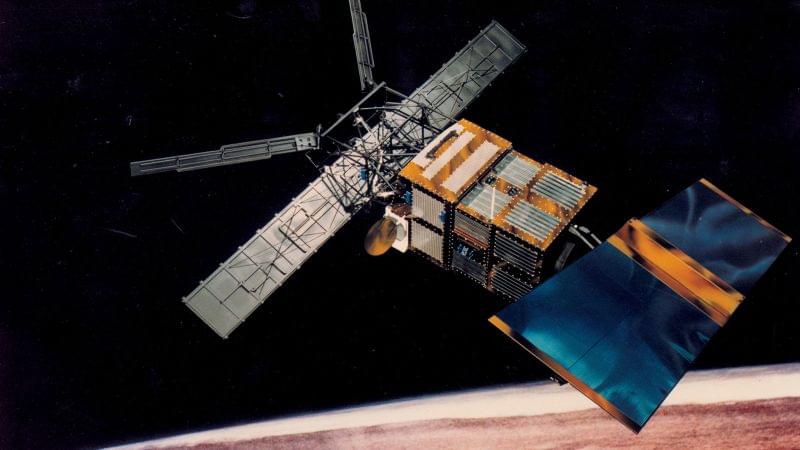
A European Space Agency satellite is expected to reenter and largely burn up in Earth’s atmosphere on Wednesday morning.
The agency’s Space Debris Office, along with an international surveillance network, is monitoring and tracking the Earth-observing ERS-2 satellite, which is predicted to make its reentry at 3:53 p.m. ET Wednesday, with a 7.5-hour window of uncertainty. The ESA is also providing live updates on its website.
“As the spacecraft’s reentry is ‘natural’, without the possibility to perform manoeuvers, it is impossible to know exactly where and when it will reenter the atmosphere and begin to burn up,” according to a statement from the agency.