Google’s sixth-generation TPU claims major cost and performance gains, but its single-cloud reliance faces stiff competition from NVIDIA GPUs and Amazon’s Trainium.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 439

AI Agents: Easier To Build, Harder To Get Right
Today, AI agents have evolved to become more modular and sophisticated. Agents like ChatGPT can engage in conversations and assist in a wide range of workflows, including customer service and financial decision-making.
Technologies such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) allow AI systems to combine different data sources dynamically, making them more adaptive and helpful in real-world applications. As AI’s influence expands into industries such as finance, healthcare and cybersecurity, it is becoming clear that AI agents are critical components of modern business operations.
Despite the remarkable progress in AI, deploying these systems presents several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the risk of bias embedded in the datasets used to train AI agents. AI systems learn from historical data, which can contain patterns of discrimination that, if unchecked, lead to biased decisions, such as favoring particular groups over others in hiring or lending scenarios.

AI tool will be able to trace dolphins by their regional accent
Sea mammal expert Dr Julie Oswald, of the University of St Andrews’ Scottish Oceans Institute, created the tool, known as the Real-time Odontocete Call Classification Algorithm (Rocca), using AI.
It can categorise dolphin calls by species and comes in different versions linked to different geographical areas.
There are around 42 species of dolphin and they use hundreds of different sounds to communicate.

Off The Grid: Technological Autonomy
Use code isaacarthur at the link below to get an exclusive 60% off an annual Incogni plan: https://incogni.com/isaacarthur.
Technology offers us many options, including less reliance on others, but what does that entail and how autonomous can a person get?
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Off The Grid: Technological Autonomy.
Episode 477; December 12, 2024
Produced, Narrated \& Written: Isaac Arthur.
Editor: Donagh Broderick.
Graphics: Mafic Studios.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Stellardrone, \
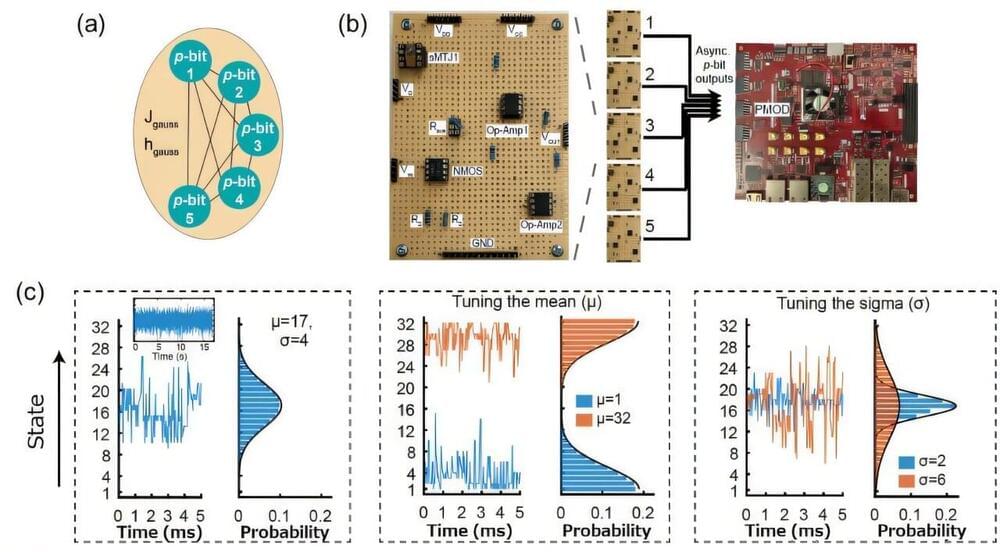
Researchers develop spintronics platform for energy-efficient generative AI
Researchers at Tohoku University and the University of California, Santa Barbara, have developed new computing hardware that utilizes a Gaussian probabilistic bit made from a stochastic spintronics device. This innovation is expected to provide an energy-efficient platform for power-hungry generative AI.
As Moore’s Law slows down, domain-specific hardware architectures—such as probabilistic computing with naturally stochastic building blocks—are gaining prominence for addressing computationally hard problems. Similar to how quantum computers are suited for problems rooted in quantum mechanics, probabilistic computers are designed to handle inherently probabilistic algorithms.
These algorithms have applications in areas like combinatorial optimization and statistical machine learning. Notably, the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton for their groundbreaking work in machine learning.

Secret Blizzard Deploys Kazuar Backdoor in Ukraine Using Amadey Malware-as-a-Service
Secret Blizzard has a track record of targeting various sectors to facilitate long-term covert access for intelligence collection, but their primary focus is on ministries of foreign affairs, embassies, government offices, defense departments, and defense-related companies across the world.
The latest report comes a week after the tech giant, along with Lumen Technologies Black Lotus Labs, revealed Turla’s hijacking of 33 command-and-control (C2) servers of a Pakistan-based hacking group named Storm-0156 to carry out its own operations.
The attacks targeting Ukrainian entities entail commandeering Amadey bots to deploy a backdoor known as Tavdig, which is then used to install an updated version of Kazuar, which was documented by Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 in November 2023.