The futurist argues that advances in AI and medicine will offer us unprecedented freedom.



Nanobots are tiny, ~50–100 nm wide robots that perform a single, highly specialized task. They work incredibly well for administering drugs. Drugs typically act throughout the body before entering the diseased area. The medication can be precisely targeted with nanotechnology, increasing its effectiveness and lowering the possibility of negative side effects. Special sensor nanobots can be inserted into the blood under the skin where microchips, coated with human molecules and designed to emit an electrical impulse signal, monitor the sugar level in the blood.
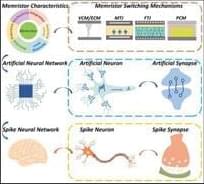
In recent years, there have been many reviews investigating neuromorphic computing from the perspectives of device electrical properties,[ 9, 10 ] resistive switching materials,[ 11, 12 ] memristive synapses and neurons,[ 13 ] algorithm optimization,[ 14 ] and circuit design.[ 15 ] Different from the existing literature, we discuss the possibility of achieving brain-like computing from the perspective of memristor technology and review the establishment of spiking neural network neuromorphic computing systems. In this article, we first review the resistive switching mechanisms of different types of memristors and focus on factors, which affect device stability and the corresponding optimization measures that have been applied. Furthermore, we study the stochasticity, power consumption, switching speed, retention, endurance, and other properties of memristors, which are the basis for neuromorphic computing implementations. We then review various memristor-based neural networks and the building of spike neural network neuromorphic computing systems. Finally, we shed light upon the major challenges and offer our perspectives and opinions for memristor-based brain-like computing systems.

Unitree’s humanoid robot just got a mass production upgrade. The G1 will now feature stronger performance, the “ultimate appearance,” and is now more in line with mass production requirements according to Unitree.
Mashable is your source for the latest in tech, culture, and entertainment.
Follow us:
Check out https://mashable.com/
Facebook: / mashable.
Twitter: / mashable.
Instagram: / mashable.

Serious Question, does anyone in here know people who made said AI or run named company? would be interested in system described.
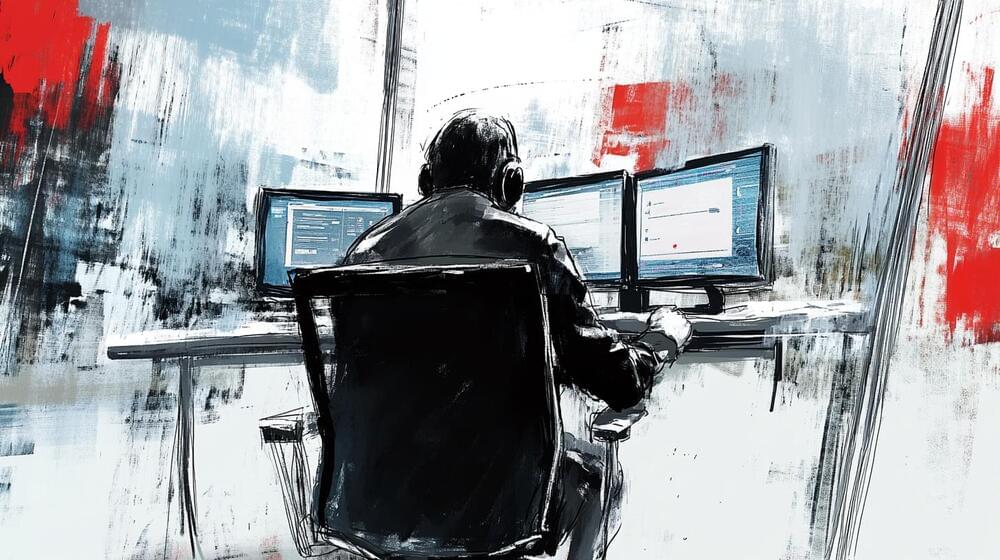
Artificial intelligence is being tested at the Integrated Control Center in Ludwigshafen to save precious time during emergency calls. For example, a computer voice translates for callers who speak a foreign language.
According to an SWR report, the Integrated Control Center in Ludwigshafen is using artificial intelligence (AI) to speed up emergency call handling. Until now, it took valuable minutes when callers only spoke a foreign language. Dispatchers had to quickly find a colleague who could translate, which cost time and caused stress, says Manuel Fischer, head of the integrated rescue service department.
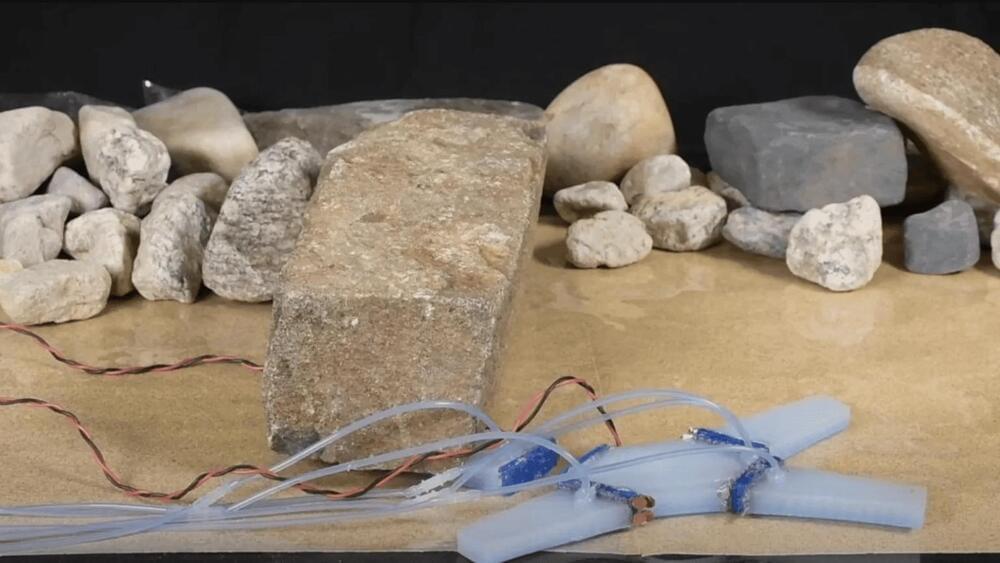

In another case of technology being inspired by nature, roboticists at The Faboratory at Yale University have developed a way for soft robots to replicate animals and insects by self-amputating a limb or building bridges by temporarily fusing their bodies.
In one of the demo videos, a soft quadruped robot crawls when a falling rock traps its back leg. The reversible joint attaching the leg is heated with current, allowing the robot to break free of its leg and escape, after which the joint could be reattached.
Another video released by the team shows a single crawler robot that’s originally unable to cross the gap between tables. Three robots are then fused together using joints that have been heated and softened by electric current, which allows them to cross the chasm as one unit.

More details of OpenAI’s secretive Project Strawberry have dropped, including its expected release date and the areas it will specialize in.
A recent report in The Information quotes “two people who have been involved in the effort”, and goes on to say that Project Strawberry could drop this Fall, and be better at math and programming than any chatbot we’ve seen so far.