admitted.