The robot will undergo a four-month testing phase at the Orano Melox facility in France to assess its mobility and precision.
France has deplopyed Hoxo, an AI-powered humanoid robot, to enhance safety and efficiency in nuclear plant operations.


Can an AI persona detect when a human is lying—and should we trust it if it can?
Artificial intelligence, or AI, has had many recent advances and continues to evolve in scope and capability. A new Michigan State University-led study is diving deeper into how well AI can understand humans by using it to detect human deception.
In the study, published in the Journal of Communication, researchers from MSU and the University of Oklahoma conducted 12 experiments with over 19,000 AI participants to examine how well AI personas were able to detect deception and truth from human subjects.

In an MIT classroom, a professor lectures while students diligently write down notes they will reread later to study and internalize key information ahead of an exam.
Humans know how to learn new information, but large language models can’t do this in the same way. Once a fully trained LLM has been deployed, its “brain” is static and can’t permanently adapt itself to new knowledge.
This means that if a user tells an LLM something important today, it won’t remember that information the next time this person starts a new conversation with the chatbot.
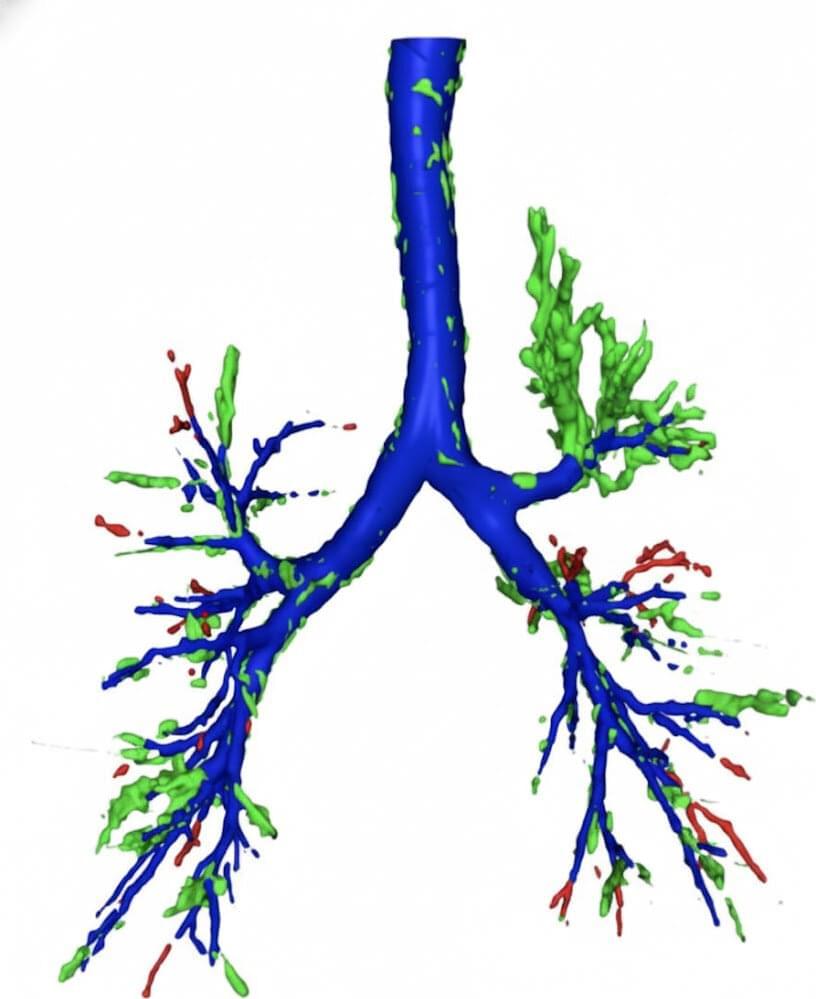
Researchers at the University of Southampton have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that can spot hard-to-see objects lodged in patients’ airways better than expert radiologists.
In a study published in npj Digital Medicine, the AI model outperformed radiologists in checking CT scans for objects that don’t show up well on scans. The paper is titled “Automated Detection of Radiolucent Foreign Body Aspiration on Chest CT Using Deep Learning.”
These accidentally inhaled objects can cause coughing, choking, difficulty breathing and sometimes lead to more serious complications if not treated properly.
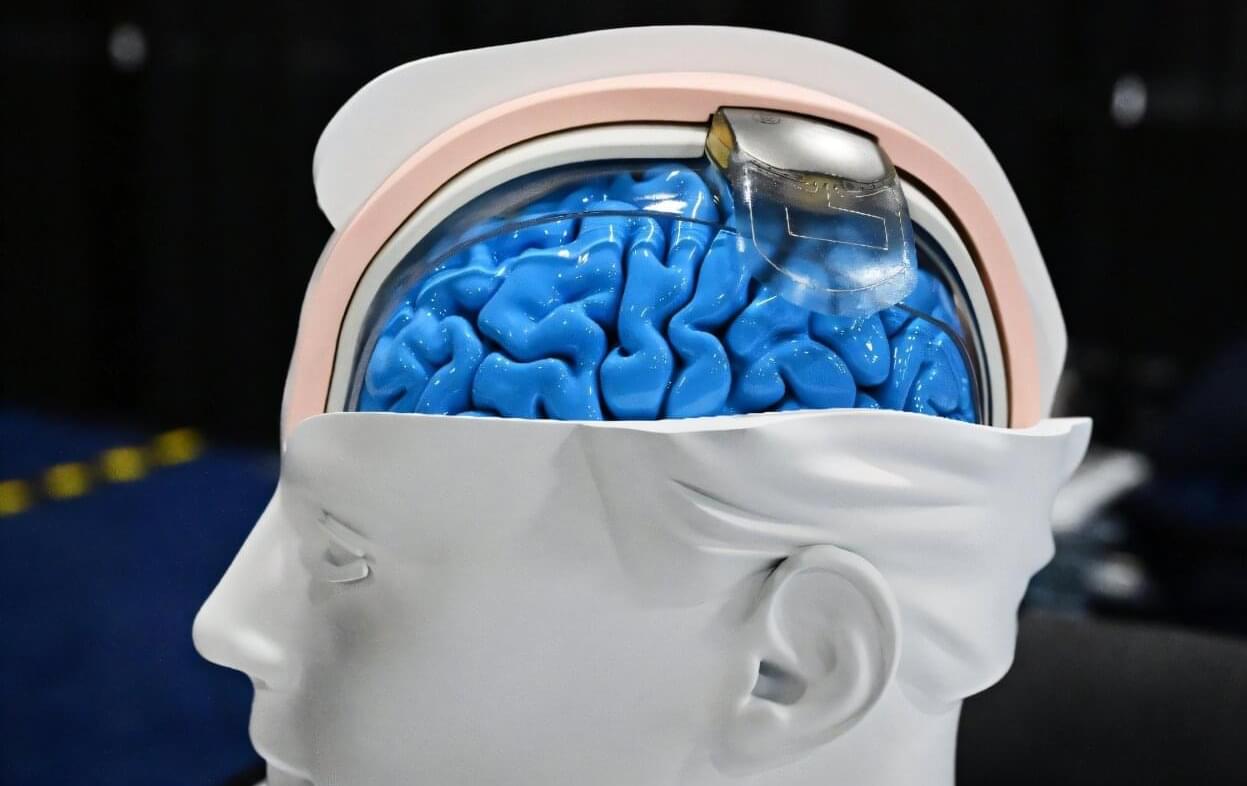
From translating thoughts into words to allowing paralyzed people to walk, the field of neurotechnology has been quietly surging ahead, raising hopes of medical breakthroughs—and profound ethical concerns.
Some observers even think that neurotech could end up being as revolutionary as the far more hyped rise of artificial intelligence (AI).
“People do not realize how much we’re already living in science fiction,” King’s College London researcher Anne Vanhoestenberghe told AFP.

“One of the most surprising findings was that participants disclosed more and felt more comforted by a chatbot introduced as a human, even though almost everyone knew they were still talking to a chatbot. This means the effect wasn’t driven by deception or belief that the chatbot was human, but rather by the framing itself, how the chatbot was introduced and named. That subtle change alone was enough to activate more social and affective responses. Therefore, people’s behaviour toward chatbots can be shaped not just by what the chatbot does, but by what they expect it to be, showing how powerful simple context cues are in guiding our interactions with AI.”
Not all the differences favored the chatbot presented as a human. Although participants disclosed less to Chatbot D12, they rated it as slightly friendlier. Their answers to D12 were also more sentimental, meaning they expressed stronger emotions, both positive and negative. Despite these differences, participants did not rate either chatbot as significantly more trustworthy, and both were rated similarly in terms of overall interaction quality.
“When framing a chatbot more like a person, by giving it a human name and introducing it as a human, people tend to open up more, attribute social traits to it, and feel more comforted when speaking with it, even when they suspect it’s still a bot. But there’s a catch: when a ‘human-like’ chatbot doesn’t fully meet our social expectations, people judge it as less friendly or trustworthy. So, design cues that make chatbots feel human can encourage self-disclosure, but they need to be balanced with transparency and realistic expectations.”


A research team at the Jülich Supercomputing Center, together with experts from NVIDIA, has set a new record in quantum simulation: for the first time, a universal quantum computer with 50 qubits has been fully simulated—a feat achieved on Europe’s first exascale supercomputer, JUPITER, inaugurated at Forschungszentrum Jülich in September.
The result surpasses the previous world record of 48 qubits, established by Jülich researchers in 2022 on Japan’s K computer. It showcases the immense computational power of JUPITER and opens new horizons for developing and testing quantum algorithms. The research is published on the arXiv preprint server.
Quantum computer simulations are vital for developing future quantum systems. They allow researchers to verify experimental results and test new algorithms long before powerful quantum machines become reality. Among these are the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE), which can model molecules and materials, and the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), used for optimization problems in logistics, finance, and artificial intelligence.

Researchers studying how large AI models such as ChatGPT learn and remember information have discovered that their memory and reasoning skills occupy distinct parts of their internal architecture. Their insights could help make AI safer and more trustworthy.
AI models trained on massive datasets rely on at least two major processing features. The first is memory, which allows the system to retrieve and recite information. The second is reasoning, solving new problems by applying generalized principles and learned patterns. But up until now, it wasn’t known if AI’s memory and general intelligence are stored in the same place.
So researchers at the startup Goodfire.ai decided to investigate the internal structure of large language and vision models to understand how they work.