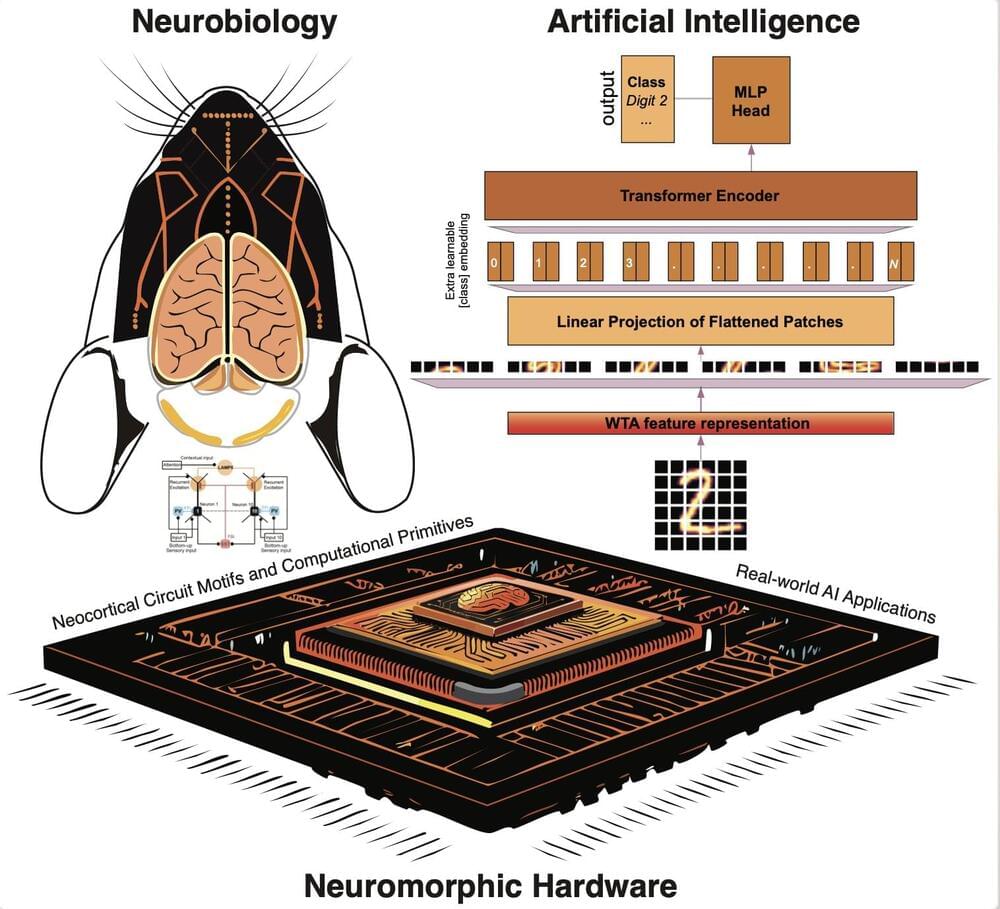
Over the past decade or so, computer scientists have developed increasingly advanced computational techniques that can tackle real-world tasks with human-comparable accuracy. While many of these artificial intelligence (AI) models have achieved remarkable results, they often do not precisely replicate the computations performed by the human brain.
Researchers at Tibbling Technologies, Broad Institute at Harvard Medical School, The Australian National University and other institutes recently tried to use AI to mimic a specific type of computation performed by circuits in the neocortex, known as “winner-take-all” computations.
Their paper, published on the bioRxiv preprint server, reports the successful emulation of this computation and shows that adding it to transformer-based models could significantly improve their performance on image classification tasks.