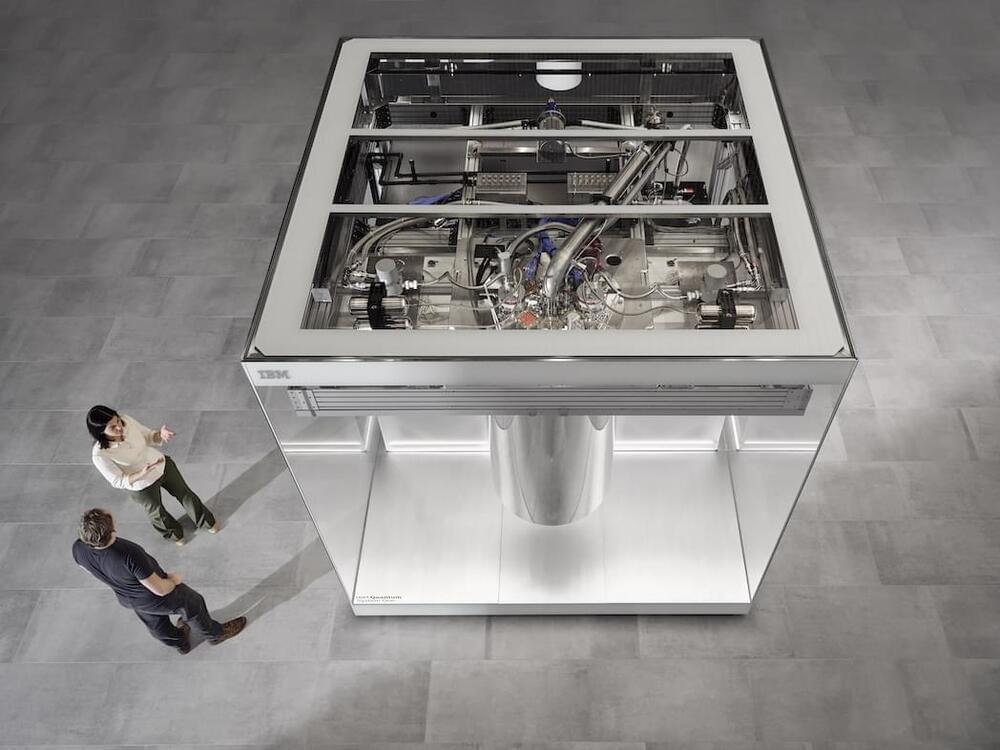
Should you start exploring quantum computing? Yes, said a panel of analysts convened at Tabor Communications HPC and AI on Wall Street conference earlier this year.
Without doubt, the quantum computing landscape remains murky. Yet in the past ~5 years virtually every aspect of quantum computing has raced forward. At least one 1000-plus-qubit system is edging towards user access now and another is expected by year-end. There’s been a proliferation of software offerings up and down the “quantum stack” though it’s hardly complete. Most promising, what were a few POC use-case explorations has mushroomed into very many efforts across many sectors.
What are we waiting for? Against the backdrop of astonishing progress are also very hard technical problems. Error correction/mitigation tops the list. Effective quantum networking is another. Polished applications. Too many qubit types to choose from (at least for now.) Scale matters – it’s expected that millions of qubits may be needed for practical quantum computing These aren’t trivial challenges. Why bother?