Zero 2 Infinity wants to launch passengers 40 kilometers into space with helium balloons at a much lower price, at just over $130000.



Shouldn’t NASA — National Aeronautics and Space Administration already be building a moon-base with Elon Musk at SpaceX as well as Russia and China? Congress should fund space travel.
RUSSIA and China are joining forces as they prepare to sign a historic deal to build the first moon base after they snubbed the US.
The two countries are to collaborate on the international lunar structure, which was thought up by China — the latest build in the space-race against America.
🚀 Follow our Mars landing live blog for up the minute updates from Perseverance…
The purpose of the International Lunar Research Stations (ILRS), is to create a long-term robotic presence on the Moon by the start of the next decade, before eventually establishing a sustained human presence.





A veteran #Falcon9 is set to become @SpaceX’s 3rd most-flown booster later tonight, as B1059 launches for the 6th time.
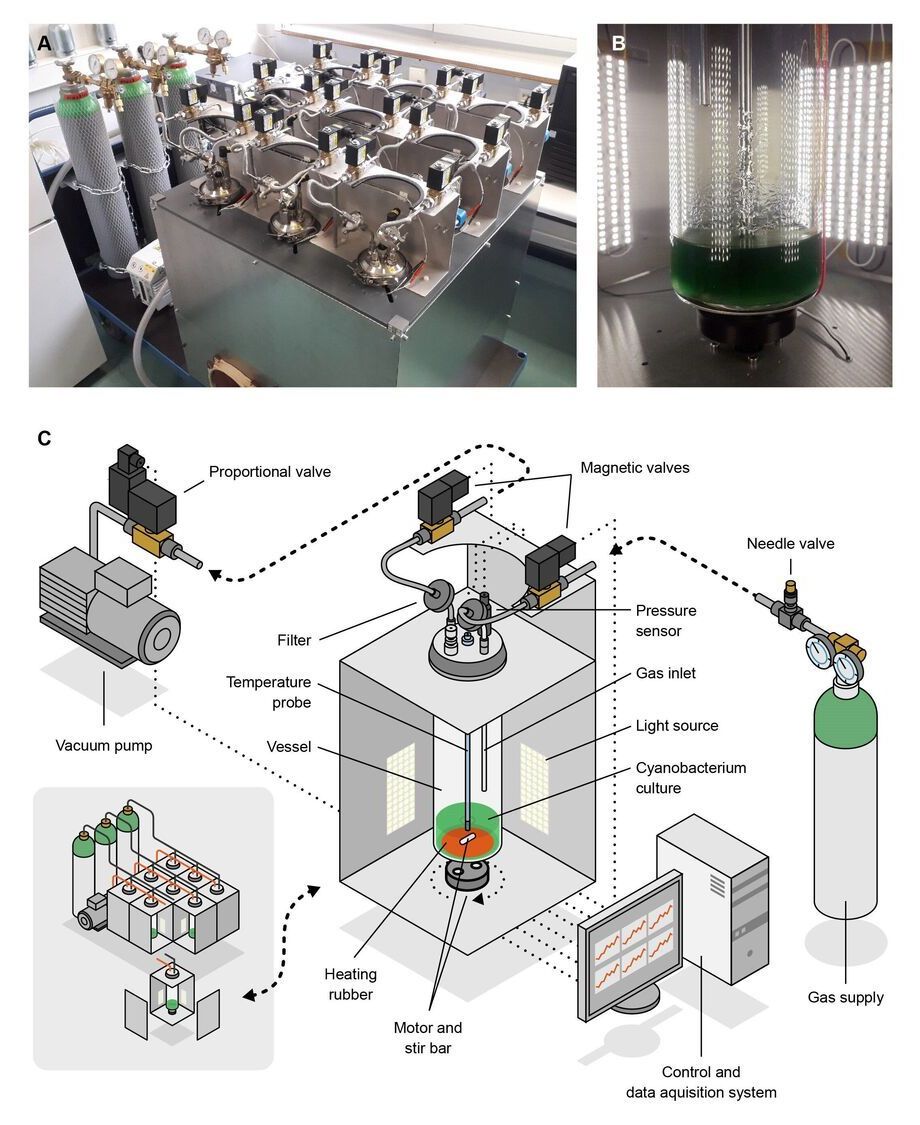
NASA, in collaboration with other leading space agencies, aims to send its first human missions to Mars in the early 2030s, while companies like SpaceX may do so even earlier. Astronauts on Mars will need oxygen, water, food, and other consumables. These will need to be sourced from Mars, because importing them from Earth would be impractical in the long term. In Frontiers in Microbiology, scientists show for the first time that Anabaena cyanobacteria can be grown with only local gases, water, and other nutrients and at low pressure. This makes it much easier to develop sustainable biological life support systems.
