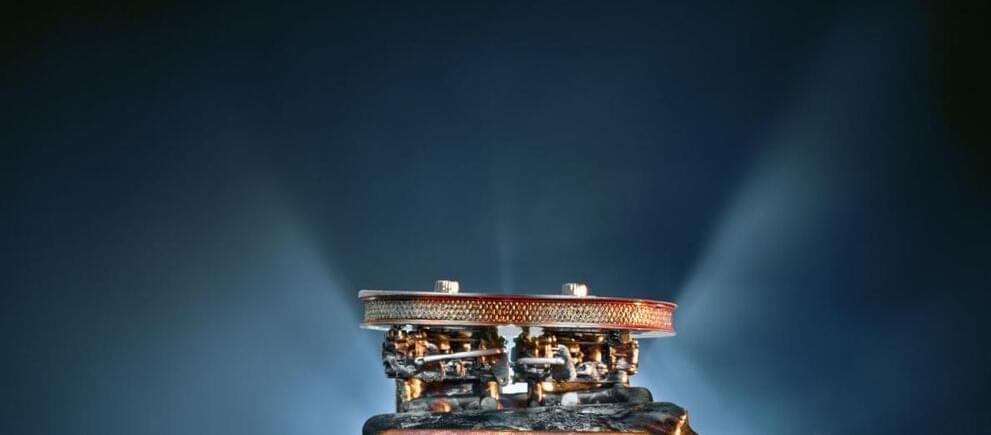
Scientists integrated lab-grown brain organoids with robots, creating hybrid intelligence. It offers new potential for neurological condition treatments.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 395
Nick bostroms simulation argument.
Have you ever paused, looked around, and wondered if everything you see, feel, and experience is real? Or could it be that we’re living in a sophisticated simulation, indistinguishable from reality?
This thought isn’t just a plot from a sci-fi movie; it’s a serious philosophical argument proposed by Nick Bostrom, known as the Simulation Argument. If you’ve ever questioned the nature of reality or pondered over the mysteries of existence, this exploration is for you.
Nick Bostrom, a prominent figure in the realm of philosophical and technological inquiry, has significantly contributed to the discourse on existential risks and the future of humanity. With a background that spans physics, computational neuroscience, and philosophy, Bostrom has established himself as a leading thinker in assessing the implications of emerging technologies. His work, which often explores the intersection of life, consciousness, and artificial intelligence, has paved the way for a deeper understanding of the potential futures humanity might face.
Are you ready to learn about the most exciting AI model of the year? OpenAI has just unveiled…
The robotics startup provides a modular cell-based matrix structure through which an AI-powered bot navigates to move materials.
What Creates Consciousness?
Posted in futurism, robotics/AI
Renowned researchers David Chalmers and Anil Seth join Brian Greene to explore how far science and philosophy have gone toward explaining the greatest of all mysteries, consciousness–and whether artificially intelligent systems may one day possess it.
This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
Participants:
David Chalmers.
Anil Seth.
Moderator:
Brian Greene.
00:00 — Introduction.
02:35 — Participant Introductions.
03:50 — Will an Artificial System Ever Become Conscious?
05:32 — The Hard Problem of Consciousness.
08:32 — Thought Experiment: Mary and the Nature of Conscious Experience.
13:28 — The Hard Problem and The Real Problem of Consciousness.
21:53 — The Brain as a Prediction Machine.
25:41 — Possible Solutions to the Hard Problem.
33:15 — Will AI Systems Become Conscious and How Will We Know?
40:11 — Is Human Consciousness the Only One Example of Conscious-like Experience?
42:19 — The Future of Creating Consciousness and the Ethical Questions.
44:39 — Credits.
Imagine a world where machines not only understand our words, but grasp the nuances of our emotions, anticipate our needs, and even surpass our own intelligence. This is the dream, and perhaps the near reality, of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
For many years, the idea of achieving AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) has only existed in the realm of science fiction. It’s been seen as a futuristic utopia where machines can seamlessly integrate into our lives. However, this perception is changing. Advances in AI technology are blurring the lines between fiction and reality, leading to both excitement and apprehension regarding its potential impact on society.
In this blog post, we’ll embark on a journey to explore the fascinating world of AGI. We’ll peek into the current state of AI and the significant innovations that are inching us toward AGI.
What if I told you that OpenAI just revealed something groundbreaking about AGI levels? In this…
Major study backed by OpenAI’s Sam Altman shows unconditional cash has benefits that have nothing to do with AI.
One of the largest-ever studies on basic income in the US suggests it can benefit people with low incomes, even if AI doesn’t steal anyone’s job.
This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
Experts from the Universities of East Anglia, Sheffield, and Leeds have developed a new groundbreaking AI method that improves the accuracy and efficiency of analyzing MRI heart scans. This innovation could provide a way for faster, more accurate, and non-invasive diagnosis of heart failure and other cardiac conditions, thus saving valuable time and resources for the healthcare sector.
According to Innovation News Network, the research team used data from 814 patients at Sheffield and Leeds Teaching Hospitals to train an AI model, which was then tested using scans and data from 101 patients at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals to ensure accuracy.