Historian and Sapiens author says sophistication of technology makes it difficult to forecast its dangers.



It’s no secret that foundation models have transformed AI in the digital world. Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, LLaMA, and Bard revolutionized AI for language. While OpenAI’s GPT models aren’t the only large language model available, they have achieved the most mainstream recognition for taking text and image inputs and delivering human-like responses — even with some tasks requiring complex problem-solving and advanced reasoning.
ChatGPT’s viral and widespread adoption has largely shaped how society understands this new moment for artificial intelligence.
The next advancement that will define AI for generations is robotics. Building AI-powered robots that can learn how to interact with the physical world will enhance all forms of repetitive work in sectors ranging from logistics, transportation, and manufacturing to retail, agriculture, and even healthcare. It will also unlock as many efficiencies in the physical world as we’ve seen in the digital world over the past few decades.

Each iteration of ChatGPT has demonstrated remarkable step function capabilities. But what’s next? Ilya Sutskever, Co-Founder & Chief Scientist at OpenAI, joins Sarah Guo and Elad Gil to discuss the origins of OpenAI as a capped profit company, early emergent behaviors of GPT models, the token scarcity issue, next frontiers of AI research, his argument for working on AI safety now, and the premise of Superalignment. Plus, how do we define digital life?
Ilya Sutskever is Co-founder and Chief Scientist of OpenAI. He leads research at OpenAI and is one of the architects behind the GPT models. He co-leads OpenAI’s new “Superalignment” project, which tries to solve the alignment of superintelligences in 4 years. Prior to OpenAI, Ilya was co-inventor of AlexNet and Sequence to Sequence Learning. He earned his Ph.D in Computer Science from the University of Toronto.
00:00 — Early Days of AI Research.
06:49 — Origins of Open AI & CapProfit Structure.
13:54 — Emergent Behaviors of GPT Models.
18:05 — Model Scale Over Time & Reliability.
23:51 — Roles & Boundaries of Open Source in the AI Ecosystem.
28:38 — Comparing AI Systems to Biological & Human Intelligence.
32:56 — Definition of Digital Life.
35:11 — Super Alignment & Creating Pro Human AI
41:20 — Accelerating & Decelerating Forces.

Twitter CEO Linda Yaccarino regrets that she was not able to use her boss Elon Musk’s wildly vulgar AI chatbot to teach her kids about sex. You know, regular stuff for an exec to say publicly!
To back up for a second: Grok, as the AI is called, was released this weekend to a small group of test users. Whereas other chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard have been criticized by many on the right for being too liberal, Grok is specifically designed to be anti-“woke,” like a seasoned Twitter troll; it has the humor of a 13-year-old boy, and yet somehow a 53-year-old man. Unsurprisingly, the limited users with access quickly took to X-formerly-Twitter to share the AI’s sometimes tame-ish, sometimes deranged outputs with their followers.
One of those posts, shared to X on Tuesday by Babylon Bee staffer Ashley St. Clair and reshared by Musk, featured Grok’s response to the question of how babies are made.
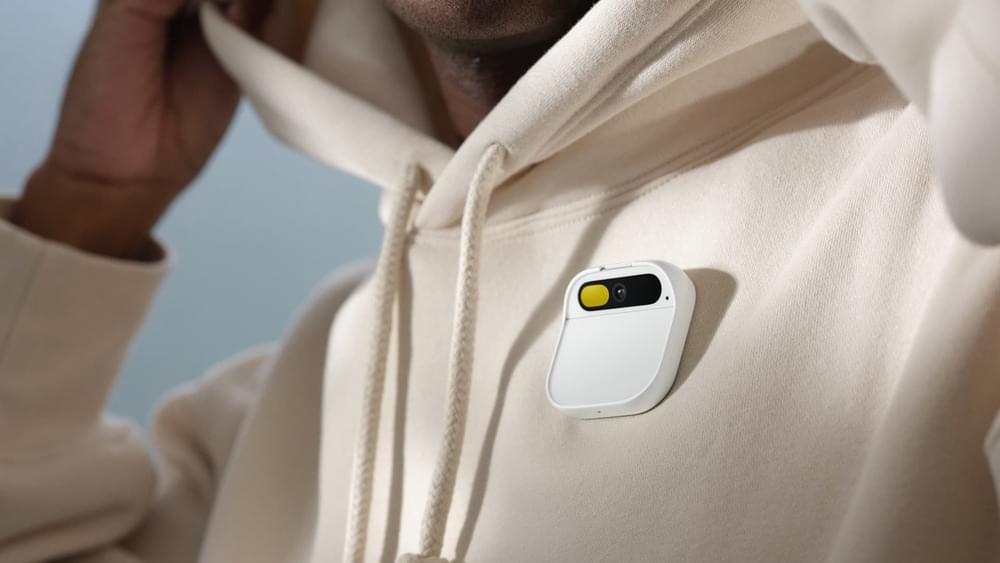

The Humane AI Pin is designed to replace your smartphone, allowing the user to make calls, send texts and look up information through voice controls. It also has a laser display, turning your palm into a mini screen that can show the time, date or what’s nearby.
“There are no wake words so it’s not always listening or always recording,” Chaudhri said at the beginning of a 10-minute launch video on the company’s website. “In fact, it doesn’t do anything until you engage with it, and your engagement comes through your voice, touch, gesture or the laser ink display.”
In addition to the upfront cost of the device, customers will have to pay a $24 monthly data subscription to T-Mobile, the company said. Having a separate phone number means that, unlike smart watches, the pin isn’t tethered to a smartphone.
We present Neural Signal Operated Intelligent Robots (NOIR), a general-purpose, intelligent brain-robot interface system that enables humans to command robots to perform everyday activities through brain signals. Through this interface, humans communicate their intended objects of interest and actions to the robots using electroencephalography (EEG). Our novel system demonstrates success in an expansive array of 20 challenging, everyday household activities, including cooking, cleaning, personal care, and entertainment. The effectiveness of the system is improved by its synergistic integration of robot learning algorithms, allowing for NOIR to adapt to individual users and predict their intentions. Our work enhances the way humans interact with robots, replacing traditional channels of interaction with direct, neural communication.

OpenAI has confirmed that a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is behind “periodic outages” affecting ChatGPT and its developer tools.
ChatGPT, OpenAI’s AI-powered chatbot, has been experiencing sporadic outages for the past 24 hours. Users who attempted to access the service have been greeted with a message stating that “ChatGPT is at capacity right now,” and others, including TechCrunch, have been unable to log into the service.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman initially blamed the issue on interest in the platform’s new features, unveiled at the company’s first developer conference on Monday, “far outpacing our expectations.” OpenAI said the issue was fixed at approximately 1 p.m. PST on November 8.

The technology that makes it possible, called semantic hearing, could pave the way for smarter hearing aids and earphones, allowing the wearer to filter out some sounds while boosting others.
The system, which is still in prototype, works by connecting off-the-shelf noise-canceling headphones to a smartphone app. The microphones embedded in these headphones, which are used to cancel out noise, are repurposed to also detect the sounds in the world around the wearer. These sounds are then played back to a neural network, which is running on the smartphone; then certain sounds are boosted or suppressed in real time, depending on the user’s preferences. It was developed by researchers from the University of Washington, who presented the research at the ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST) last week.
The team trained the network on thousands of audio samples from online data sets and sounds collected from various noisy environments. Then they taught it to recognize 20 everyday sounds, such as a thunderstorm, a toilet flushing, or glass breaking.