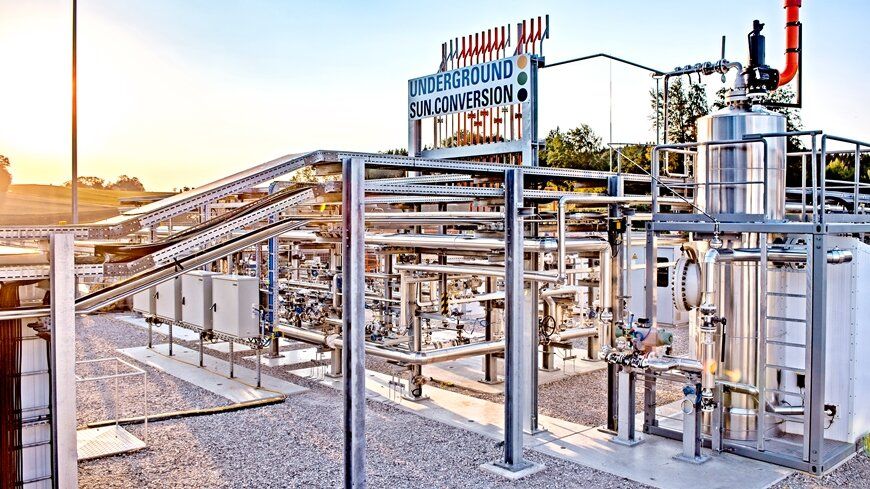
During the winter months, renewable energy is in short supply throughout Europe. An international project is now considering an unconventional solution: Renewable hydrogen and carbon dioxide are pumped into the ground together, where naturally occurring microorganisms convert the two substances into methane, the main component of natural gas.
Underground Sun Conversion technology, patented by the Austrian energy company RAG Austria AG, offers a way to seasonally store renewable energy on a large scale and make it available all year round. In summer, this involves converting surplus renewable energy—solar power, for instance—into hydrogen (H2). This is then stored together with carbon dioxide (CO2) in natural underground storage facilities—for example, former natural gas deposits—at a depth of over 1000 meters.
This is where little helpers come into play: Microorganisms from prehistoric times, so-called archaea, convert hydrogen and CO2 into renewable methane (CH4) via their metabolism. Archaea are found all over the world, mainly in anaerobic, i.e. low-oxygen environments; they were responsible for converting biomass into natural gas millions of years ago. By feeding hydrogen and CO2 into suitable porous sandstone deposits, this process can be started all over again. The methane “produced” in the depth can then be withdrawn from the reservoirs during winter and used in a variety of ways as CO2-neutral natural gas.