Artificial intelligence has the potential to significantly boost margins across various industries in the coming years, most notably software, semiconductors, and energy.



She’s not long on charisma or passion but keeps perfect rhythm and is never prone to temperamental outbursts against the musicians beneath her three batons. Meet MAiRA Pro S, the next-generation robot conductor who made her debut this weekend in Dresden.
Her two performances in the eastern German city are intended to show off the latest advances in machine maestros, as well as music written explicitly to harness 21st-century technology. The artistic director of Dresden’s Sinfoniker, Markus Rindt, said the intention was “not to replace human beings” but to perform complex music that human conductors would find impossible.
Roli, the maker of quirky, portable, and expressive digital pianos and keyboard instruments, has a new device that can both teach budding pianists how to play music and provide seasoned musicians with a new way of adding filters and effects to their songs by waving their hands and wiggling their fingers.
The Roli Airwave is a 14.5-inch tall stand with a camera on top. The camera is positioned downward to track the movements of a player’s fingers as they dance across a keyboard sitting at the base of the stand. The movements of a player’s hands that are captured by the camera are streamed in real time onto the screen of a tablet that sits on the easel-like Airwave stand. The visuals can be used as a teaching tool to show the player which fingers should strike which keys, or offer some additional guidance on how to play a song just right. Of course, the Airwave uses machine intelligence and computer vision to track the player’s hands and to offer its advice on where those hands should be placed.
The system costs $299 and should start shipping in February 2025. You’ll also need one of Roli’s keyboards (which range from $249 to $1,399) to pair with it. If you want to use it as a teaching tool, you’ll also need an iPad or other tablet to set onto the stand to supply the visuals.

Can Tesla meet the production timeline for Optimus? Share your thoughts in the comments.
Tesla’s humanoid robot, Optimus, is set to enter production by 2025. Elon Musk announced that low production for internal use will begin next year, with high production for external companies expected in 2026. Optimus Gen 2, featuring a new design, was showcased at the 2024 World Artificial Intelligence Conference in Shanghai. Tesla has been conducting field tests in its gigafactories, indicating progress towards Musk’s timeline for Optimus’ production.


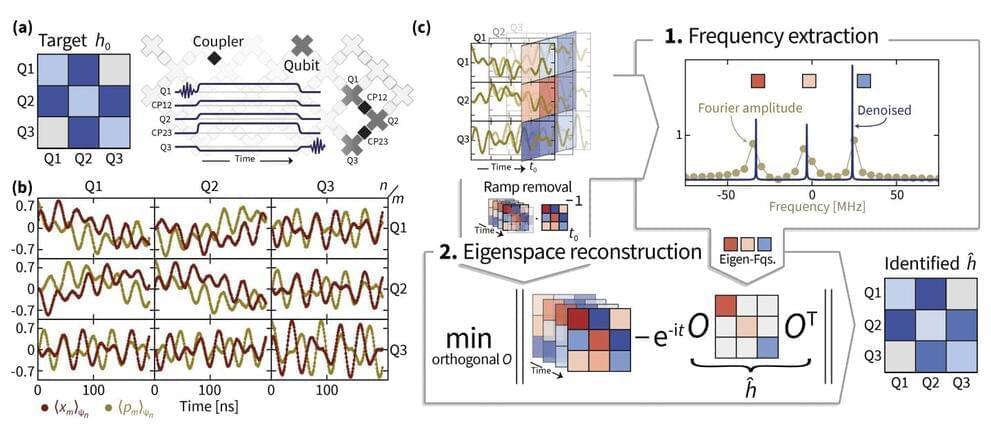
Researchers at Freie Universität Berlin, University of Maryland and NIST, Google AI, and Abu Dhabi set out to robustly estimate the free Hamiltonian parameters of bosonic excitations in a superconducting quantum simulator. The protocols they developed, outlined in a paper pre-published on arXiv, could contribute to the realization of highly precise quantum simulations that reach beyond the limits of classical computers.