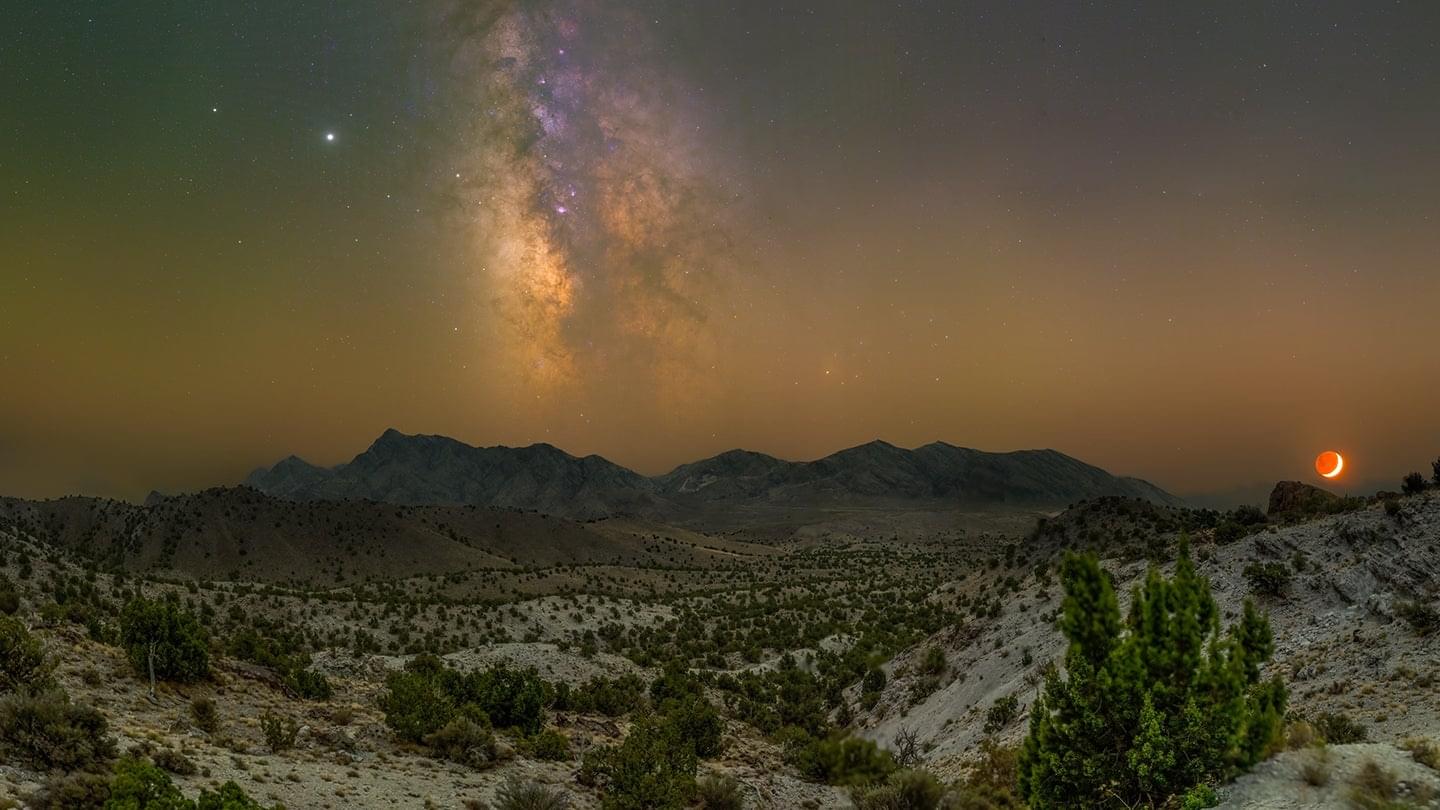
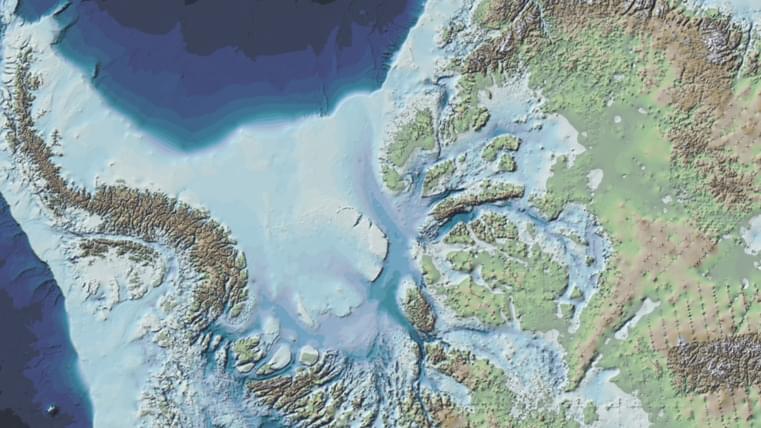
Bedmap3 is the most fine-grain map to date of the landscape beneath Antarctica’s ice. Scientists created it using more than 60 years’ worth of data from satellites, ships and dog-drawn sleds.


Discovering new deposits of critical and rare earth minerals is paramount to delivering global net-zero ambitions. However, finding new ore bodies is becoming more challenging due to increasing costs and geopolitical tensions. What is more, much of the low-hanging fruit, so to speak, has already been exploited.
Could technological advances help broaden the search and speed up the process? Dr Bryony Richards, a senior research scientist with the Energy & Geoscience Institute at the University of Utah in the US, believes so.
Richards and her colleagues are incorporating NASA’s and Japan’s global Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) imagery with that of new satellite data, advances in computing power and AI. With this approach, they are developing a comprehensive first-of-a-kind method to uncover the ‘fingerprints’ of mineral deposits that could eventually provide a more cost and time-effective way of mapping minerals in remote areas.
Researchers in Utah are combining satellites, hyperspectral imaging and AI to discover mineral deposits in remote locations.
NASA’s upcoming EZIE mission will use three small satellites to study electrojets — powerful electrical currents in the upper atmosphere linked to auroras. These mysterious currents influence geomagnetic storms that can disrupt satellites, power grids, and communication systems. By mapping how electrojets evolve, EZIE will improve space weather predictions, helping to safeguard modern technology.
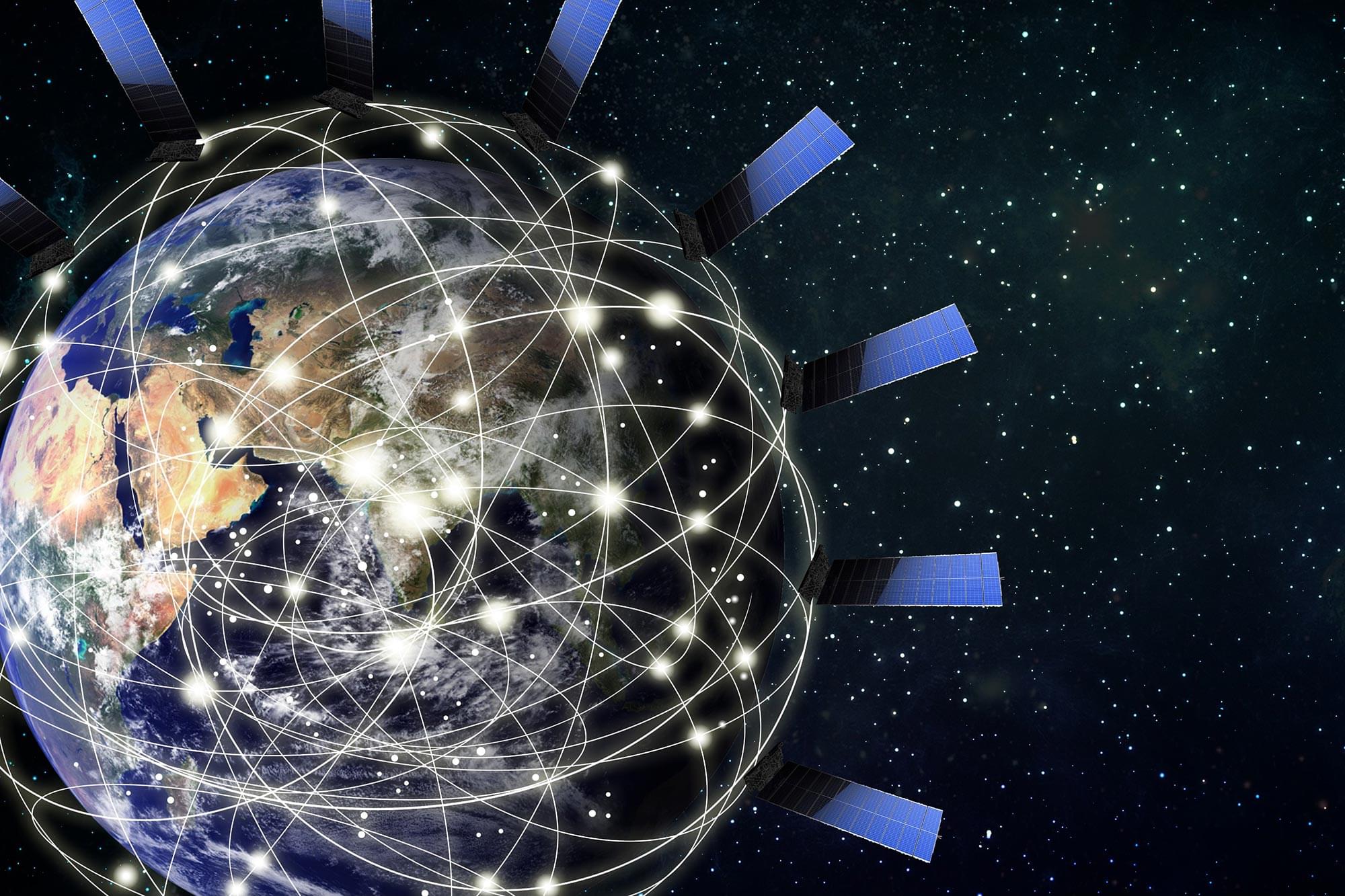

Unlocking New Data for Earth Observation
Reliable data is one of the most valuable tools in scientific research. The more data sources scientists can access, the more accurate their findings become. Until recently, researchers in navigation and satellite geodesy saw a major missed opportunity — while thousands of satellites in mega-constellations orbited Earth for communication purposes, their signals couldn’t be used for positioning or Earth observation.

TAMPA, Fla. — Star Catcher Industries, a startup designing spacecraft to beam solar energy to other satellites in low Earth orbit, has secured funding from Florida’s economic development agency to demonstrate the technology at a former Space Shuttle landing site.
Space Florida is providing a $2 million financial package for the one-year-old venture, Star Catcher CEO Andrew Rush told SpaceNews March 7, with most of the funds supporting tests this summer from Space Florida’s Launch and Landing Facility at the Cape — one of the longest runways in the world.
Rush said Star Catcher plans to use the facility to demonstrate its ability to beam hundreds of watts of energy to multiple simulated satellites simultaneously from more than a kilometer away, marking a critical proof point for the Jacksonville, Florida-based startup’s technology.

Imagine a large city recovering from a devastating hurricane. Roads are flooded, the power is down, and local authorities are overwhelmed. Emergency responders are doing their best, but the chaos is massive.
AI-controlled drones survey the damage from above, while intelligent systems process satellite images and data from sensors on the ground and air to identify which neighborhoods are most vulnerable.
Meanwhile, AI-equipped robots are deployed to deliver food, water and medical supplies into areas that human responders can’t reach. Emergency teams, guided and coordinated by AI and the insights it produces, are able to prioritize their efforts, sending rescue squads where they’re needed most.

NASA and the Italian Space Agency made history on March 3 when the Lunar GNSS Receiver Experiment (LuGRE) became the first technology demonstration to acquire and track Earth-based navigation signals on the moon’s surface.
The LuGRE payload’s success in lunar orbit and on the surface indicates that signals from the GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) can be received and tracked at the moon. These results mean NASA’s Artemis missions, or other exploration missions, could benefit from these signals to accurately and autonomously determine their position, velocity, and time. This represents a steppingstone to advanced navigation systems and services for the moon and Mars.
“On Earth we can use GNSS signals to navigate in everything from smartphones to airplanes,” said Kevin Coggins, deputy associate administrator for NASA’s SCaN (Space Communications and Navigation) Program. “Now, LuGRE shows us that we can successfully acquire and track GNSS signals at the moon. This is a very exciting discovery for lunar navigation, and we hope to leverage this capability for future missions.”

Back in 1971, a couple of British astronomers predicted the existence of a black hole at the center of our galaxy. And in 1974, other astronomers found it, naming it Sagittarius A*.
Since then, astronomers have discovered that a similar “supermassive black hole” sits at the center of almost every other large galaxy. In 2019, they took the first image of a supermassive black hole. Today, these exotic objects are a fundamental part of our understanding of how galaxies form and evolve.
But what of smaller astronomical bodies, like the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy that is expected to collide with the Milky Way in 2.4 billion years? Nobody is quite sure whether clouds like this might also house supermassive black holes.
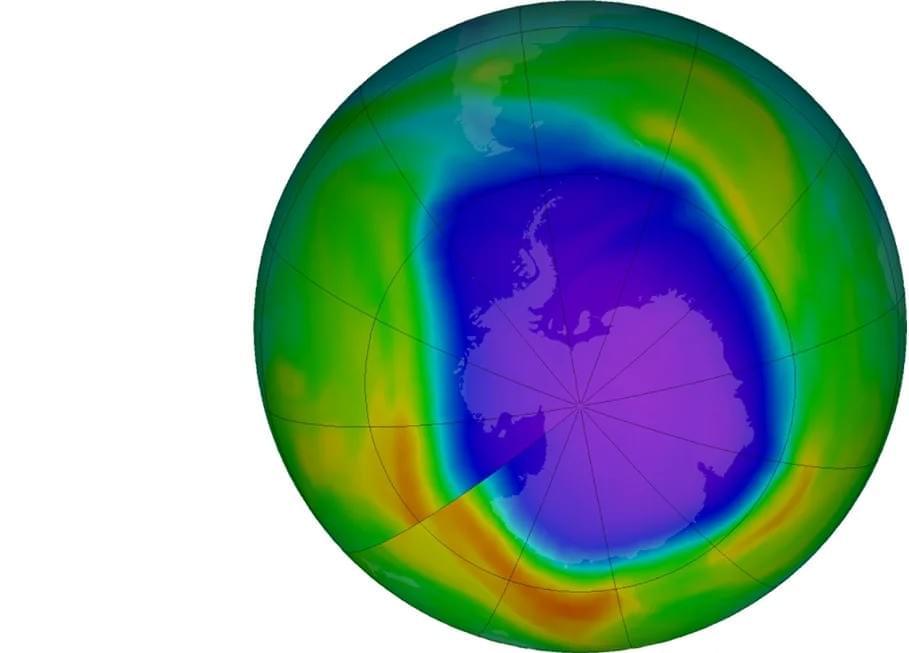
What impacts have climate change mitigation strategies had on the ozone layer? This is what a recent study published in Nature hopes to address as a team of researchers led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) investigated the rate of Antarctic ozone recovery due to a reduction in human-caused ozone-depleting substances (ODSs). This study has the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, legislators, and the public better understand the benefits of climate change mitigation strategies on healing the environment for both the short and long term.
For the study, the researchers used a combination of satellite imagery data and a series of computer models to ascertain the extent of the Antarctic ozone recovery based on seasons and altitude between 2005 and now. The team conducted various models to identify a pattern in Antarctic ozone recovery, which they call a “fingerprint”. After comparing this to the satellite data, the team ascertained that the Antarctic ozone has been healing due to decreased levels of ODSs.
“After 15 years of observational records, we see this signal to noise with 95 percent confidence, suggesting there’s only a very small chance that the observed pattern similarity can be explained by variability noise,” said Peidong Wang, who is a PhD student in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences and lead author of the study. “This gives us confidence in the fingerprint. It also gives us confidence that we can solve environmental problems. What we can learn from ozone studies is how different countries can swiftly follow these treaties to decrease emissions.”
Optical atomic clocks have the potential to improve timekeeping and GPS
GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information anywhere on or near the Earth’s surface. It consists of a network of satellites, ground control stations, and GPS receivers, which are found in a variety of devices such as smartphones, cars, and aircraft. GPS is used for a wide range of applications including navigation, mapping, tracking, and timing, and has an accuracy of about 3 meters (10 feet) in most conditions.