AI can spot patterns in the data from blood tests that can give an early warning of disease.



Domo arigato, Mr. Botto.
The next artistic masterpiece may be more machine than man: An artificial intelligence design program called Botto has sold computerized works for megabucks and could revolutionize the creative space.
Since its creation in 2021, Botto has created more than 150 works of various disciplines that have cumulatively raked in over $5 million at auction, CNBC reported.
Journey into one of humanity’s most ambitious space missions as we explore JAXA’s groundbreaking Hayabusa2 mission to asteroid Ryugu! Discover how this remarkable spacecraft not only achieved the first successful deployment of rovers on an asteroid but also brought back precious samples that could reveal secrets about our solar system’s formation. From the dramatic touchdown on Ryugu’s surface to the revolutionary MASCOT and MINERVA rovers that hopped across its microgravity environment, this video breaks down the incredible technology and scientific discoveries from this historic asteroid sample return mission. Learn how these primitive asteroid samples are reshaping our understanding of the early solar system and what this means for future space exploration.


Leveraging the success of this new program, just about two years from its launch DeepMind’s AI spinout Isomorphic announced two drug discovery deals, worth $3 billion each, with Eli Lilly and Novartis.
Earlier this year, microprocessor giant NVIDIA also dove head first into AI for drug discovery, making big investments and deals with leaders like Recursion Pharmaceuticals and Genentech.
AI in drug discovery seems to be having a moment.
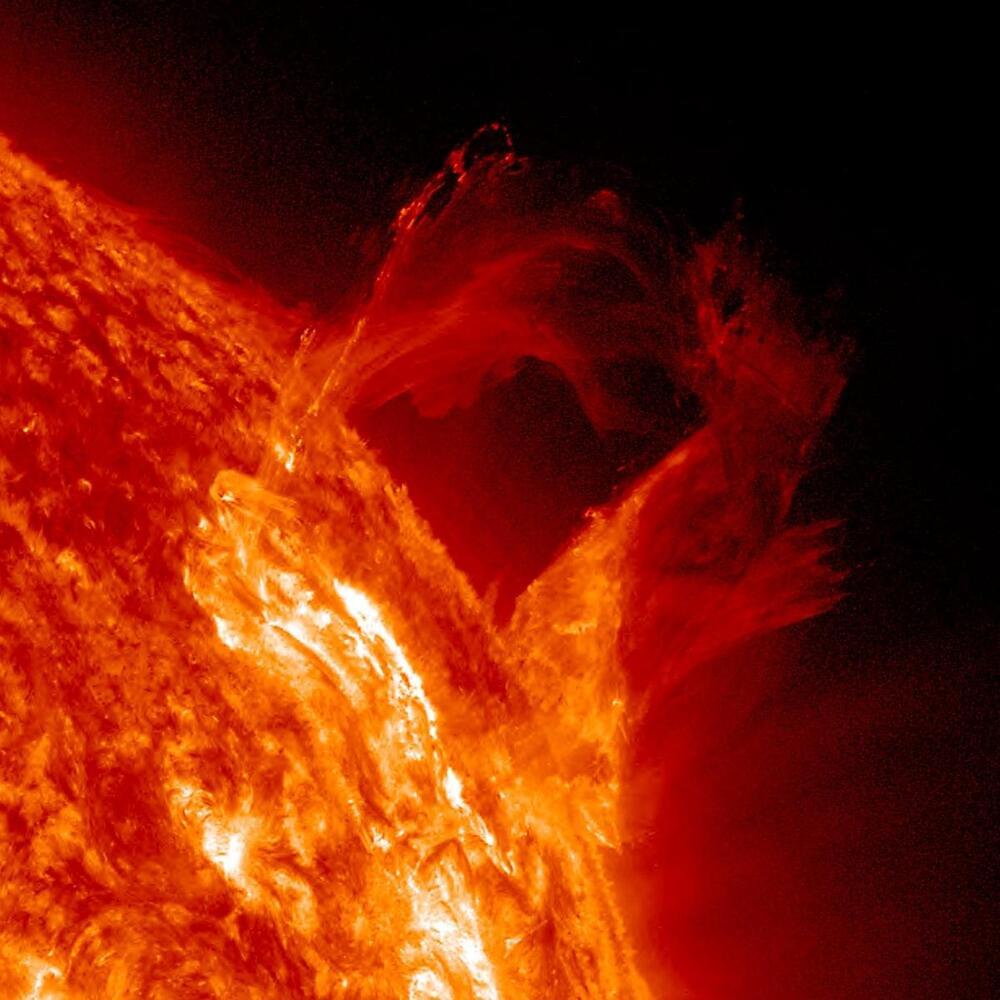



The Parker Solar Probe will swoop just 6.1 million kilometers above the sun’s surface on Christmas Eve. Scientists are thrilled at what we might learn.
By Jonathan O’Callaghan edited by Lee Billings
There are some places in the solar system no human will ever go. The surface of Venus, with its thick atmosphere and crushing pressure, is all but inaccessible. The outer worlds, such as Pluto, are too remote to presently consider for anything but robotic exploration. And the sun, our bright burning ball of hydrogen and helium, is far too hot and tumultuous for astronauts to closely approach. In our place, one intrepid robotic explorer, the Parker Solar Probe, has been performing a series of dramatic swoops toward our star, reaching closer than any spacecraft before to unlock its secrets. Now it is about to perform its final, closest passes, skimming inside the solar atmosphere like never before.