Japan’s upcoming space-based solar power demonstration will beam power to Earth next year.



Now that we can generate clean, renewable energy from the wind and sun, one of the most pressing questions facing the clean energy transition is how to effectively store that energy for future use. For one city in Finland, the answer is a giant underground cavern.
Vantaan Energia has announced that it will construct a massive underground seasonal thermal energy storage facility for the city of Vantaa, the country’s fourth-most-populous municipality. The facility will be twice the size of Madison Square Garden, New Atlas reported.
“The world is undergoing a huge energy transition,” Vantaan Energia CEO Jukka Toivonen said. “Wind and solar power have become vital technologies in the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy. The biggest challenge of the energy transition so far has been the inability to store these intermittent forms of energy for later use. Unfortunately, small-scale storage solutions, such as batteries or accumulators, are not sufficient; large, industrial-scale storage solutions are needed.”
A couple of solar-sector manufacturers have a powerhouse agreement that reaches a unique benchmark. Thanks to a $400 million, three-year deal between Heliene and Suniva, solar panels and cells will be entirely made in the U.S., a unique combination until now.
Electrek reports that to this point, solar cells — the contraption that turns sunlight into electricity — were imported.
“Heliene is proud to embark on this historic partnership with Suniva at a time when the U.S. is poised to capture a greater share of the global solar market by bolstering domestic manufacturing and onshoring of supply,” Heliene CEO Martin Pochtaruk said in a press release.
Scientists developed a device that combines wind and solar to harvest clean energy more efficiently and create a self-cleaning solar panel.

Researchers at Aalto University have discovered a new force acting on water droplets moving over superhydrophobic surfaces like black silicon by adapting a novel force measurement technique to uncover the previously unidentified physics at play. This force, identified as air-shearing, challenges previous understandings and suggests modifications in the design of these surfaces to reduce drag, potentially improving their efficiency and application in various fields.
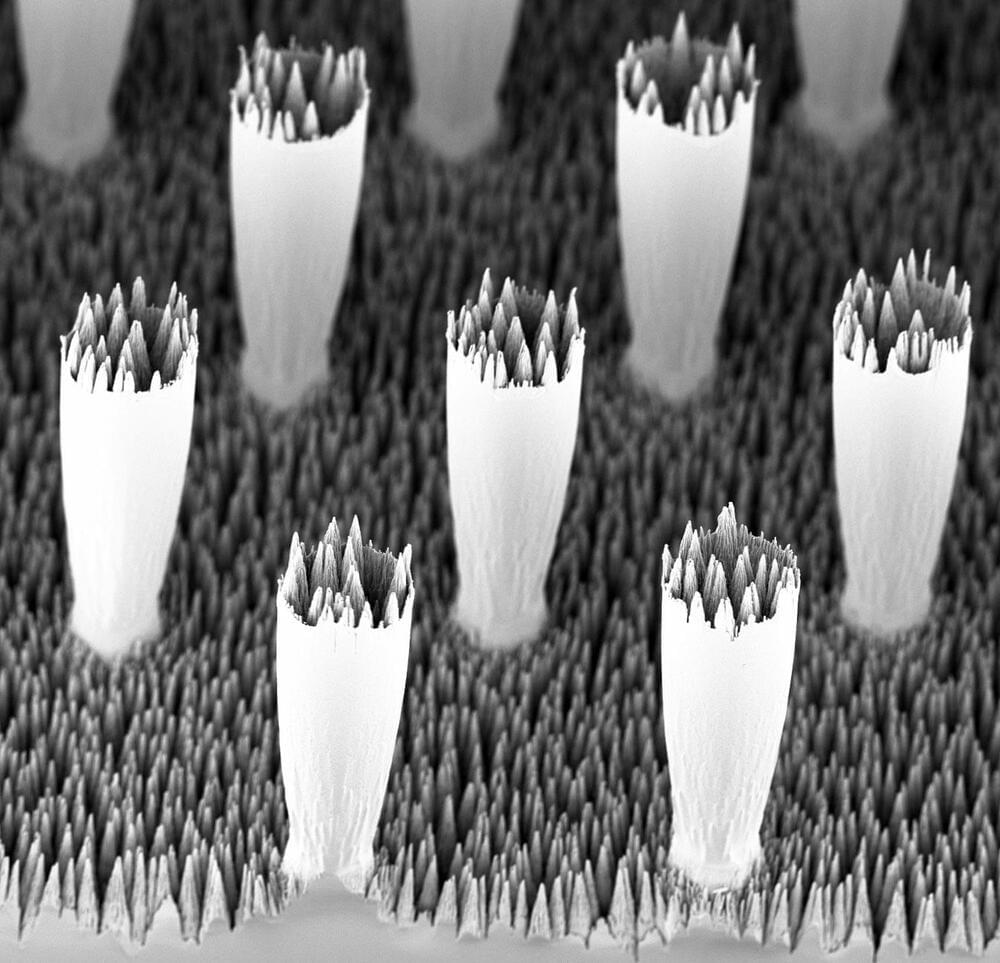
Microscopic chasms forming a sea of conical jagged peaks stipple the surface of a material called black silicon. While it’s commonly found in solar cell tech, black silicon also moonlights as a tool for studying the physics of how water droplets behave.
Black silicon is a superhydrophobic material, meaning it repels water. Due to water’s unique surface tension properties, droplets glide across textured materials like black silicon by riding on a thin air-film gap trapped beneath. This works great when the droplets move slowly—they slip and slide without a hitch.
Battery prices are dropping significantly, leading to a future of cheaper electric vehicles, battery storage, solar energy, and cleaner air Questions to inspire discussion What is the impact of dropping battery prices? —Dropping battery prices will lead to cheaper electric vehicles, battery storage, solar energy, and.
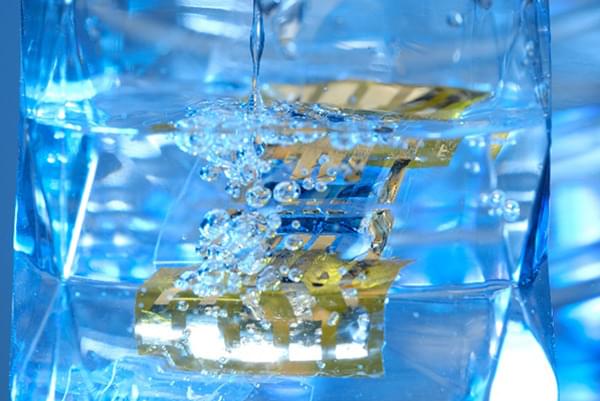

Researchers from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science and collaborators have developed an organic photovoltaic film that is both waterproof and flexible, allowing a solar cell to be put onto slothes and still function correctly after being rained on or even washed.
One of the potential uses of organic photovoltaics is to create wearable electronics — devices that can be attached to clothing that can monitor medical devices, for example, without requiring battery changes.
However, researchers have found it challenging to achieve waterproofing without the use of extra layers that end up decreasing the flexibility of the film.

The 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was focused on quantum dots – objects so tiny, they’re controlled by the strange and complex rules of quantum physics. Many quantum dots used in electronics are made from toxic substances, but their nontoxic counterparts are now being developed and explored for uses in medicine and in the environment. One team of researchers is focusing on carbon-and sulfur-based quantum dots, using them to create safer invisible inks and to help decontaminate water supplies.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
Quantum dots are synthetic nanometer-scale semiconductor crystals that emit light. They are used in applications such as electronics displays and solar cells. “Many conventional quantum dots are toxic, because they’re derived from heavy metals,” explains Md Palashuddin Sk, an assistant professor of chemistry at Aligarh Muslim University in India. “So, we’re working on nonmetallic quantum dots because they’re environmentally friendly and can be used in biological applications.”