Five aerospace companies are bidding for the $6 billion contract to produce new unmanned aircraft for the Air Force. The planes will be AI-piloted and will be able to perform dangerous maneuvers.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 819
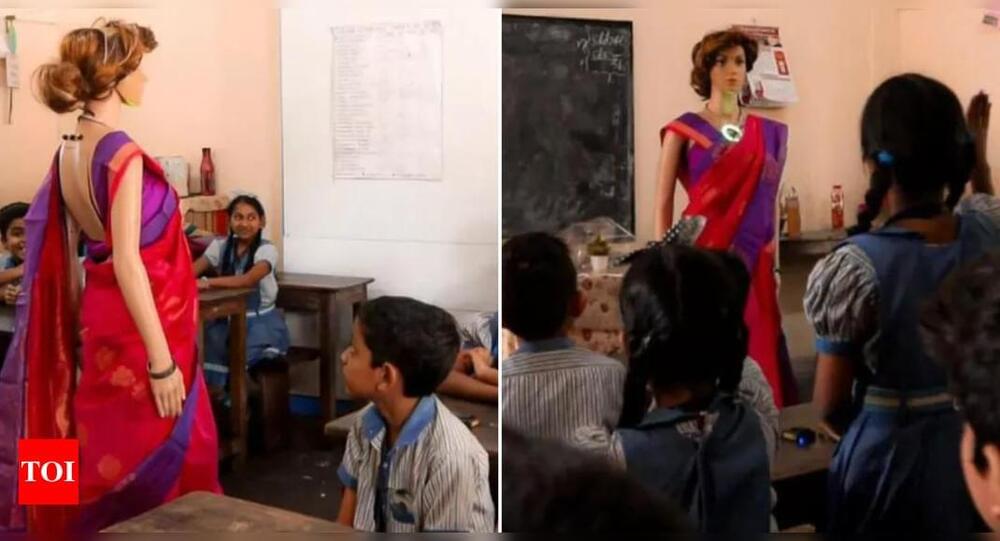

Watch: Kerala School gets India’s First AI Teacher, Iris
Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala: A school in Kerala is taking what may be called a revolutionary step towards revamping education with the introduction of Iris, claimed to be the first-ever AI teacher robot in the state.
The KTCT Higher Secondary School, a venture of the Kaduvayil Thangal Charitable Trust, unveiled Iris last month in collaboration with Makerlabs Edutech Private Limited. The Iris robot is designed to be more than just a robot. Built as part of the Atal Tinkering Lab (ATL) project by NITI Aayog, Iris is equipped to answer complex questions across various subjects in three different languages. It can also provide personalized voice assistance and facilitate interactive learning experiences.
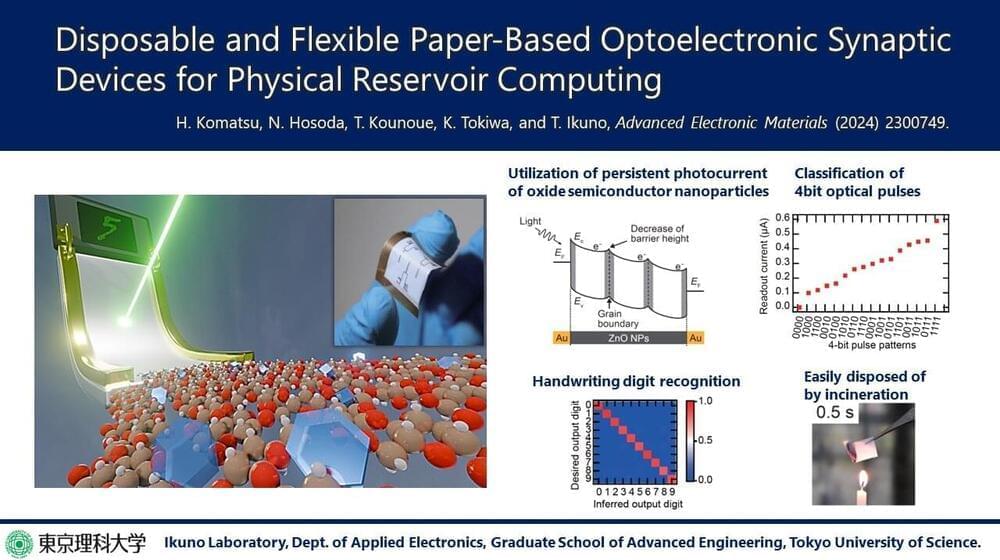
Flexible AI optoelectronic sensors pave the way for standalone energy-efficient health monitoring devices
From creating images, generating text, and enabling self-driving cars, the potential uses of artificial intelligence (AI) are vast and transformative. However, all this capability comes at a very high energy cost. For instance, estimates indicate that training OPEN AI’s popular GPT-3 model consumed over 1,287 MWh, enough to supply an average U.S. household for 120 years.
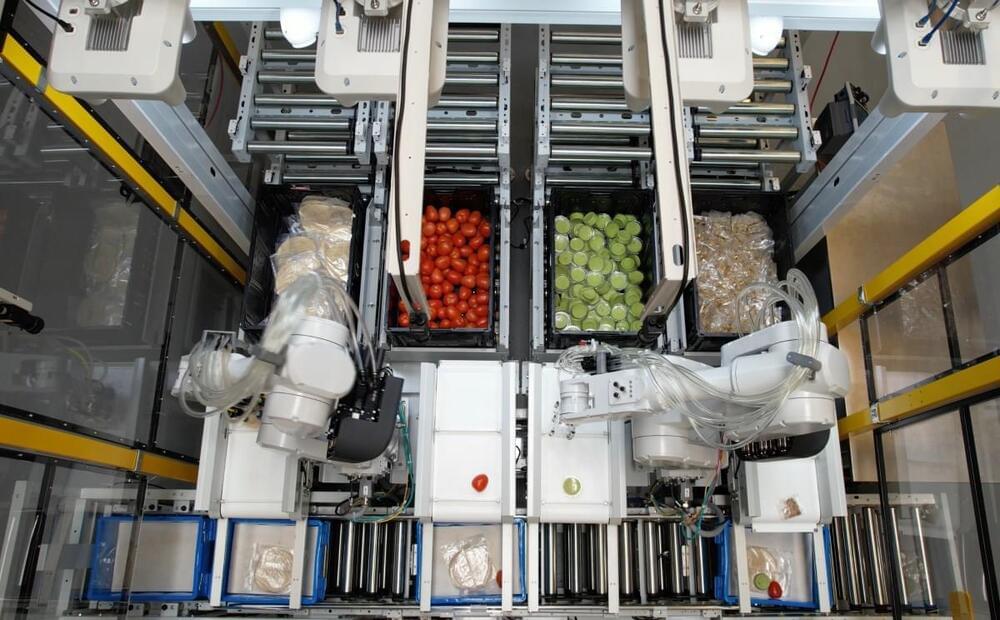

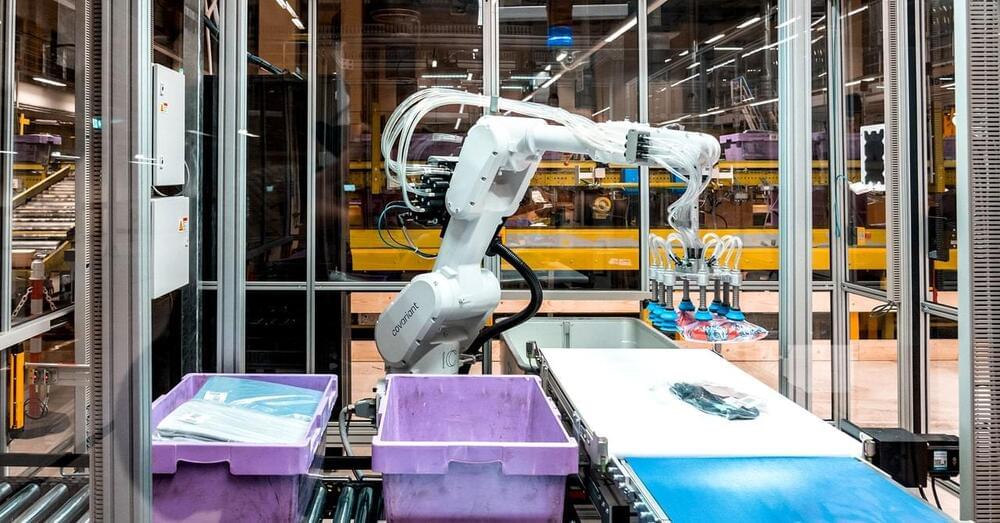
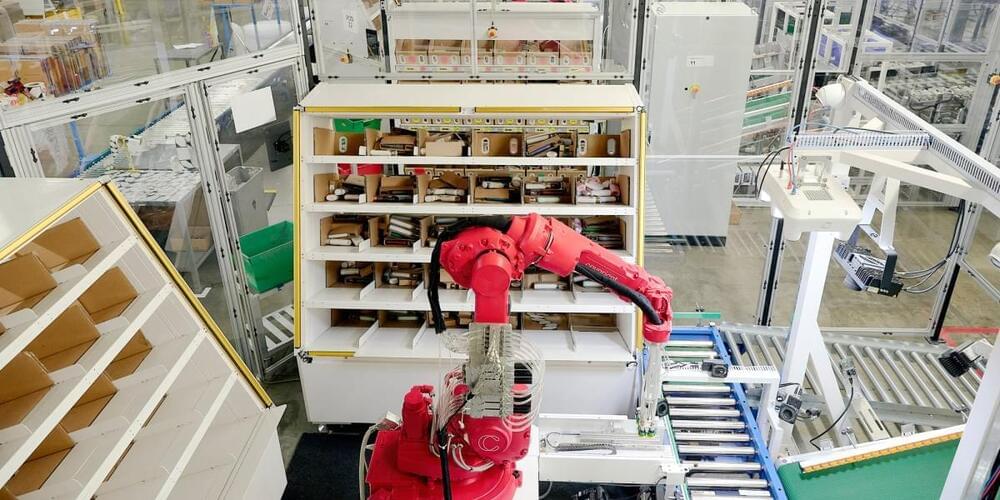
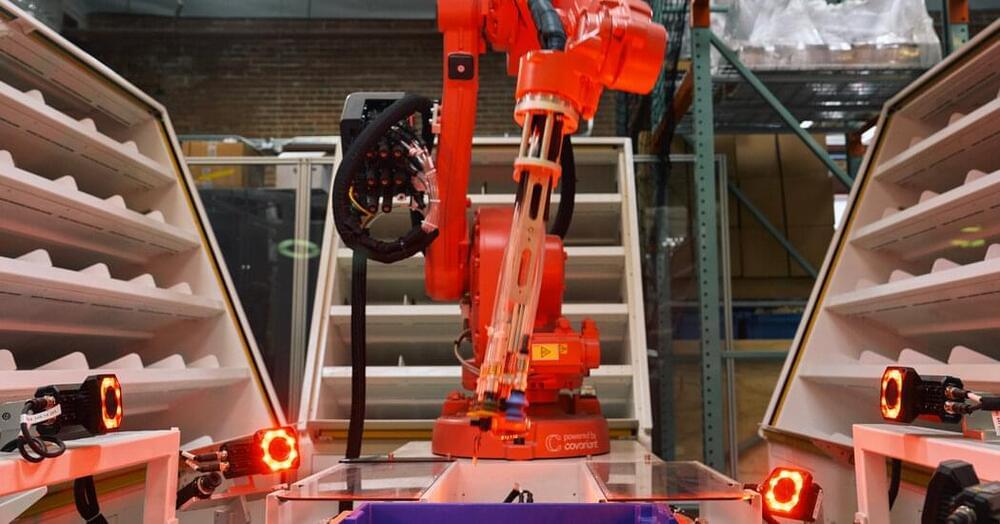
Covariant is building ChatGPT for robots
Covariant this week announced the launch of RFM-1 (Robotics Foundation Model 1). Peter Chen, the co-founder and CEO of the UC Berkeley artificial intelligence spinout tells TechCrunch the platform, “is basically a large language model (LLM), but for robot language.”
RFM-1 is the result of, among other things, a massive trove of data collected from the deployment of Covariant’s Brain AI platform. With customer consent, the startup has been building the robot equivalent of an LLM database.
“The vision of RFM-1 is to power the billions of robots to come,” Chen says. “We at Covariant have already deployed lots of robots at warehouses with success. But that is not the limit of where we want to get to. We really want to power robots in manufacturing, food processing, recycling, agriculture, the service industry and even into people’s homes.”



How The Telecom Industry Can Accelerate Growth From Generative AI
I have been engaged in the telecommunication industry for over 25 years, and it is so refreshing to see the positive energy moving into this sector as a result of applying generative AI technologies.
The telecom industry can accelerate growth from generative AI. Here are use cases for the telco industry.

