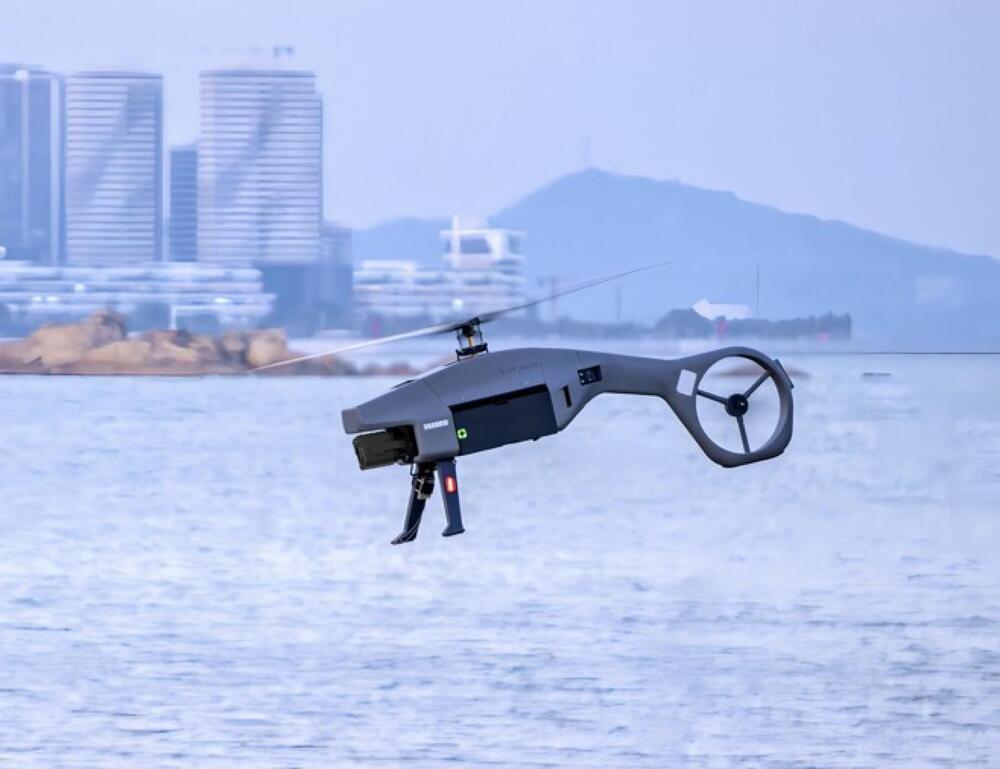
Ziyan’s Shadow S3 sets new standards with a sub-7kg take-off weight, exceptional wind resistance, and an impressive 100-minute endurance.



The chatbot’s creators, from the AI company Limbic, set out to investigate whether AI could lower the barrier to care by helping patients access help more quickly and efficiently.
A new study, published today in Nature Medicine, evaluated the effect that the chatbot, called Limbic Access, had on referrals to the NHS Talking Therapies for Anxiety and Depression program, a series of evidence-based psychological therapies for adults experiencing anxiety disorders, depression, or both.
It examined data from 129,400 people visiting websites to refer themselves to 28 different NHS Talking Therapies services across England, half of which used the chatbot on their website and half of which used other data-collecting methods such as web forms. The number of referrals from services using the Limbic chatbot rose by 15% during the study’s three-month time period, compared with a 6% rise in referrals for the services that weren’t using it.
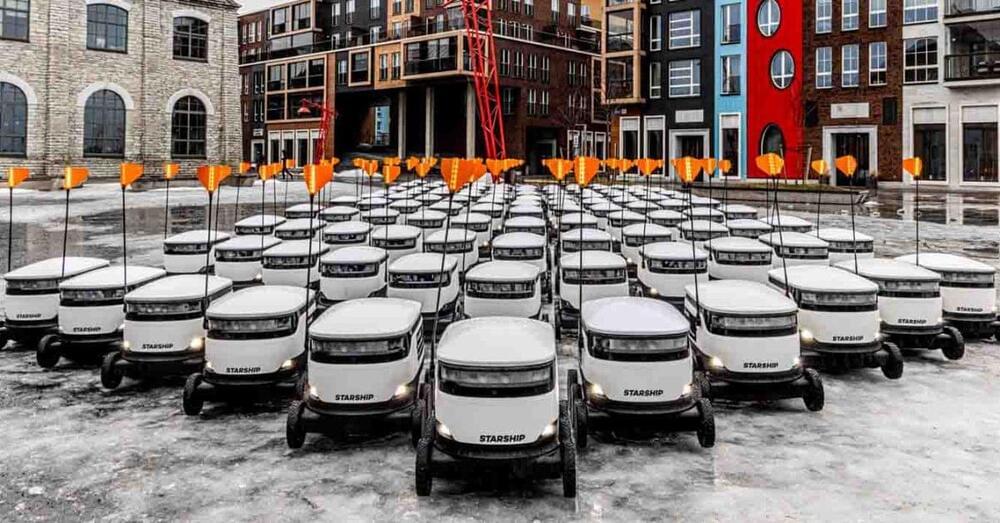

Veteran autonomous delivery robot developer Starship Technologies announced it had raised an additional $90 million in funding to help expand its micro-logistics service to additional territories around the globe.
Starship Technologies was founded in 2014 by Skype co-founders Ahti Heinla and Janus Friis based on the idea that autonomy can help many of the challenges in last-mile deliveries. The company’s L4 autonomous delivery robots have completed over six million trips to date, transporting meals, packages, groceries, and important documents to students and other customers.
In August 2023, that mileage total was five million, operating in 30 different areas. Today, Starship’s robots have expanded to 80 locations worldwide, including the US, UK, Germany, Denmark, Estonia, and Finland.

Sidewalk delivery robot services appear to be stalling left and right, but a pioneer in the concept says it is profitable and has now raised a round of funding to scale up to meet market demand. Starship Technologies, a startup out of Estonia that was an early mover in the delivery robotics space, has picked up $90 million in funding as it works to cement its position at the top of its category.
This latest investment round is being co-led by two previous backers: Plural, the VC with roots in Estonia and London that announced a new $430 million fund last month; and Iconical, the London-based investor backed by Janus Friis, the serial entrepreneur who was a co-founder of Skype, and who is also a co-founder of Starship itself.
It brings the total raised by Starship to $230 million, with previous backers including the Finnish-Japanese firm NordicNinja, the European Investment Bank, Morpheus Ventures and TDC.
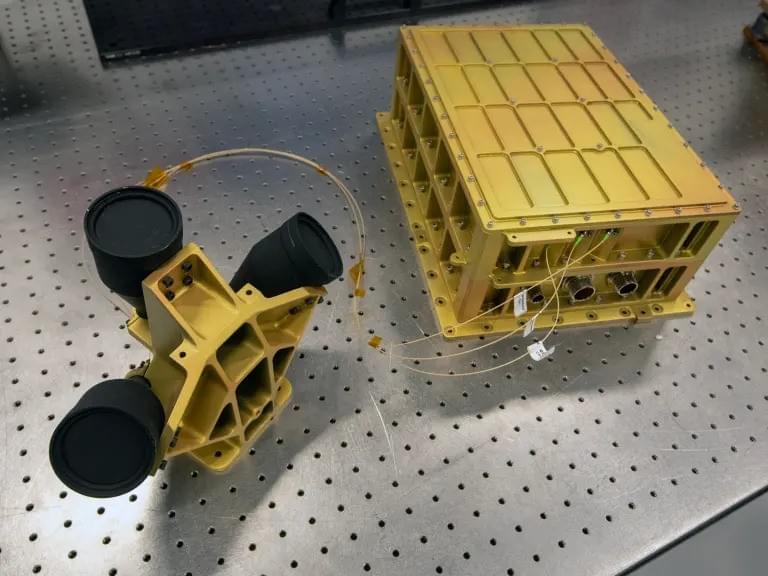

Read about NASA’s new instrument for landing on other worlds!
Landing on planetary bodies is both risky and hard, and landing humans is even riskier and harder. This is why technology needs to be developed to mitigate the risks associated with landing large spacecraft on the Moon and other planetary bodies we plan to continue exploring, both in the near and distant future. This is what makes the Nova-C lunar lander from Intuitive Machines—which is scheduled to launch to the Moon on February 13 and also called Nova-C (IM-1) —so vital to returning humans to the Moon. One of its NASA science payloads will be the Navigation Doppler Lidar (NDL), which will serve as a technology demonstration for future landers to help them navigate risky terrain and land safely.
Image of the Navigation Doppler Lidar which will be a technology demonstration during the IM-1 mission. (Credit: NASA/David C. Bowman)
When NASA was landing robots on Mars in the 1990s and 2000s, they discovered that radar and radio waves were insufficient for accurate landing measurements, so the engineers had to come up with their own plan to land spacecraft on extraterrestrial worlds.


Researchers have not only built an AI child, but are now training AI using headcam footage from a human baby as well.
In a press release, New York University announced that its data science researchers had strapped a camera to the head of a real, live, human toddler for 18 months to see how much an AI model could learn from it.
Most large language models (LLMs), like OpenAI’s GPT-4 and its competitors, are trained on “astronomical amounts of language input” that are many times larger than what infants receive when learning to speak a language during the first years of their lives.


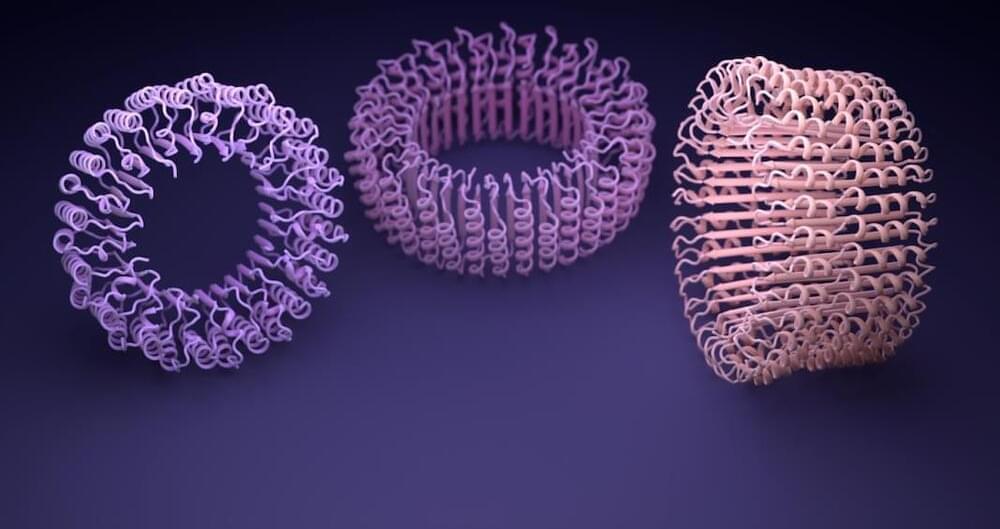
Two decades ago, engineering designer proteins was a dream.
Now, thanks to AI, custom proteins are a dime a dozen. Made-to-order proteins often have specific shapes or components that give them abilities new to nature. From longer-lasting drugs and protein-based vaccines, to greener biofuels and plastic-eating proteins, the field is rapidly becoming a transformative technology.
Custom protein design depends on deep learning techniques. With large language models—the AI behind OpenAI’s blockbuster ChatGPT—dreaming up millions of structures beyond human imagination, the library of bioactive designer proteins is set to rapidly expand.