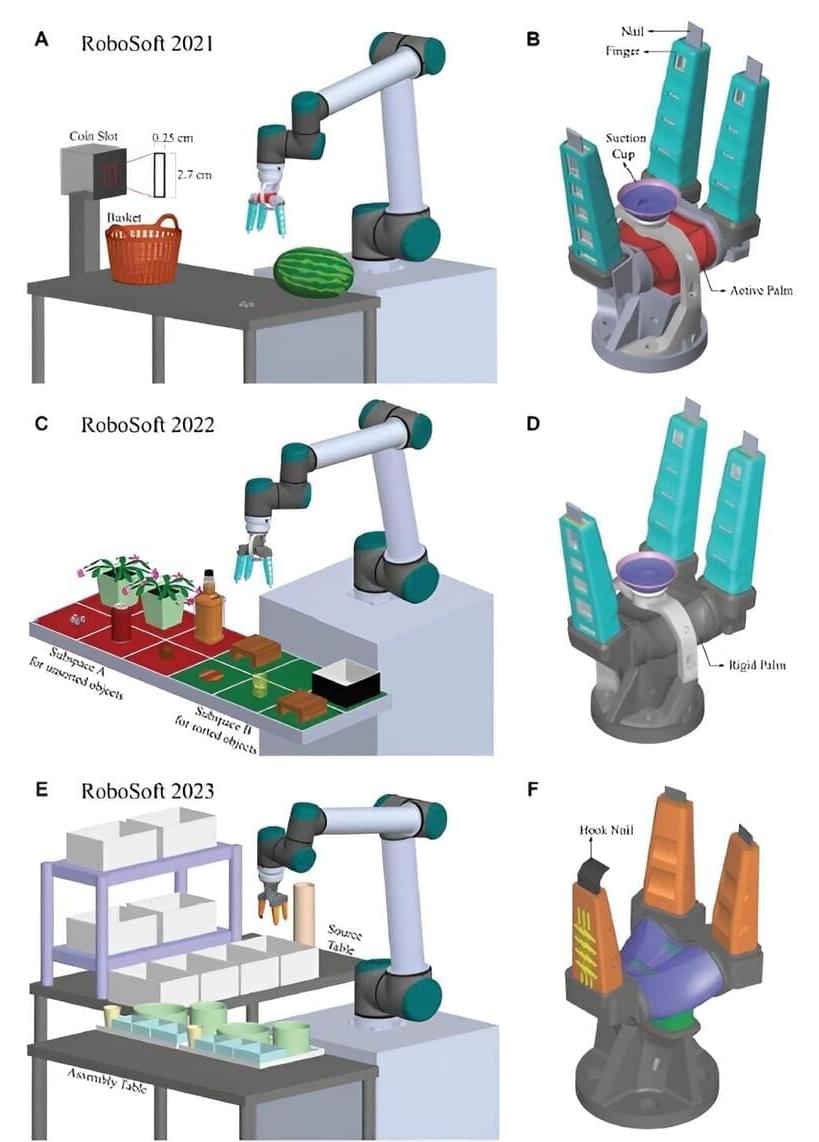
Robotic automation has become a game-changer in addressing labor shortages. While traditional rigid grippers have effectively automated various routine tasks, boosting efficiency and productivity in industries that deal with objects of well-defined specifications, they fall short in sectors like the food industry, where delicate objects of varying sizes and shapes need to be handled. In these cases, a more specialized type of gripper is required.
“Bioinspired soft robotics seeks to develop technologies that draw inspiration from nature and leverage advanced materials and fabrication processes,” said Dr. Pablo Valdivia y Alvarado, Associate Professor at the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD).
Soft grippers inspired by the natural dexterity and control of human hands are particularly well-suited to the food industry. They can adapt to objects of varying sizes and shapes while distributing forces more evenly, making them ideal for handling delicate items.