Deep learning and global workspace theory.
Shared with Dropbox.


Assessing AI risks in the context of their use, rather than as inherent in the technologies themselves, leads to smarter and safer implementations.

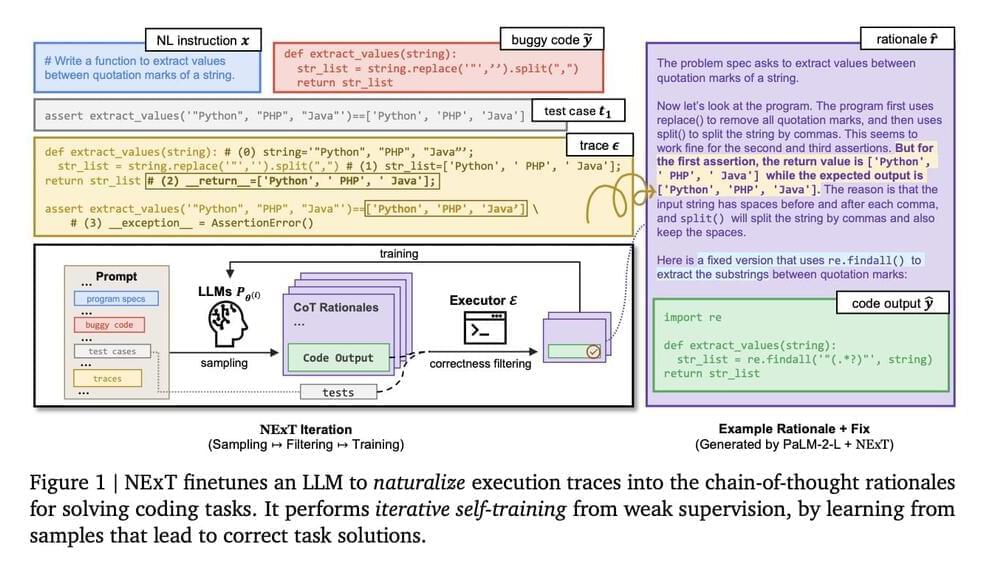
Understanding and reasoning about program execution is a critical skill for developers, often applied during tasks like debugging and code repair. Traditionally, developers simulate code execution mentally or through debugging tools to identify and fix errors. Despite their sophistication, large language models (LLMs) trained on code have struggled to grasp the deeper, semantic aspects of program execution beyond the superficial textual representation of code. This limitation often affects their performance in complex software engineering tasks, such as program repair, where understanding the execution flow of a program is essential.
Existing research in AI-driven software development includes several frameworks and models focused on enhancing code execution reasoning. Notable examples include CrossBeam, which leverages execution states in sequence-to-sequence models, and specialized neural architectures like the instruction pointer attention graph neural networks. Other approaches, such as the differentiable Forth interpreter and Scratchpad, integrate execution traces directly into model training to improve program synthesis and debugging capabilities. These methods pave the way for advanced reasoning about code, focusing on both the process and the dynamic states of execution within programming environments.
Researchers from Google DeepMind, Yale University, and the University of Illinois have proposed NExT, which introduces a novel approach by teaching LLMs to interpret and utilize execution traces, enabling more nuanced reasoning about program behavior during runtime. This method stands apart due to its incorporation of detailed runtime data directly into model training, fostering a deeper semantic understanding of code. By embedding execution traces as inline comments, NExT allows models to access crucial contexts that traditional training methods often overlook, making the generated rationales for code fixes more accurate and grounded in actual code execution.
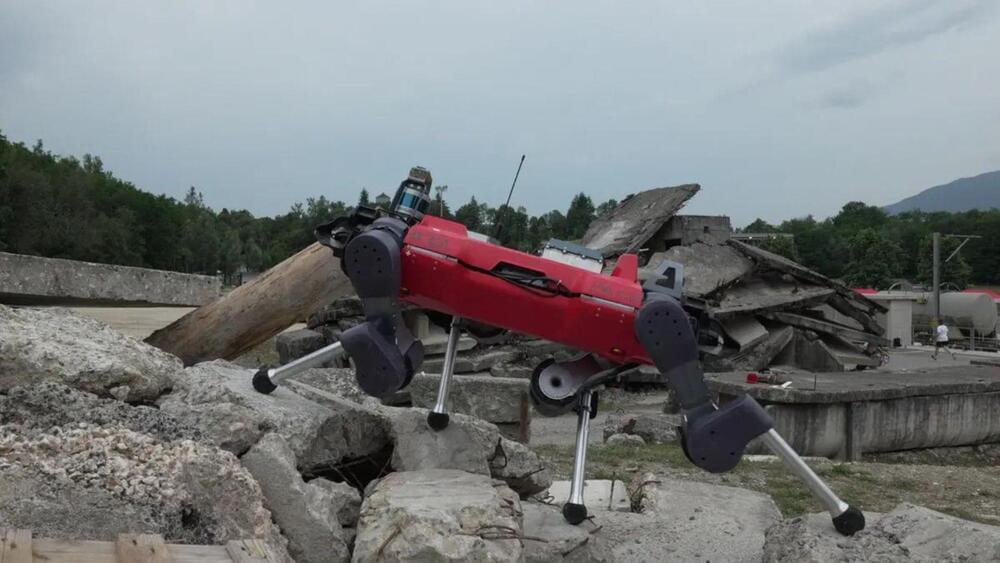

ETH Zurich researchers have developed a locomotor control that can enable wheeled-legged robots to autonomously navigate various urban environments.
The robot was equipped with sophisticated navigational abilities thanks to a combination of machine learning algorithms. It was tested in the cities of Seville, Spain, and Zurich, Switzerland.
With little assistance from humans, the team’s ANYmal wheeled-legged robot accomplished autonomous operations in urban settings at the kilometer scale.