48 likes, — designdelulu on May 23, 2024: ‘Jensen Huang says designing computer chips and writing software can no longer be done without AI and he wants to turn NVIDIA into one giant AI’



Identifying one faulty turbine in a wind farm, which can involve looking at hundreds of signals and millions of data points, is akin to finding a needle in a haystack.
Engineers often streamline this complex problem using deep-learning models that can detect anomalies in measurements taken repeatedly over time by each turbine, known as time-series data.
But with hundreds of wind turbines recording dozens of signals each hour, training a deep-learning model to analyze time-series data is costly and cumbersome. This is compounded by the fact that the model may need to be retrained after deployment, and wind farm operators may lack the necessary machine-learning expertise.
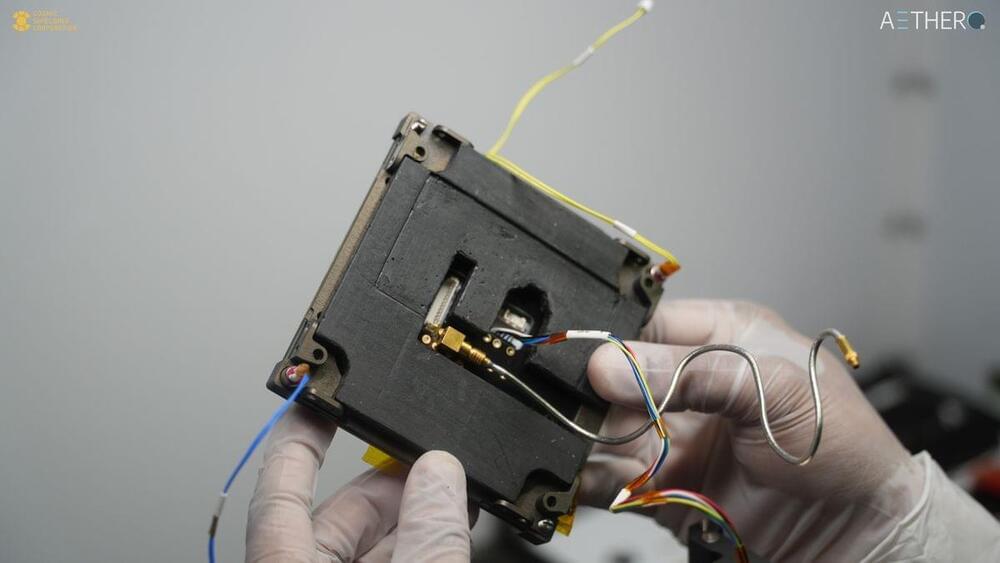
“This is going to be the fastest AI computer ever launched to space,” Yanni Barghouty, CSC’s cofounder and CEO, told Space.com. “The goal of this mission is simply to demonstrate the successful operation of an AI-capable Nvidia GPU on orbit with minimal to no errors while operating.”
The GPU will fly aboard a cubesat built by San Francisco-based company Aethero, a maker of high-performance, space-rated computers. The GPU’s only task during its four-month orbital mission will be to make mathematical calculations, the results of which will be beamed to Earth and carefully checked.
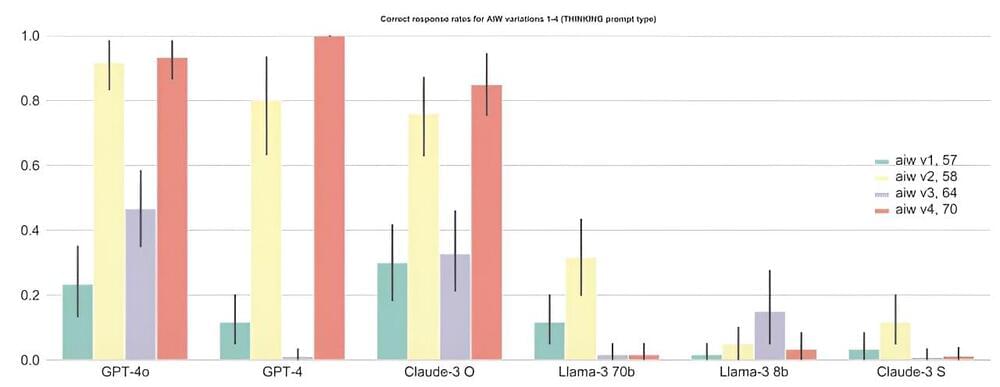
Even the best AI large language models (LLMs) fail dramatically when it comes to simple logical questions. This is the conclusion of researchers from the Jülich Supercomputing Center (JSC), the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at the University of Bristol and the LAION AI laboratory.
In their paper posted to the arXiv preprint server, titled “Alice in Wonderland: Simple Tasks Showing Complete Reasoning Breakdown in State-Of-the-Art Large Language Models,” the scientists attest to a “dramatic breakdown of function and reasoning capabilities” in the tested state-of-the-art LLMs and suggest that although language models have the latent ability to perform basic reasoning, they cannot access it robustly and consistently.
The authors of the study—Marianna Nezhurina, Lucia Cipolina-Kun, Mehdi Cherti and Jenia Jitsev—call on “the scientific and technological community to stimulate urgent re-assessment of the claimed capabilities of the current generation of LLMs.” They also call for the development of standardized benchmarks to uncover weaknesses in language models related to basic reasoning capabilities, as current tests have apparently failed to reveal this serious failure.
The uptake of artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision and machine learning has been high in some industries, such as retail (see AiFi and Standard AI) and automotive (see Waymo and Tesla), but we’re now starting to see it break into some of the most critical aspects of society.
The recent accelerations in healthcare are perhaps the best example of this. Over 90% of hospitals and healthcare systems now have an AI or automation strategy in place, up from 53% in 2019, and “the global market for surgical robotics and computer-assisted surgery is anticipated to grow from $6.1 billion in 2020 to $11.6 billion by 2025.”
AI is starting to become more than just a buzzword. At this very moment, we’re starting to see AI-enhanced advanced tooling augment human capabilities and reshape how surgical procedures are planned, executed and managed. With aging populations, rising costs, lack of medical staff and backlogs worse than ever (almost 8 million people in the U.K.), the demand for AI-driven efficiency and surgery precision is escalating like never before.


While generative AI tools have been heralded as the future of education, more than 40 years of academic research suggests that it could also harm learning in realms from online tutoring to employee training for three reasons. First, the best student-teacher relationships are empathetic ones but it is biologically impossible for humans and AI to develop mutual empathy. Second, AI might help us bypass the boring task of knowledge accumulation but it is only through that process that we develop higher order thinking skills. Finally, digital tools are notoriously distracting and multitasking diminishes learning. As we think about the benefits of new technology, we must also consider the risks.
Page-utils class= article-utils—vertical hide-for-print data-js-target= page-utils data-id= tag: blogs.harvardbusiness.org, 2007/03/31:999.387329 data-title= The Limits of GenAI Educators data-url=/2024/07/the-limits-of-genai-educators data-topic= AI and machine learning data-authors= Jared Cooney Horvath data-content-type= Digital Article data-content-image=/resources/images/article_assets/2024/07/Jul24_17_545985287-383x215.jpg data-summary=
Three fundamental problems with using LLMs as teachers, tutors, and trainers.
👉 Researchers have developed an AI system called “The AI Scientist” that can perform scientific research on its own, from brainstorming and experimenting to writing full papers.
A new AI system called “The AI Scientist” can perform scientific research completely autonomously, from brainstorming and experimenting to writing complete papers.
Ad.
Researchers from the University of British Columbia, University of Oxford, and AI startup Sakana AI have developed an AI system capable of conducting scientific research independently. Named “The AI Scientist,” the system can generate new research ideas, write code, perform experiments, visualize results, and even compose complete scientific papers.
