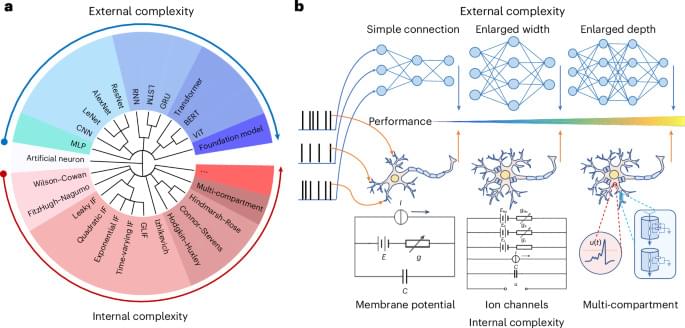
This study shows that by enhancing internal complexity of neurons in a Hodgkin–Huxley network, similar performance to larger, simpler networks can be achieved, suggesting an alternative path for powerful AI systems by focusing on neuron complexity.

The services are necessary to maintain a domestic trusted source for strategic radiation-hardened microelectronics to meet the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) certification to Congress, as stipulated by the fiscal 2018 National Defense Authorization Act Section 1,670, DOD officials say.
Radiation-hardened microelectronics components are necessary for manned and unmanned spacecraft operating on long-duration orbital missions in high-radiation space environments like geosynchronous orbits.

The problem of intelligence — its nature, how it is produced by the brain and how it could be replicated in machines — is a deep and fundamental problem that cuts across multiple scientific disciplines. Philosophers have studied intelligence for centuries, but it is only in the last several decades that developments in science and engineering have made questions such as these approachable: How does the mind process sensory information to produce intelligent behavior, and how can we design intelligent computer algorithms that behave similarly? What is the structure and form of human knowledge — how is it stored, represented, and organized? How do human minds arise through processes of evolution, development, and learning? How are the domains of language, perception, social cognition, planning, and motor control combined and integrated? Are there common principles of learning, prediction, decision, or planning that span across these domains?
This course explores these questions with an approach that integrates cognitive science, which studies the mind; neuroscience, which studies the brain; and computer science and artificial intelligence, which study the computations needed to develop intelligent machines. Faculty and postdoctoral associates affiliated with the Center for Brains, Minds and Machines discuss current research on these questions.

A new algorithm may make robots safer by making them more aware of human inattentiveness. In computerized simulations of packaging and assembly lines where humans and robots work together, the algorithm developed to account for human carelessness improved safety by about a maximum of 80% and efficiency by about a maximum of 38% compared to existing methods.
The work is reported in IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems.
“There are a large number of accidents that are happening every day due to carelessness—most of them, unfortunately, from human errors,” said lead author Mehdi Hosseinzadeh, assistant professor in Washington State University’s School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering.
A tiny battery designed by MIT engineers could enable the deployment of cell-sized, autonomous robots for drug delivery within in the human body, as well as other applications such as locating leaks in gas pipelines.
The new battery, which is 0.1 millimeters long and 0.002 millimeters thick—roughly the thickness of a human hair—can capture oxygen from air and use it to oxidize zinc, creating a current of up to 1 volt. That is enough to power a small circuit, sensor, or actuator, the researchers showed.
“We think this is going to be very enabling for robotics,” says Michael Strano, the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT and the senior author of the study. “We’re building robotic functions onto the battery and starting to put these components together into devices.”
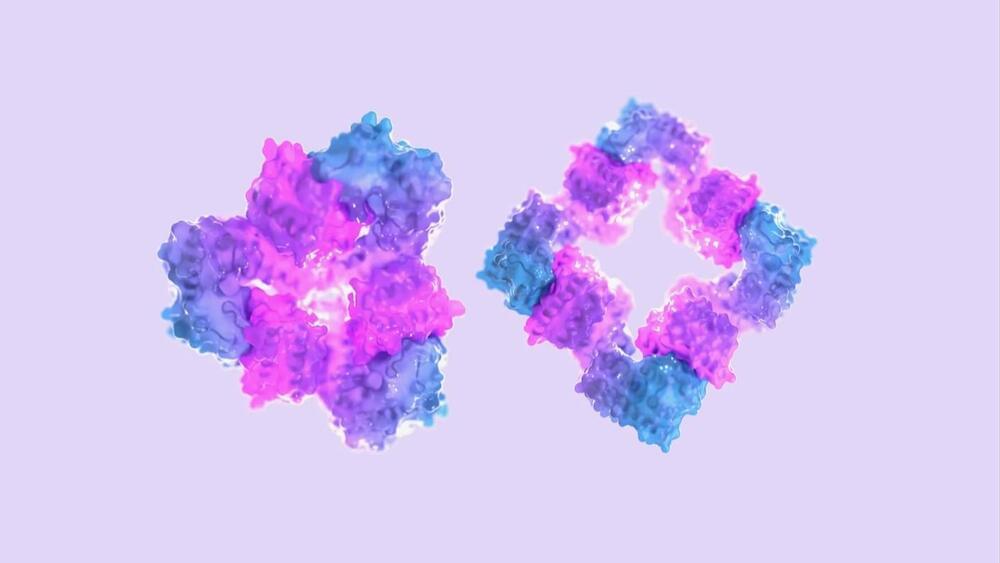

This type of molecular collaboration has inspired scientists for nearly a century. Here, oxygen is the effector. It flips a protein switch, helping proteins better carry oxygen through the body. In other words, it may be possible to optimize protein functions with an alternative effector drug.
The problem? The original inspiration is wonky. Sometimes hemoglobin proteins carry oxygen. Other times they don’t. In 1965, a French and American collaboration found out why. Each protein alternates between two three-dimensional shapes—one that carries oxygen and another that doesn’t. The shapes can’t coexist in the assembled protein to carry oxygen: It’s all-or-none, depending on the presence and amount of the effector.
The new study built on these lessons to guide their AI-designed proteins.


Could food delivery robots with zero carbon emissions influence a customer’s decision to buy food using them instead of robot vehicles that emit carbon into the atmosphere? This is what a recent study published in the International Journal of Hospitality Management hopes to address as a tea of researchers from Washington State University (WSU) investigated how a customer’s knowledge of an automatic delivery robot’s (ADR) environment impact influences their choice regarding which type of robot they want delivering their food. This study holds the potential to help scientists, environmental conservationists, and the public better understand the benefits of eco-friendly delivery robots for both the short and long term.
“Much of the marketing focus has been on the functionality and the convenience of these automatic delivery robots, which is really important, but it would enhance these efforts to promote their green aspects as well,” said Jennifer Han, who is a doctoral student in WSU’s Carson College of Business and lead author of the study.
For the study, the researchers used the Amazon crowdsourcing platform, MTurk, to conduct an online survey comprised of 418 adults who were instructed to watch videos about ADRs followed by a questionnaire regarding the environmental impact and the risk of using ADRs for their food delivery service. In the end, the team discovered a connection between participants who found ADRs were less risky and wanted an eco-friendly ADR compared to participants who thought ADRs were riskier but weren’t concerned about the environmental consequences.