In this episode of Universe of Art, astrophysicist Dr. Erin Macdonald talks about consulting on the famous series and the real (and fictional) science on screen.
Learn more www.sciencefriday.com/startrek
In this episode of Universe of Art, astrophysicist Dr. Erin Macdonald talks about consulting on the famous series and the real (and fictional) science on screen.
Learn more www.sciencefriday.com/startrek
👉 Invest in Blue-chip Art by signing up for Masterworks: https://www.masterworks.art/anastasi.
Purchase shares in great masterpieces from Pablo Picasso, Banksy, Andy Warhol, and more.
See important Masterworks disclosures: https://www.masterworks.com/about/disclaimer?utm_source=anas…subscriber.
Mentioned Videos:
AI designing Computer Chips: https://youtu.be/NeHgMaIkPuY
Deepmind AI made a Breakthrough in Math: https://youtu.be/DU6WINoehrg.
Deepmind Paper “Faster sorting algorithms discovered using deep reinforcement learning”:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06004-9
👉 Support me at Patreon ➜ https://www.patreon.com/AnastasiInTech.
📩 Sign up for my Deep In Tech Newsletter for free! ➜ https://anastasiintech.substack.com
Dr. Michael Roberts, Ph.D. is Chief Science Officer of the International Space Station National Laboratory (https://www.issnationallab.org/), and Vice President at the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS — https://www.issnationallab.org/about/center-for-the-advancem…dership/), which as manager of the ISS National Laboratory in partnership with NASA, is responsible to the nation for enabling access to the International Space Station for research, technology development, STEM education, and commercial innovation in space as a public service to foster a scalable and sustainable low Earth orbit economy.
Before joining CASIS in 2013, Dr. Roberts worked as a microbial ecologist, principal investigator, and research group lead in the NASA Advanced Life Support program at the Kennedy Space Center.
Prior to arriving at NASA-KSC in 1999, Dr. Roberts completed an undergraduate degree in biology at Maryville College, a doctorate in microbiology at Wesleyan University and post-doctoral research at the Center for Microbial Ecology at Michigan State University and the RIKEN Institute in Wako-shi, Japan.

Human cerebral organoids are three-dimensional biological cultures grown in the laboratory to mimic as closely as possible the cellular composition, structure, and function of the corresponding organ, the brain. For now, cerebral organoids lack blood vessels and other characteristics of the human brain, but are also capable of having coordinated electrical activity. They have been usefully employed for the study of several diseases and the development of the nervous system in unprecedented ways. Research on human cerebral organoids is proceeding at a very fast pace and their complexity is bound to improve. This raises the question of whether cerebral organoids will also be able to develop the unique feature of the human brain, consciousness. If this is the case, some ethical issues would arise. In this article, we discuss the necessary neural correlates and constraints for the emergence of consciousness according to some of the most debated neuroscientific theories. Based on this, we consider what the moral status of a potentially conscious brain organoid might be, in light of ethical and ontological arguments. We conclude by proposing a precautionary principle and some leads for further investigation. In particular, we consider the outcomes of some very recent experiments as entities of a potential new kind.


Philosophy is often ridiculed by scientists as being little more than armchair speculation. Stephen Hawking famously declared it “dead.” This is unfortunate because the scientific method itself is a manifestation of philosophical thought arising from the subdiscipline known as epistemology. Historically, science and philosophy have worked hand-in-glove to advance our understanding of the world. In fact, “science” went by the moniker “natural philosophy” for much of history.
Scientists perhaps should be a bit more grateful. Advances in social and political philosophy helped prevent some scientists who upset the established order from being executed — but that’s a discussion for another day. Here, we will examine three philosophical insights that directly led to advances in how science is performed.
“What makes science different from everything else?” is inherently a philosophical question. That means that philosophy helps define what science is. This is important because, to learn about the world, we need to be sure of the validity of our methods. For most of the history of Western philosophy, Aristotle’s ideas reigned supreme. While Aristotle’s idea of finding causes through science was largely based on deductive reasoning, experimentation was not seen as a vital part of science.
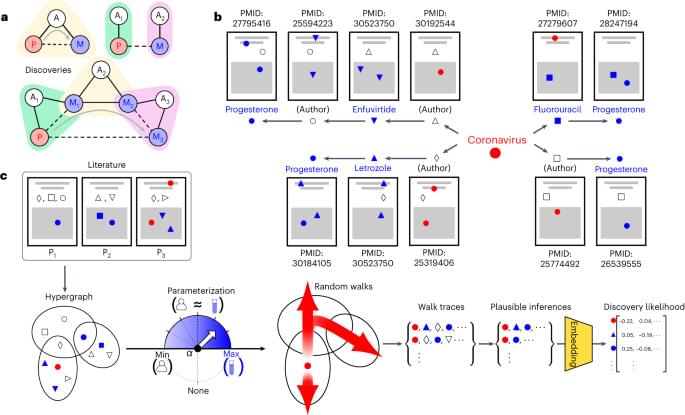
Can human-aware artificial intelligence help accelerate science? In this article, the authors incorporate the distribution of human expertise by training unsupervised models on simulated inferences cognitively accessible to experts and show that this substantially improves the models’ predictions of future discoveries, but also enables AI to generate high-value alternatives that complement human discoveries.

In today’s column, I am going to identify and explain the momentous pairing of both generative AI and data science. These two realms are each monumental in their own respective ways, thus they are worthy of rapt attention on a standalone basis individually. On top of that, when you connect the dots and bring them together as a working partnership, you have to admire and anticipate big changes that will arise, especially as the two fields collaboratively reinvent data strategies all told.
This is entirely tangible and real-world, not merely something abstract or obtuse.
I will first do a quick overview of generative AI. If you are already versed in generative AI, perhaps do a fast skim on this portion.
Foundations Of Generative AI
Generative AI is the latest and hottest form of AI and has caught our collective devout attention for being seemingly fluent in undertaking online interactive dialoguing and producing essays that appear to be composed by the human hand. In brief, generative AI makes use of complex mathematical and computational pattern-matching that can mimic human compositions by having been data-trained on the text and other content found on the Internet. For my detailed elaboration on how this works see the link here.