Could your driving habits reveal your mental health? Research shows AI can analyze driving data to identify depression risk in older adults.


Meta AI will soon become one of the social media company’s standalone apps, joining Facebook, Instagram and WhatsApp, CNBC has learned.
S plans to make his company the leader in artificial intelligence by the end of the year, ahead of competitors such as OpenAI and Alphabet, said the people, who asked not to be named because the project is confidential. + The Meta AI chatbot launched in September 2023, with the company pitching it as a generative AI-powered digital assistant that can provide responses and create images based on user prompts within its existing apps. The company brought Meta AI to the forefront of its apps in April, when it replaced the search feature for Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp and Messenger with the chatbot.
S generative AI technologies to billions of consumers. This is going to be the year when a highly intelligent and personalized AI assistant reaches more than 1 billion people, and I expect Meta AI to be that leading AI assistant, Zuckerberg told analysts during the company s apps such as Facebook and WhatsApp. Although Meta [ https://open.substack.com/pub/remunerationlabs/p/meta-ai-cou…Share=true](https://open.substack.com/pub/remunerationlabs/p/meta-ai-cou…Share=true)
The Meta AI app marks a major step in CEO Mark Zuckerberg’s plan to make his company the leader in AI by the end of the year, ahead of competitors such as OpenAI and Alphabet, the people said.
Subscribe and hit the bell for NFT alerts:
GM. Nothing here is financial advice, dyor. These are NFT Projects I am currently interested in. What is an NFT? A NFT is a non-fungible token that is a non-interchangeable unit of data stored on the blockchain, which is a form of digital ledger. The most common one is bitcoin, a cryptocurrency. NFTs can be digital files such as photos, videos or audio. Although we like NFTs such as Bored Ape Yacht Club, Doodles, CryptoPunks, Cool Cats, and VeeFriends…The NFTs we are mainly interested in have certain utility or membership tied to them. #Shorts
Discover the groundbreaking advancements in robotics as Annie Jacobsen and Joe Rogan discuss a startling innovation: a robot made from living human skin. This fascinating creation not only smiles but raises ethical questions about the future of artificial humans. How close are we to creating a fully artificial person? Join the conversation about the implications of these technologies, especially in countries with different regulations. Don’t miss this eye-opening discussion!
In a scientific breakthrough, Japanese scientists have found a way to attach artificially created living skin to robot faces for more realistic smiles and facial expressions.
#japan #robots #wion.
About Channel:
WION The World is One News examines global issues with in-depth analysis. We provide much more than the news of the day. Our aim is to empower people to explore their world. With our Global headquarters in New Delhi, we bring you news on the hour, by the hour. We deliver information that is not biased. We are journalists who are neutral to the core and non-partisan when it comes to world politics. People are tired of biased reportage and we stand for a globalized united world. So for us, the World is truly One.
Please keep discussions on this channel clean and respectful and refrain from using racist or sexist slurs and personal insults.
Check out our website: http://www.wionews.com.
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander is set to make history as it targets a March 2 lunar landing near Mare Crisium, a vast plain on the Moon’s near side. Carrying NASA’s cutting-edge science and technology, this mission marks another crucial step in humanity’s return to the Moon under the Artemis program. As part of NASA’s CLPS initiative, Blue Ghost’s success will pave the way for future lunar and Martian exploration.
Mission Overview: Blue Ghost’s Lunar Delivery.
Launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 on January 15, Blue Ghost carries 10 NASA payloads designed to investigate the Moon’s environment and test new technologies for future missions. These experiments will provide critical data on lunar surface conditions, radiation levels, thermal properties, and advanced landing systems—all essential for upcoming crewed missions.
Live Landing Coverage & Key Moments.
The landing event, hosted by NASA and Firefly Aerospace, will be streamed live on NASA+ and Firefly’s YouTube channel starting at 2:20 a.m. EST on March 2, roughly 75 minutes before touchdown. The stream will cover the final descent, landing confirmation, and initial mission updates. A post-landing press conference will follow, where experts will discuss the mission’s success and upcoming science operations on the lunar surface.
Why This Mission Matters.
Blue Ghost is a key part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, which enables private companies to deliver science and technology to the Moon. These robotic landings will support Artemis astronauts, testing vital systems for future long-term lunar habitation and, ultimately, crewed missions to Mars. NASA’s collaboration with companies like Firefly Aerospace ensures rapid progress in space exploration, resource utilization, and sustainable lunar development.
The Future of Lunar Exploration.
With CLPS contracts valued at $2.6 billion through 2028, NASA is committed to building a strong commercial space ecosystem. The $101.5 million contract awarded to Firefly for this mission underscores the agency’s dedication to fostering innovative, cost-effective lunar transportation solutions. Future missions will refine navigation, in-situ resource utilization, and long-duration surface operations, bringing us closer to a permanent human presence beyond Earth.
🚀 Subscribe to Space Googlevesaire! 🚀
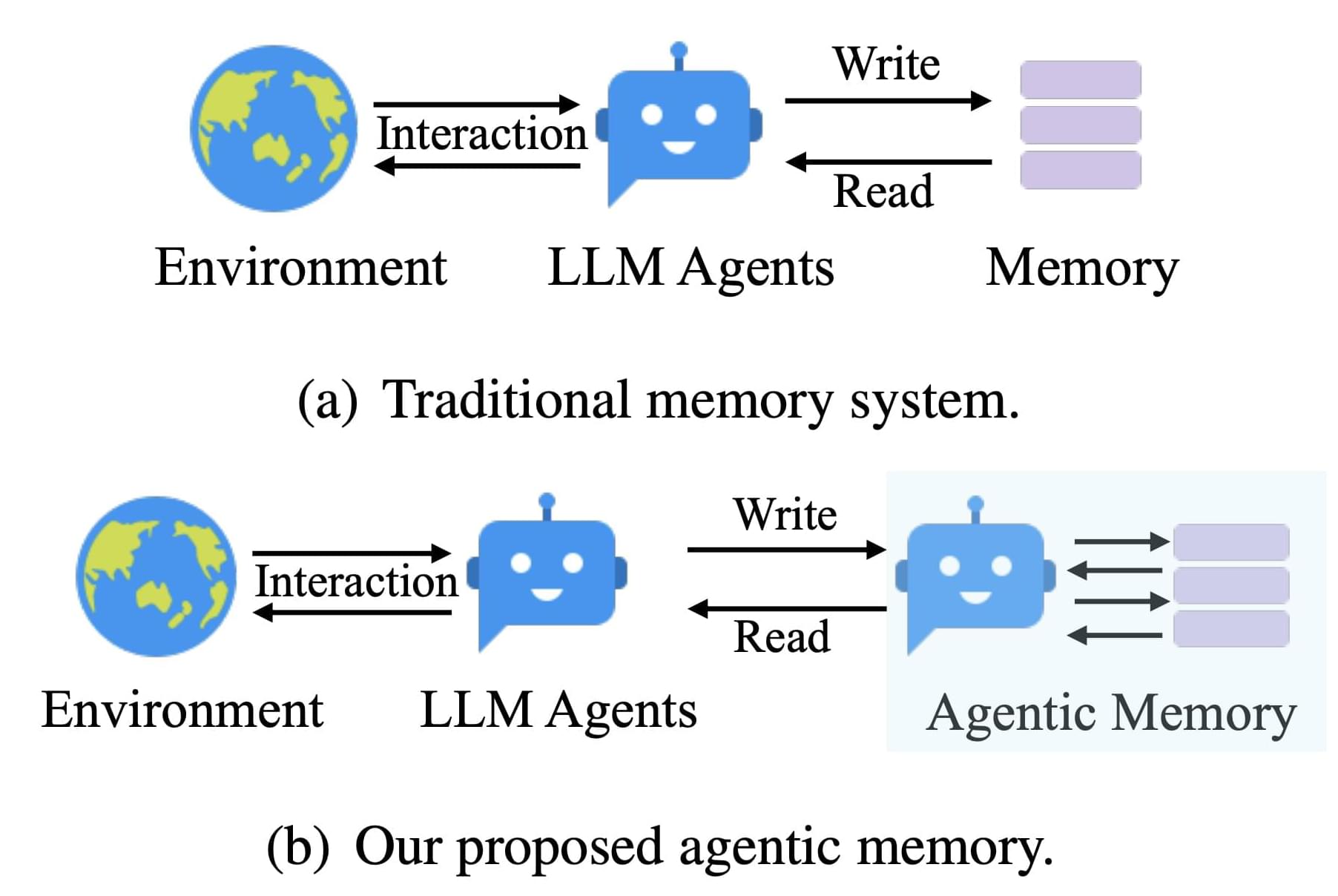
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.12110v1
GitHub Page: https://github.com/WujiangXu/AgenticMemory
Current memory systems for large language model (LLM) agents often struggle with rigidity and a lack of dynamic organization. Traditional approaches rely on fixed memory structures—predefined storage points and retrieval patterns that do not easily adapt to new or unexpected information. This rigidity can hinder an agent’s ability to effectively process complex tasks or learn from novel experiences, such as encountering a new mathematical solution. In many cases, the memory operates more as a static archive than as a living network of evolving knowledge. This limitation becomes particularly apparent during multi-step reasoning tasks or long-term interactions, where flexible adaptation is crucial for maintaining consistency and depth in understanding.
Researchers from Rutgers University, Ant Group, and Salesforce Research have introduced A-MEM, an agentic memory system designed to address these limitations. A-MEM is built on principles inspired by the Zettelkasten method—a system known for its effective note-taking and flexible organization. In A-MEM, each interaction is recorded as a detailed note that includes not only the content and timestamp, but also keywords, tags, and contextual descriptions generated by the LLM itself. Unlike traditional systems that impose a rigid schema, A-MEM allows these notes to be dynamically interconnected based on semantic relationships, enabling the memory to adapt and evolve as new information is processed.
At its core, A-MEM employs a series of technical innovations that enhance its flexibility. Each new interaction is transformed into an atomic note, enriched with multiple layers of information—keywords, tags, and context—that help capture the essence of the experience. These notes are then converted into dense vector representations using a text encoder, which enables the system to compare new entries with existing memories based on semantic similarity. When a new note is added, the system retrieves similar historical memories and autonomously establishes links between them. This process, which relies on the LLM’s ability to recognize subtle patterns and shared attributes, goes beyond simple matching to create a more nuanced network of related information.

Breakthrough in early detection of cholangiocarcinoma using ai-powered spectroscopy.
In a major advancement for cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) detection, researchers have developed a cutting-edge AI-driven diagnostic method that could revolutionize early cancer screening. Utilizing Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS), a powerful non-invasive technique, the team introduced a novel approach combining Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) with a one-dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D CNN) to distinguish early-stage CCA from precancerous, inflammatory, and healthy conditions.
Unlike traditional Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with Support Vector Machine (SVM), which struggles with nonlinear SERS data and only differentiates late-stage CCA, the new AI-enhanced method provides greater accuracy in detecting early-stage cancer, a crucial factor in improving survival rates. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis confirmed its superior performance.
The study, conducted on hamster serum, opens the door for future applications in human diagnostics, potentially transforming cancer detection and treatment. This breakthrough underscores the potential of AI and advanced signal processing in enhancing precision medicine and saving lives through early intervention.
This Early detection of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is critical for improving patient prognosis and survival rates. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) offers a promising non-invasive diagnostic tool due to its high sensitivity and specificity. In this study, we propose a novel approach combining Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and a onedimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D CNN) for the detection and differentiation of first stage CCA from precancerous, inflammation, and healthy states using SERS data. Our method is compared with a traditional Principal Component Analysis (PCA) followed by Support Vector Machine (SVM) classification. In contrast, the PCA + SVM method could only differentiate late-stage CCA and healthy states due to the nonlinearity of the SERS dataset. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis further validates the superior performance of our proposed method. We studied on hamster serum and the concept can be extended to human serum in the near future work.
OpenAi has launched GPT-4.5, which is the company’s largest and best model. The company is releasing a research preview of GPT‑4.5 that’s a step forward in scaling up pre-training and post-training. The latest model improves its ability to recognize patterns, draw connections, and generate creative insights without reasoning.
OpenAI revealed that as per early testing, interacting with GPT‑4.5 feels more natural. It has broader knowledge base, improved ability to follow user intent, and greater “EQ” make it useful for tasks like improving writing, programming, and solving practical problems.

A workshop led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory sketched a road map toward a longtime goal: development of autonomous, or self-driving, next-generation research laboratories.
Download the report of the “Shaping the Future of Self-Driving Autonomous Laboratories” workshop.
Scientists have dreamed for generations of high-tech laboratories operated via robotics at the push of a button. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence bring those dreams closer to reality than ever before, said Rafael Ferreira da Silva, an ORNL senior research scientist and lead author of the workshop’s report.