🌟 Unlock Your Creative Potential with Pictory.ai! 🎨Looking to level up your design game? Look no further! Explore the amazing world of design with Pictory…
Category: robotics/AI – Page 882
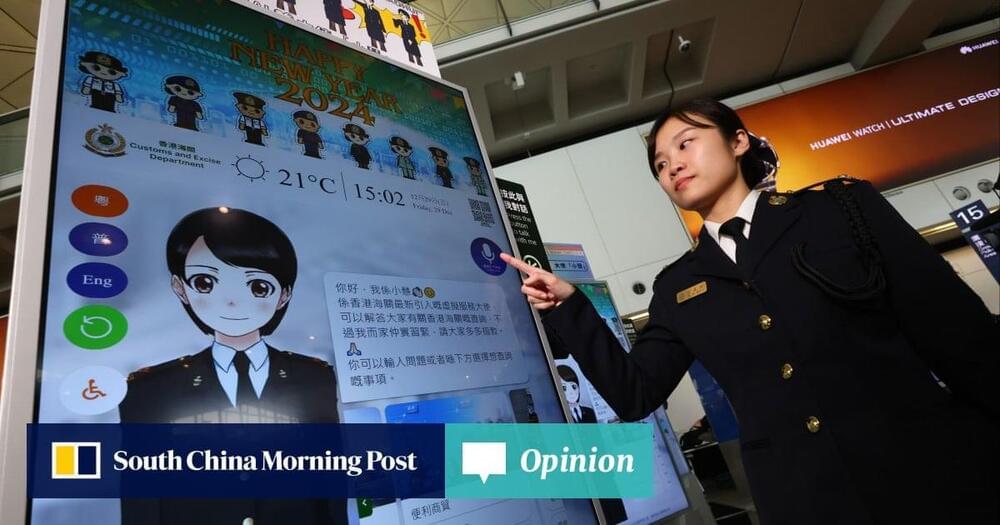


Opinion: Generative AI is also expected to play a significant role in 6G mobile technology
Generative AI is also expected to play a significant role in 6G mobile technology. This year, work to set and agree on 6G standards will continue with the anticipation that the first standards could be introduced between 2027 and 2028, and the technology could reach commercialisation by 2030. Generative AI can be applied to various aspects of 6G, such as network resource management, spectrum allocation and network topology optimisation.
It is also capable of meeting the demands of “connective intelligence” for new technologies. Connective intelligence is a key force driving the development of the 6G network, enabling real-time, reliable and ubiquitous interaction and communication between humans, the physical world and the digital world. This results in the creation of a decentralised and continually evolving intelligence, making it easier for users to share their discoveries and experiences with each other.
In summary, by the end of 2024, generative AI will become an invaluable assistant, providing support and help across different industries. Its powerful analysis and predictive capabilities will enable people to handle complex tasks and problems more efficiently, offering real-time solutions and recommendations.


Ant behavior inspires autonomous material assembly research
The survival strategies employed by one of the most aggressive, territorial and venomous ant species may pave the way to revolutionize robotics, medicine and engineering.
Fire ants survive floods by temporarily interlinking their legs to create a raft-like structure, allowing them to float collectively to safety as a unified colony and then releasing to resume their individual forms.
Drawing inspiration from this natural process, researchers at Texas A&M University discovered a method that allows synthetic materials to mimic the ants’ autonomous assembly, reconfiguration and disassembly in response to environmental changes such as heat, light or solvents.
Scientists Use AI To Unlock the Secrets of Bacterial Languages
Machine learning and laboratory experiments have provided scientists with insights into the different languages bacteria use to communicate. By understanding the ways in which bacteria interact and the circumstances under which their communication is disrupted, researchers can tackle issues related to drug-resistant bacteria and advance the development of biocomputing technologies.
The study builds on an earlier project in which the researchers showed that disrupting bacterial communication is an effective way to fight multidrug-resistant bacteria. Bacteria use small molecules to communicate with each other and coordinate infection, and the team showed that interfering with bacterial communication by blocking these molecules reduced inflammation and made the bacteria more vulnerable to antibiotics.

Super Humanity | Breakthroughs in Neuroscience
Super Humanity — This documentary examines breakthroughs in neuroscience and technology. Imagine a future where the human brain and artificial intelligence connect.
Super Humanity (2019)
Director: Ruth Chao.
Writers: Ruth Chao, Paula Cons, Alphonse de la Puente.
Genre: Documentary, Sci-Fi.
Country: Portugal, Spain.
Language: English.
Release Date: December 27, 2019 (Spain)
Also Known As (AKA):
(original title) O Futuro da Mente.
El futuro de la mente.
Netherlands O Futuro da Mente.
Poland O Futuro da Mente.
Portugal O Futuro da Mente.
South Korea O Futuro da Mente.
Spain El futuro de la mente.
United States Mind Forward.
SUPPORT US!
✘ Membership — https://bit.ly/3q5XPBh.
MORE DOCS!
► Gold: https://bit.ly/2IRZ0OA
► World Economy: https://bit.ly/36QlhEM
► All Playlists: https://bit.ly/3lOiCll.
#finance #documentaries #economy.

How Lightmatter Breaks Bandwidth Bottlenecks With Silicon Photonics
Without question, the biggest bottleneck in artificial intelligence and for a lot of HPC workloads today is bandwidth. Bandwidth at the network level; bandwidth at the socket level; bandwidth at the compute and memory level. No matter how many teraflops one single chip can push at high precision, once your workload scales beyond a single accelerator, node, or rack, bandwidth quickly becomes the limiting factor.
We have seen chipmakers grapple with this on a number of levels, by packing more high-bandwidth memory onto their chips, boosting interconnect speeds, and by using chiplets to push beyond reticle limits. Intel’s “Ponte Vecchio” Max Series GPU and AMD’s recently announced “Antares” Instinct MI300X GPU are prime examples of the latter. Driving data between chiplets does introduce I/O bottlenecks in its own right, but we can’t exactly make the dies any bigger.
Aside from needing a socket that is bigger than the reticle limit of lithography machines, we still need more capacity to satiate the demands of modern AI and HPC workloads. Over the past few years, we’ve seen a trend toward denser boxes, racks, and clusters. Cloud providers, hyperscalers, and GPU bit barns are now deploying clusters with tens of thousands of accelerators to keep up with demand for AI applications. It’s at this beach head that silicon photonics startup Lightmatter, now valued at more than $1 billion, believes it has the market cornered.