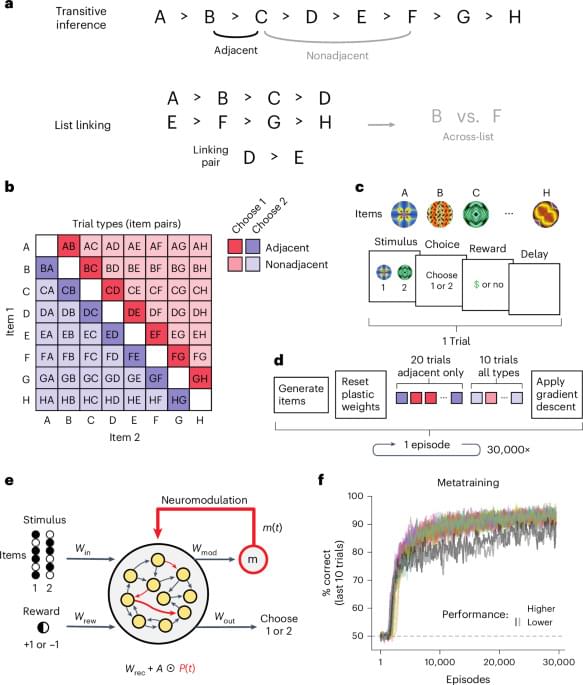
Using a metalearning approach to model relational learning, Miconi and Kay show neural mechanisms for structured generalization and rapid learning.




By the end of 2024, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) had established themselves as the main transformative forces behind recent technological advancements in healthcare. A report by Silicon Valley Bank states that in 2024, the amount of VC investment in health AI in the U.S. was expected to reach $11.1 billion, the highest number since 2021.
In my experience, the main driver behind the AI investment and adoption craze is the measurable value technology offers healthcare providers. A 2023 National Bureau of Economic Research study indicates that integrating AI can save the U.S. healthcare system up to $360 billion annually. A 2023 survey by the AMA shows that physicians see AI as a way to reduce the administrative burden of documentation (54%) and improve workflow efficiency (69%).
But do these positive changes reflect on the quality of care, and do patients benefit from AI and ML-powered solutions? In this article, I share my take on the transformative potential of AI and ML in the modern care delivery process.
A huge number of ultracold atoms have been corralled into a grid that could form the basis of the next largest quantum computer.

Just as ChatGPT signaled an inflection point for AI to enter the mainstream; robots may be nearing a similar breakout moment.

In today’s AI news, Synthesia, a generative AI start-up based in Britain, has raised $180 million valuing it at $2.1 billion. The company uses artificial intelligence to create lifelike human faces and speech that are almost indistinguishable from real video but do not need cameras, actors or film studios.
And, shortly after OpenAI released o1, its first “reasoning” AI model, people began noting a curious phenomenon. The model would sometimes begin “thinking” in Chinese, Persian, or some other language — even when asked a question in English.
Then, MiniMax is perhaps today best known here in the U.S. as the Singaporean company behind Hailuo, a realistic, high-resolution generative AI video model. Today, for instance, it announced the release and open-sourcing of the MiniMax-01 series, a new family of models built to handle ultra-long contexts and enhance AI agent development.
Meanwhile, Google’s Gemini AI has quietly upended the AI landscape, achieving a milestone few thought possible: The simultaneous processing of multiple visual streams in real time. This breakthrough — which allows Gemini to not only watch live video feeds but also to analyze static images simultaneously — emerged from an experimental application called “AnyChat.”
In videos, IBM’s Luv Aggarwal discusses the importance of data creation, organization, storage, integration, and analytics in creating a seamless data flow that enables data-driven insights. Dive into the world of data flow and discover the key to harmonious business operations.
Eric Schmidt’s new secret project is an AI video platform called “Hooglee”. The billionaire technologist has quietly founded a startup that aims to “bring people closer, simplify communication, and enhance engagement” through artificial intelligence.
Re utilizing AI in the services and hospitality sector that include helping to manage crews and even predict demand. They speak with Caroline Hyde on “Bloomberg Technology”, about integrating AI in hospitality. ‘ + We close out with, tech visionary Martin Warner exploring the future of human potential in an AI-driven world, at TEDxSwansea. As artificial general intelligence rapidly evolves, Warner offers a compelling roadmap to outsmart machines, adapt, and thrive. This insightful guide will inspire optimism about how humanity can harness AI’s power while keeping the human spirit at the forefront.
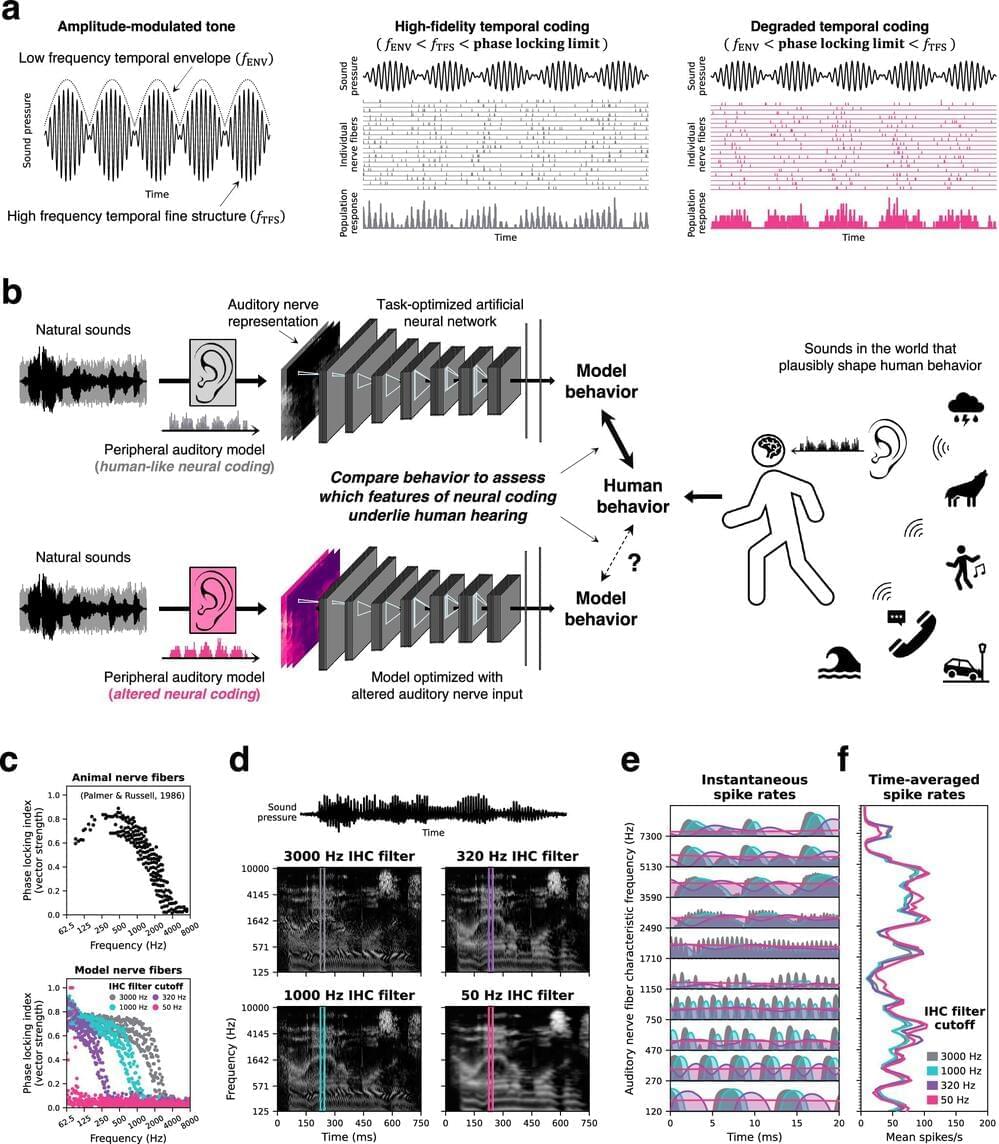
When sound waves reach the inner ear, neurons there pick up the vibrations and alert the brain. Encoded in their signals is a wealth of information that enables us to follow conversations, recognize familiar voices, appreciate music, and quickly locate a ringing phone or crying baby.
Neurons send signals by emitting spikes—brief changes in voltage that propagate along nerve fibers, also known as action potentials. Remarkably, auditory neurons can fire hundreds of spikes per second, and time their spikes with exquisite precision to match the oscillations of incoming sound waves.
With powerful new models of human hearing, scientists at MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research have determined that this precise timing is vital for some of the most important ways we make sense of auditory information, including recognizing voices and localizing sounds.
Back in the old days—the really old days—the task of designing materials was laborious. Investigators, over the course of 1,000-plus years, tried to make gold by combining things like lead, mercury, and sulfur, mixed in what they hoped would be just the right proportions. Even famous scientists like Tycho Brahe, Robert Boyle, and Isaac Newton tried their hands at the fruitless endeavor we call alchemy.
Materials science has, of course, come a long way. For the past 150 years, researchers have had the benefit of the periodic table of elements upon which to draw, which tells them that different elements have different properties, and one can’t magically transform into another. Moreover, in the past decade or so, machine learning tools have considerably boosted our capacity to determine the structure and physical properties of various molecules and substances.
New research by a group led by Ju Li—the Tokyo Electric Power Company Professor of Nuclear Engineering at MIT and professor of materials science and engineering—offers the promise of a major leap in capabilities that can facilitate materials design. The results of their investigation appear in Nature Computational Science.