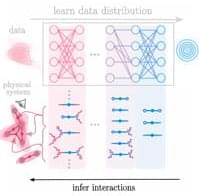
Models of systems in physics usually start with elementary processes. New work with a neural network shows how models can also be built by observing the system as a whole and deducing the underlying interactions.


OpenAI made a big splash when it showed off its new video generator Sora last month.
The text-to-video model can be used to “create videos of up to 60 seconds featuring highly detailed scenes, complex camera motion, and multiple characters with vibrant emotions,” according to OpenAI CEO Sam Altman.
And with stunning results, from a camera gliding through a snowy scene to photorealistic wooly mammoths.
This video shows the fly model reproducing a flight maneuver (spontaneous turning) of a real fly, executing commands to walk at a speed of 2 cm/s while turning left and right, and the model imitating a walking trajectory of the real fruit fly, which includes walking at different speeds, turning and briefly stopping. Credit: Vaxenburg et al.
By infusing a virtual fruit fly with artificial intelligence, Janelia and Google DeepMind scientists have created a computerized insect that can walk and fly just like the real thing.
The new virtual fly is the most realistic simulation of a fruit fly created to date. It combines a new anatomically accurate model of the fly’s outer skeleton, a fast physics simulator, and an artificial neural network trained on fly behaviors to mimic the actions of a real fly.

Legaltech News sat down with the leaders of AI detection company Copyleaks to discuss the findings of their study that found that almost 60% of OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 outputs included some form of plagiarism, and the effectiveness of uncovering AI use.

How LLM #ai is transforming the science of cells and propelling new discoveries by @carlzimmer v/EricTopol.
Given troves of data about genes and cells, A.I.
Given troves of data about genes and cells, A.I. models have made some surprising discoveries. What could they teach us someday?
Calum and David recently attended the BGI24 event in Panama City, that is, the Beneficial General Intelligence summit and unconference. One of the speakers we particularly enjoyed listening to was Daniel Faggella, the Founder and Head of Research of Emerj.
Something that featured in his talk was a 3 by 3 matrix, which he calls the Intelligence Trajectory Political Matrix, or ITPM for short. As we’ll be discussing in this episode, one of the dimensions of this matrix is the kind of end goal future that people desire, as intelligent systems become ever more powerful. And the other dimension is the kind of methods people want to use to bring about that desired future.
So, if anyone thinks there are only two options in play regarding the future of AI, for example “accelerationists” versus “doomers”, to use two names that are often thrown around these days, they’re actually missing a much wider set of options. And frankly, given the challenges posed by the fast development of AI systems that seem to be increasingly beyond our understanding and beyond our control, the more options we can consider, the better.

Coral.ai @raspberrypi =???Raspberry Pi 4 👉 https://amzn.to/3SBCRW0Coral AI USB Accelerator 👉 https://amzn.to/3SBGrzMRaspberry Pi Camera V3 Module 👉 https…
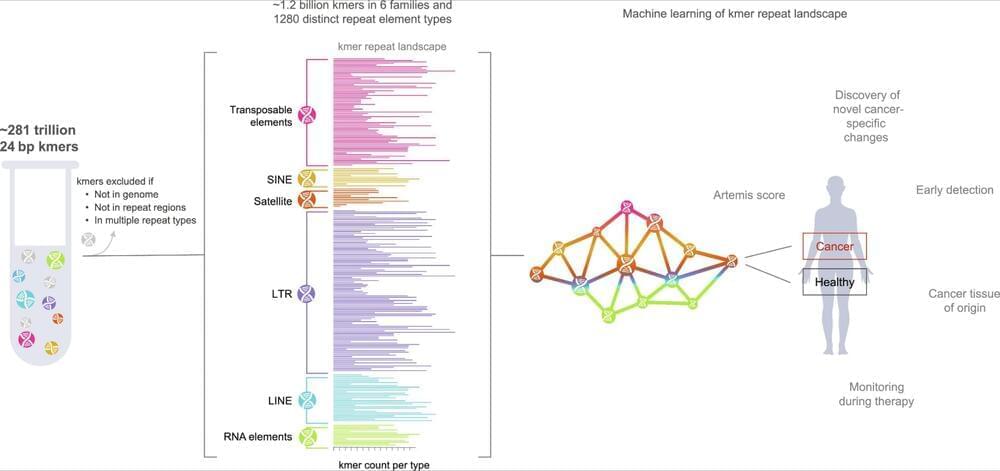
A machine learning pipeline named ARTEMIS captures how the landscape of repeat genomic sequences shifts in patients with cancer, and could facilitate earlier detection and monitoring of tumor progression.
📄:
ARTEMIS is a new approach to characterizing genome-wide repeat elements in cancer and cell-free DNA.

Apple acquired Canada-based company DarwinAI earlier this year to build out its AI team, reports Bloomberg. DarwinAI created AI technology for inspecting components during the manufacturing process, and it also had a focus on making smaller and more efficient AI systems.
DarwinAI’s website and social media accounts have been taken offline following Apple’s purchase. Dozens of former DarwinAI companies have now joined Apple’s artificial intelligence division. AI researcher Alexander Wong, who helped build DarwinAI, is now a director in Apple’s AI group.