By Rachel Tompa
Stanford Medicine researchers devise a new artificial intelligence model, SyntheMol, which creates recipes for chemists to synthesize the drugs in the lab.
By Rachel Tompa
Stanford Medicine researchers devise a new artificial intelligence model, SyntheMol, which creates recipes for chemists to synthesize the drugs in the lab.

Aardvark represents a breakthrough in AI and security research: an autonomous agent that can help developers and security teams discover and fix security vulnerabilities at scale. Aardvark is now available in private beta to validate and refine its capabilities in the field.
Aardvark continuously analyzes source code repositories to identify vulnerabilities, assess exploitability, prioritize severity, and propose targeted patches.
Aardvark works by monitoring commits and changes to codebases, identifying vulnerabilities, how they might be exploited, and proposing fixes. Aardvark does not rely on traditional program analysis techniques like fuzzing or software composition analysis. Instead, it uses LLM-powered reasoning and tool-use to understand code behavior and identify vulnerabilities. Aardvark looks for bugs as a human security researcher might: by reading code, analyzing it, writing and running tests, using tools, and more.
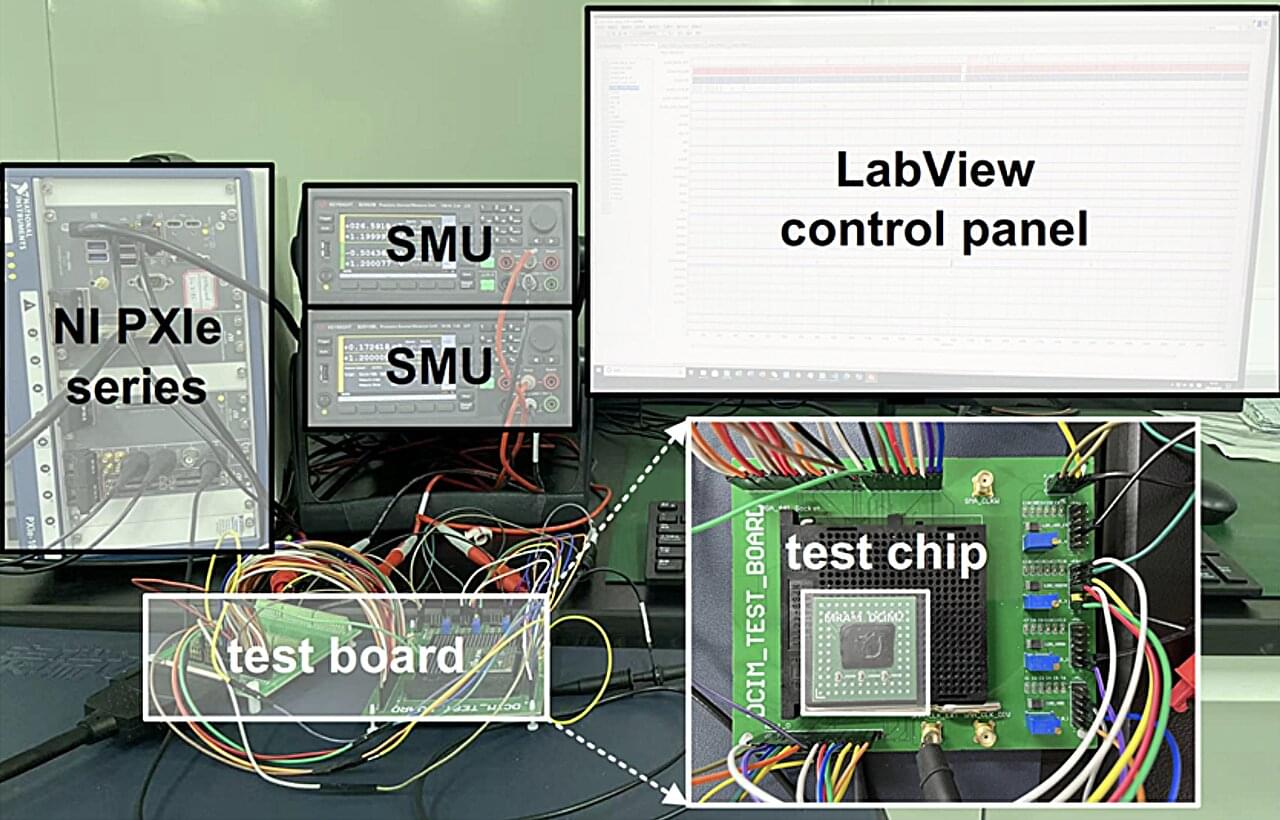
To make accurate predictions and reliably complete desired tasks, most artificial intelligence (AI) systems need to rapidly analyze large amounts of data. This currently entails the transfer of data between processing and memory units, which are separate in existing electronic devices.
Over the past few years, many engineers have been trying to develop new hardware that could run AI algorithms more efficiently, known as compute-in-memory (CIM) systems. CIM systems are electronic components that can both perform computations and store information, typically serving both as processors and non-volatile memories. Non-volatile essentially means that they can retain data even when they are turned off.
Most previously introduced CIM designs rely on analog computing approaches, which allow devices to perform calculations leveraging electrical current. Despite their good energy efficiency, analog computing techniques are known to be significantly less precise than digital computing methods and often fail to reliably handle large AI models or vast amounts of data.
As anyone who uses the internet will know, the way we find information has fundamentally changed. For the last three decades, search engines have delivered ranked lists of links in response to our queries, and it was our job to search through them to find what we wanted. Now, major search engines use generative AI tools to deliver a single coherent answer, often embedded with a few links. But how does this approach compare with the traditional method? In a comprehensive new study, scientists compared these two approaches to see what we are gaining and losing.
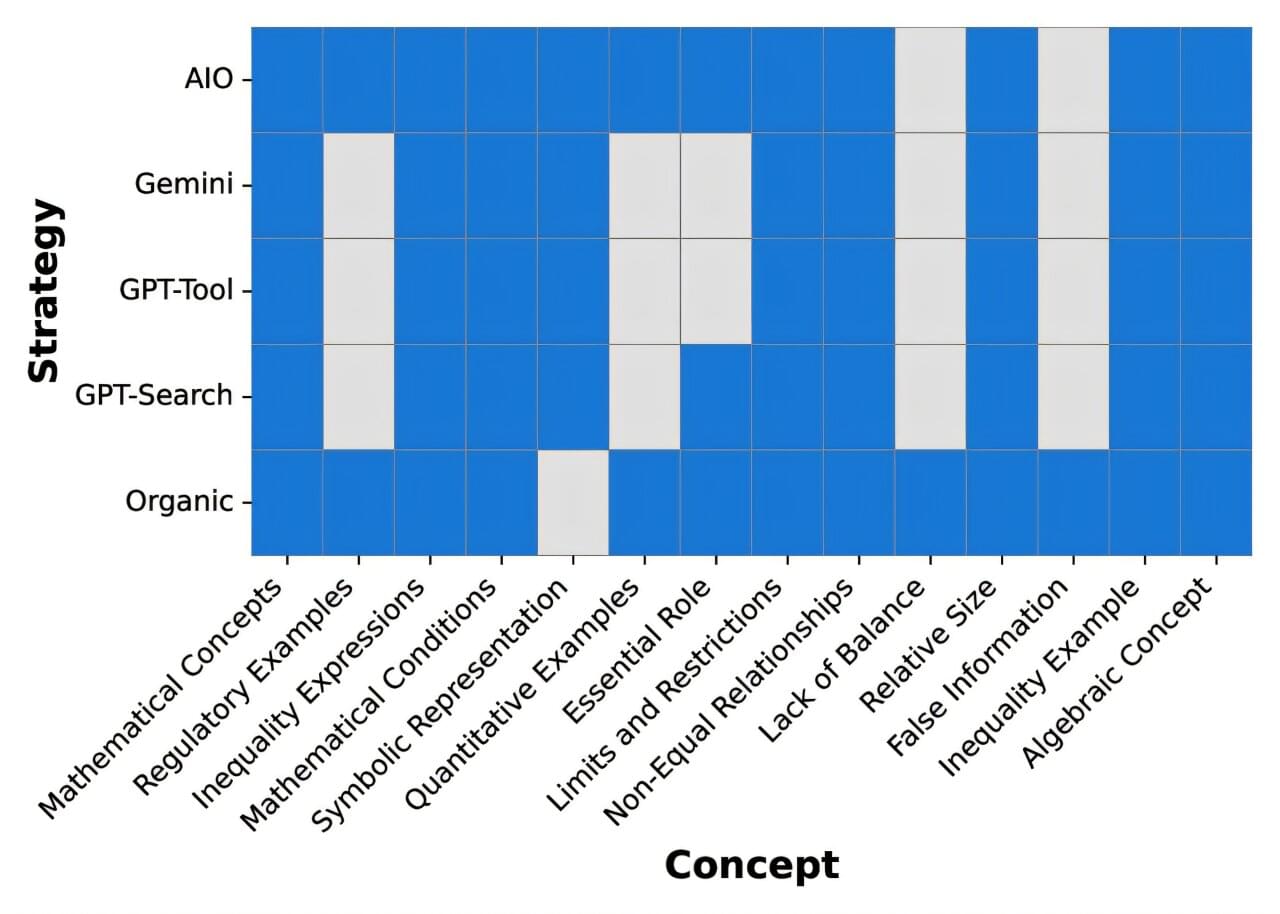
To figure this out, researchers from Ruhr University Bochum and the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems compared traditional Google Search with four generative search engines: Google AI Overview (AIO), Gemini, GPT-4o-Search and GPT-4o with Search Tool. The team ran thousands of queries covering six main areas, including general knowledge, politics, science and shopping.
Then they made a detailed comparison of the two search styles based on three key metrics. First, they analyzed source diversity by checking the websites AI used against traditional search’s top links. Second, they measured knowledge reliance to see how much AI relied on its own internal memory rather than searching the web for fresh information.

Researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering and School of Advanced Computing have developed artificial neurons that replicate the complex electrochemical behavior of biological brain cells.
The innovation, documented in Nature Electronics, is a leap forward in neuromorphic computing technology. The innovation will allow for a reduction of the chip size by orders of magnitude, will reduce its energy consumption by orders of magnitude, and could advance artificial general intelligence.
Unlike conventional digital processors or existing neuromorphic chips based on silicon technology that merely simulate neural activity, these artificial neurons physically embody or emulate the analog dynamics of their biological counterparts. Just as neurochemicals initiate brain activity, chemicals can be used to initiate computation in neuromorphic (brain-inspired) hardware devices. By being a physical replication of the biological process, they differ from prior iterations of artificial neurons that were solely mathematical equations.

Could computers ever learn more like humans do, without relying on artificial intelligence (AI) systems that must undergo extremely expensive training?
Neuromorphic computing might be the answer. This emerging technology features brain-inspired computer hardware that could perform AI tasks much more efficiently with far fewer training computations using much less power than conventional systems. Consequently, neuromorphic computers also have the potential to reduce reliance on energy-intensive data centers and bring AI inference and learning to mobile devices.
Dr. Joseph S. Friedman, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at The University of Texas at Dallas, and his team of researchers in the NeuroSpinCompute Laboratory have taken an important step forward in building a neuromorphic computer by creating a small-scale prototype that learns patterns and makes predictions using fewer training computations than conventional AI systems. Their next challenge is to scale up the proof-of-concept to larger sizes.

Machine learning models are designed to take in data, to find patterns or relationships within those data, and to use what they have learned to make predictions or to create new content. The quality of those outputs depends not only on the details of a model’s inner workings but also, crucially, on the information that is fed into the model.
Some models follow a brute force approach, essentially adding every bit of data related to a particular problem into the model and seeing what comes out. But a sleeker, less energy-hungry way to approach a problem is to determine which variables are vital to the outcome and only provide the model with information about those key variables.
Now, Adrián Lozano-Durán, an associate professor of aerospace at Caltech and a visiting professor at MIT, and MIT graduate student Yuan Yuan, have developed a theorem that takes any number of possible variables and whittles them down, leaving only those that are most important. In the process, the model removes all units, such as meters and feet, from the underlying equations, making them dimensionless, something scientists require of equations that describe the physical world. The work can be applied not only to machine learning but to any mathematical model.


