A new type of solar cell made using selenium and silicon could offer a cost advantage while also delivering energy conversion efficiency.
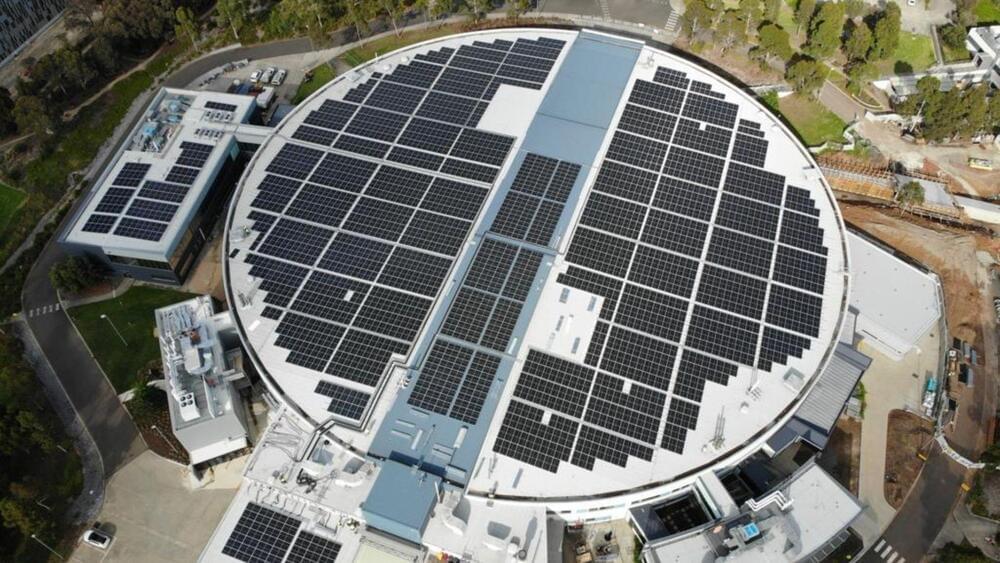


The Australian Synchrotron, a crown jewel of Australian scientific infrastructure, is making major strides towards sustainable energy independence. The nuclear research facility recently completed the installation of 3,200 solar panels which now blankets the facility’s rooftops. This move is expected to generate substantial savings and support Synchrotron’s world-class research.
The state-of-the-art particle accelerator has now gone green with a 1.59 MW/ 1,668 kWh rooftop solar system. The facility will save about $2 million in energy costs over the next five years.

An innovative, flexible solar cell being developed in South Korea has passed a crucial stress test.
Researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology (KAIST) are working on a rubber-like sun-catcher made from organic materials. The idea is for these elastic cells to one day help power the wearable technology that is becoming more prevalent in society, per a KAIST research report.
“Through this research, we not only developed the world’s best performing stretchable organic solar cell, but it is also significant that we developed a new polymer that can be applicable as a base material for various electronic devices that needs to be malleable and/or elastic,” study lead Professor Bumjoon Kim said in the summary.



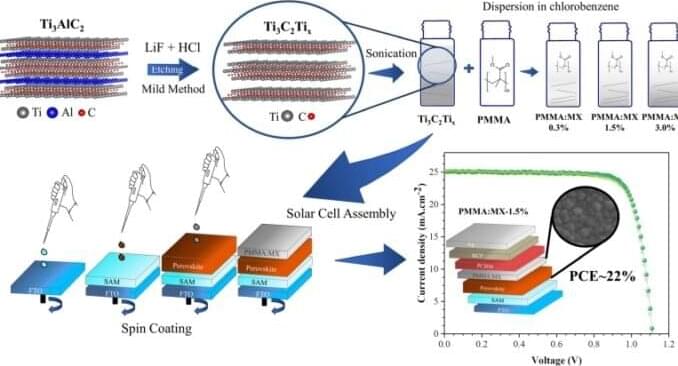
In an article published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry C, Brazilian researchers describe a strategy to enhance the efficiency and stability of solar cells made of perovskite, a semiconductor material produced in the laboratory. The results of the project could be highly positive for the future of the solar power sector.
Developed by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Bauru, Brazil, the method involves the use of a class of materials known as MXenes, a family of two-dimensional materials with a graphene-like structure combining transition metals, carbon and/or nitrogen, and surface functional groups such as fluoride, oxygen or hydroxyl. Their properties include high electrical conductivity, good thermal stability, and high transmittance (relating to the amount of light that passes through a substance without being reflected or absorbed).
In the study, the MXene Ti3C2Tx was added to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) to form a passivation coating, which was spin-coated on top of the perovskite layer of inverted solar cells. Passivation coatings are designed to mitigate possible defects in polycrystalline solids (perovskite in this case) due to interaction with the environment or to their internal structure.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform technologies as diverse as solar panels, in-body medical sensors and self-driving vehicles. But these applications are already pushing today’s computers to their limits when it comes to speed, memory size and energy use.
Fortunately, scientists in the fields of AI, computing and nanoscience are working to overcome these challenges, and they are using their brains as their models.
That is because the circuits, or neurons, in the human brain have a key advantage over today’s computer circuits: they can store information and process it in the same place. This makes them exceptionally fast and energy efficient. That is why scientists are now exploring how to use materials measured in billionths of a meter— nanomaterials—to construct circuits that work like our neurons. To do so successfully, however, scientists must understand precisely what is happening within these nanomaterial circuits at the atomic level.