February 2025 features Comet CK-25, observed with AI-driven telescopic networks for real-time imaging and analysis. A spectacular planetary alignment of Mercury, Venus, and Mars will be enhanced by augmented reality devices for interactive viewing. A partial lunar eclipse will occur on February 27th-28th, with an immersive experience via the Virtual Lunar Observation Platform (VLOP). Technological advancements highlight new methods of observing and interacting with space events, bridging Earth and the cosmos. February 2025 is set to mesmerize stargazers and tech enthusiasts alike, as the cosmos aligns with cutting-edge advancements in astronomical observation. This month isn’t just about celestial spectacles; it’s about witnessing how new technology is redefining our view of space from Earth.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 335
Does the solution to building safe artificial intelligence lie in the brain?
Now is the time to decipher what makes the brain both flexible and dependable—and to apply those lessons to AI—before an unaligned agentic system wreaks havoc.
Deepfakes threaten trust in society, says researcher
Hollywood star Brad Pitt recently opened SINTEF’s conference on digital security. Well, actually, no, he didn’t. “I cloned his voice in less than three minutes,” says Viggo Tellefsen Wivestad, researcher at SINTEF Digital.
Wivestad began his talk on deepfake with himself on video, but as Brad, with his characteristic sexy voice: “Deepfake. Scary stuff, right?” And that is precisely the researcher’s message.
Deepfake will become a growing threat to us as both private individuals and employees, and to society at large. The technology is still in its infancy. Artificial intelligence is opening up unimaginable opportunities and becoming harder and harder to detect.
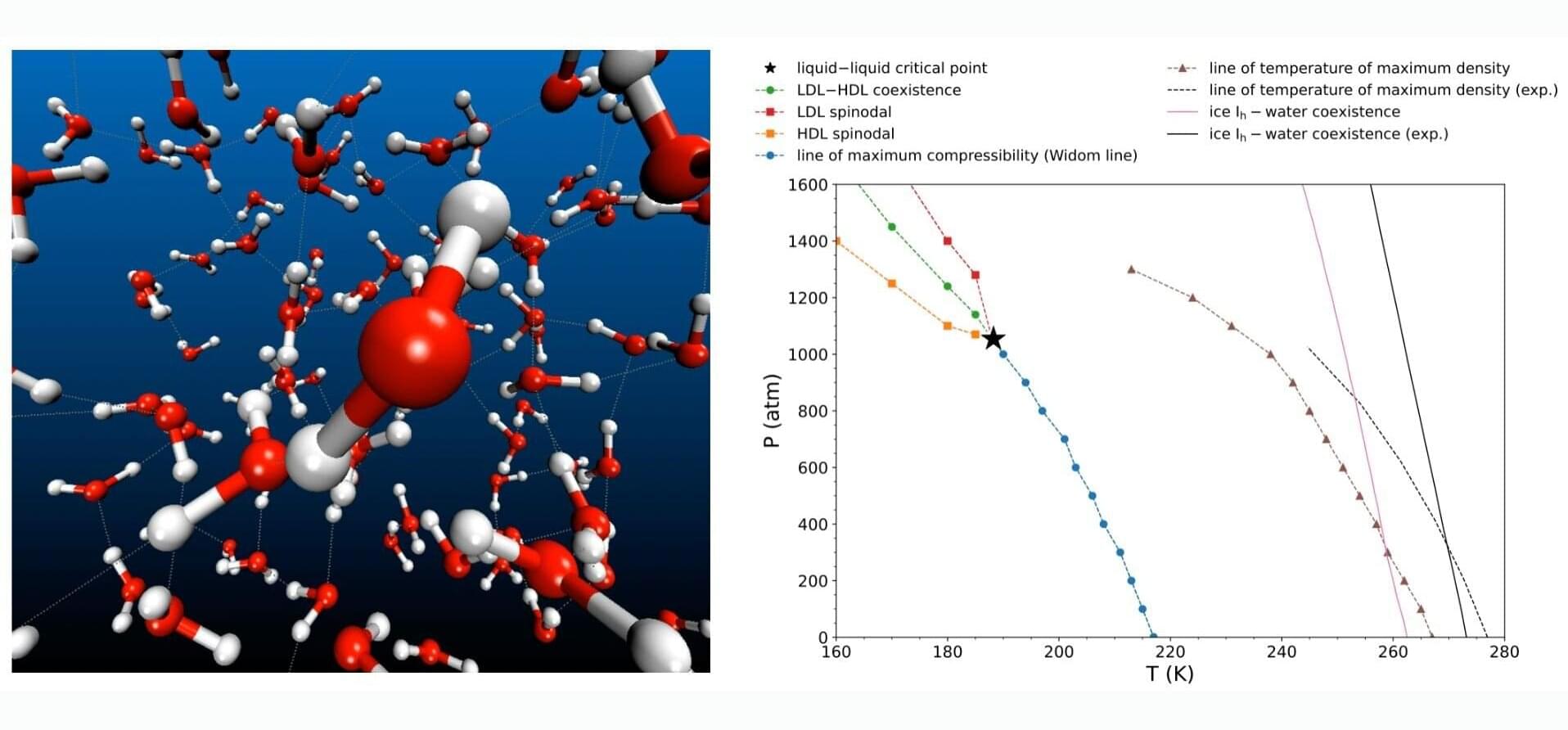
Scientists map elusive liquid-liquid transition point using deep neural network
A new Nature Physics study has shed light on the long-hypothesized liquid-liquid critical point where water simultaneously exists in two distinct liquid forms, opening new possibilities for experimental validation.
Water is known for its anomalous properties—unlike most substances, water is densest in its liquid state, not solid. This leads to unique behaviors such as ice floating on water.
One of several such unusual characteristics has prompted decades of research to understand water’s unique behavior, particularly in the supercooled regime.
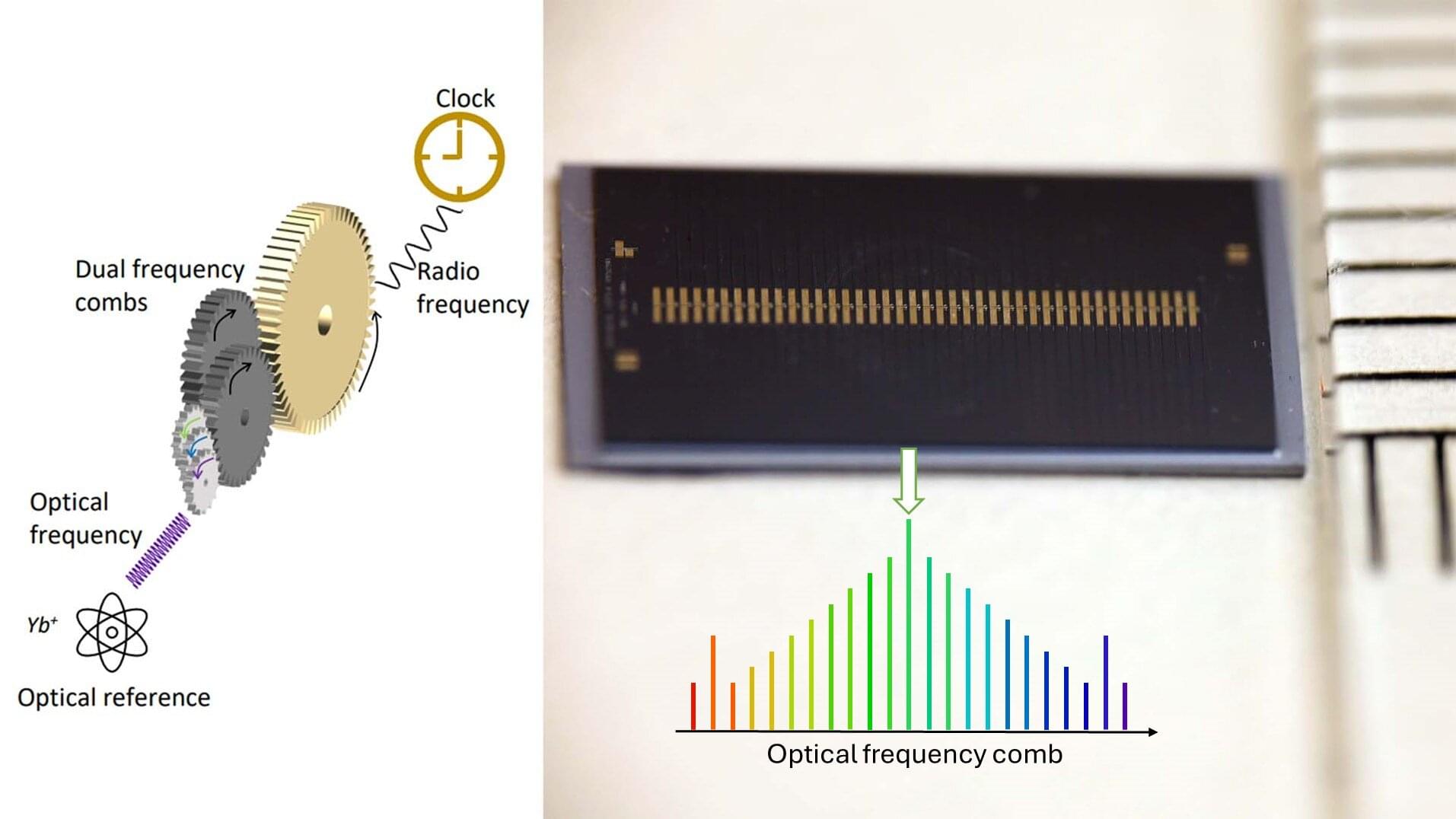
Microcomb chips show potential for centimeter-level GPS precision
Optical atomic clocks can increase the precision of time and geographic position a thousandfold in our mobile phones, computers, and GPS systems. However, they are currently too large and complex to be widely used in society.
Now, a research team from Purdue University, U.S., and Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, has developed a technology that, with the help of on-chip microcombs, could make ultra-precise optical atomic clock systems significantly smaller and more accessible—with significant benefits for navigation, autonomous vehicles, and geo-data monitoring.
The research is published in the journal Nature Photonics.
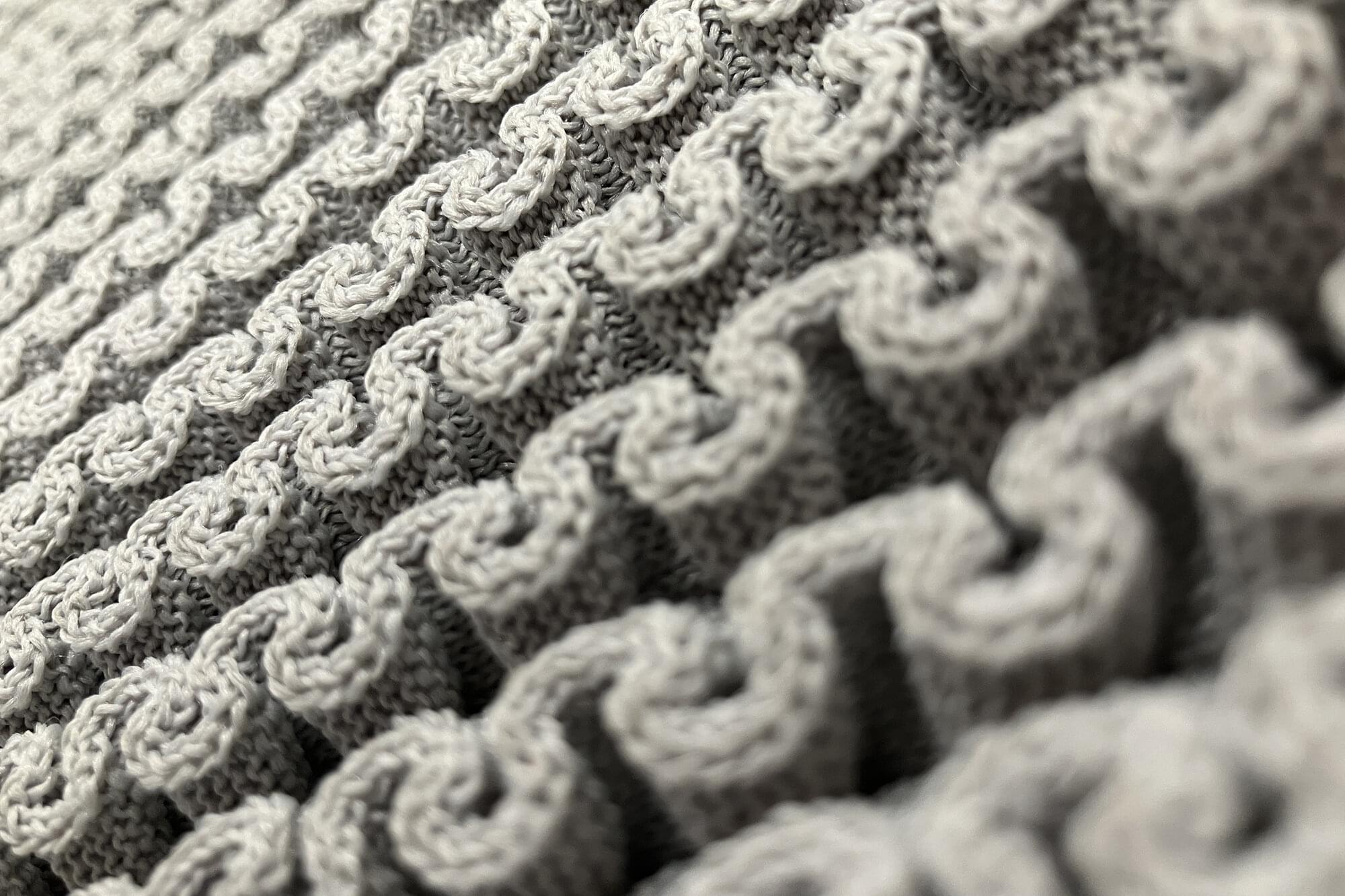

What can theoretical physics teach us about knitting?
The practice of purposely looping thread to create intricate knit garments and blankets has existed for millennia. Though its precise origins have been lost to history, artifacts like a pair of wool socks from ancient Egypt suggest it dates back as early as the third to fifth century CE. Yet, for all its long-standing ubiquity, the physics behind knitting remains surprisingly elusive.
“Knitting is one of those weird, seemingly simple but deceptively complex things we take for granted,” says theoretical physicist and visiting scholar at the University of Pennsylvania, Lauren Niu, who recently took up the craft as a means to study how “geometry influences the mechanical properties and behavior of materials.”
Despite centuries of accumulated knowledge, predicting how a particular knit pattern will behave remains difficult—even with modern digital tools and automated knitting machines. “It’s been around for so long, but we don’t really know how it works,” Niu notes. “We rely on intuition and trial and error, but translating that into precise, predictive science is a challenge.”
Taking AI Welfare Seriously
In this interview Jeff Sebo discusses the ethical implications of artificial intelligence and why we must take the possibility of AI sentience seriously now. He explores challenges in measuring moral significance, the risks of dismissing AI as mere tools, and strategies to mitigate suffering in artificial systems. Drawing on themes from the paper ‘Taking AI Welfare Seriously’ and his up and coming book ‘The Moral Circle’, Sebo examines how to detect markers of sentience in AI systems, and what to do about it. We explore ethical considerations through the lens of population ethics, AI governance (especially important in an AI arms race), and discuss indirect approaches detecting sentience, as well as AI aiding in human welfare. This rigorous conversation probes the foundations of consciousness, moral relevance, and the future of ethical AI design.
Paper ‘Taking AI Welfare Seriously’: https://eleosai.org/papers/20241030_T… — The Moral Circle by Jeff Sebo: https://www.amazon.com.au/Moral-Circl?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20… Jeff’s Website: https://jeffsebo.net/ Eleos AI: https://eleosai.org/ Chapters: 00:00 Intro 01:40 Implications of failing to take AI welfare seriously 04:43 Engaging the disengaged 08:18 How Blake Lemoine’s ‘disclosure’ influenced public discourse 12:45 Will people take AI sentience seriously if it is seen tools or commodities? 16:19 Importance, neglectedness and tractability (INT) 20:40 Tractability: Difficulties in measuring moral significance — i.e. by aggregate brain mass 22:25 Population ethics and the repugnant conclusion 25:16 Pascal’s mugging: low probabilities of infinite or astronomically large costs and rewards 31:21 Distinguishing real high stakes causes from infinite utility scams 33:45 The nature of consciousness, and what to measure in looking for moral significance in AI 39:35 Varieties of views on what’s important. Computational functionalism 44:34 AI arms race dynamics and the need for governance 48:57 Indirect approaches to achieving ideal solutions — Indirect normativity 51:38 The marker method — looking for morally relevant behavioral & anatomical markers in AI 56:39 What to do about suffering in AI? 1:00:20 Building in fault tolerance to noxious experience into AI systems — reverse wireheading 1:05:15 Will AI be more friendly if it has sentience? 1:08:47 Book: The Moral Circle by Jeff Sebo 1:09:46 What kind of world could be achieved 1:12:44 Homeostasis, self-regulation and self-governance in sentient AI systems 1:16:30 AI to help humans improve mood and quality of experience 1:18:48 How to find out more about Jeff Sebo’s research 1:19:12 How to get involved Many thanks for tuning in! Please support SciFuture by subscribing and sharing! Have any ideas about people to interview? Want to be notified about future events? Any comments about the STF series? Please fill out this form: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1mr9P… Kind regards, Adam Ford
- Science, Technology & the Future — #SciFuture — http://scifuture.org
Book — The Moral Circle by Jeff Sebo: https://www.amazon.com.au/Moral-Circl?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20…
Jeff’s Website: https://jeffsebo.net/
Eleos AI: https://eleosai.org/
Chapters:
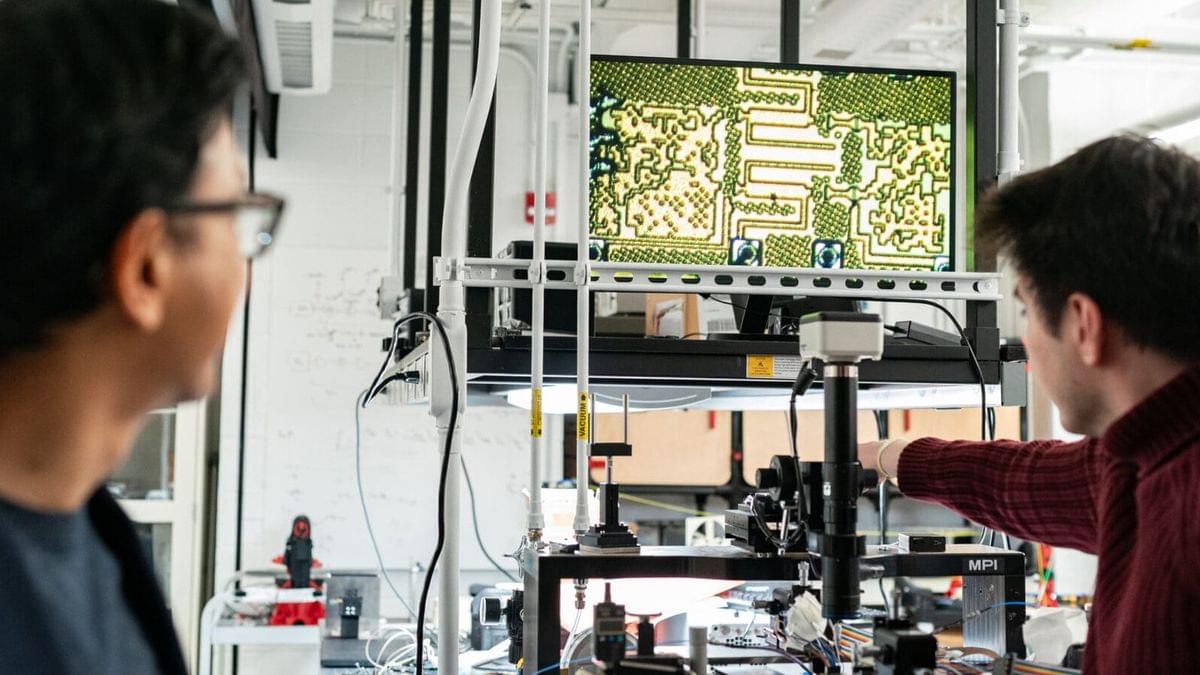

AI designs an ultralight carbon nanomaterial that’s as strong as steel
Using machine learning, a team of researchers in Canada has created ultrahigh-strength carbon nanolattices, resulting in a material that’s as strong as carbon steel, but only as dense as Styrofoam.
The team noted last month that it was the first time this branch of AI had been used to optimize nano-architected materials. University of Toronto’s Peter Serles, one of the authors of the paper describing this work in Advanced Materials, praised the approach, saying, “It didn’t just replicate successful geometries from the training data; it learned from what changes to the shapes worked and what didn’t, enabling it to predict entirely new lattice geometries.”
To quickly recap, nanomaterials are engineered by arranging atoms or molecules in precise patterns, much like constructing structures with extremely tiny LEGO blocks. These materials often exhibit unique properties due to their nanoscale dimensions.
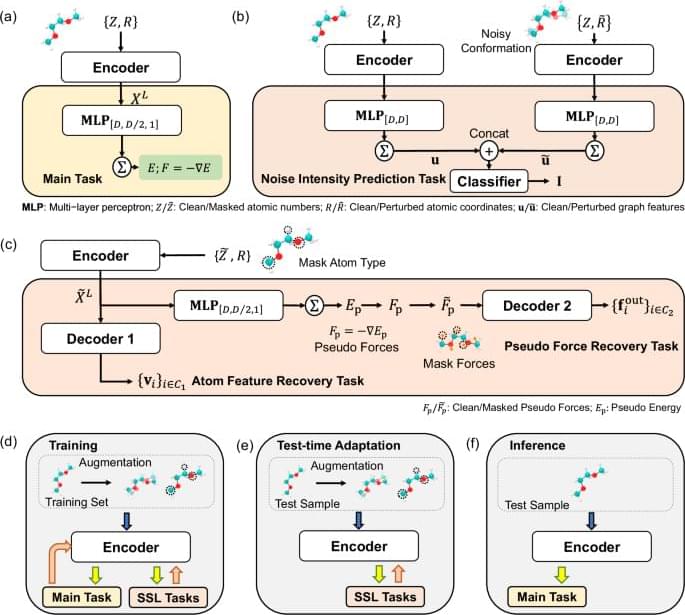
Online test-time adaptation for better generalization of interatomic potentials to out-of-distribution data
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulation serves as a crucial technique across various disciplines including biology, chemistry, and material science1,2,3,4. MD simulations are typically based on interatomic potential functions that characterize the potential energy surface of the system, with atomic forces derived as the negative gradients of the potential energies. Subsequently, Newton’s laws of motion are applied to simulate the dynamic trajectories of the atoms. In ab initio MD simulations5, the energies and forces are accurately determined by solving the equations in quantum mechanics. However, the computational demands of ab initio MD limit its practicality in many scenarios. By learning from ab initio calculations, machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) have been developed to achieve much more efficient MD simulations with ab initio-level accuracy6,7,8.
Despite their successes, the crucial challenge of implementing MLIPs is the distribution shift between training and test data. When using MLIPs for MD simulations, the data for inference are atomic structures that are continuously generated during simulations based on the predicted forces, and the training set should encompass a wide range of atomic structures to guarantee the accuracy of predictions. However, in fields such as phaseion9,10, catalysis11,12, and crystal growth13,14, the configurational space that needs to be explored is highly complex. This complexity makes it challenging to sample sufficient data for training and easy to make a potential that is not smooth enough to extrapolate to every relevant point. Consequently, a distribution shift between training and test datasets often occurs, which causes the degradation of test performance and leads to the emergence of unrealistic atomic structures, and finally the MD simulations collapse15.