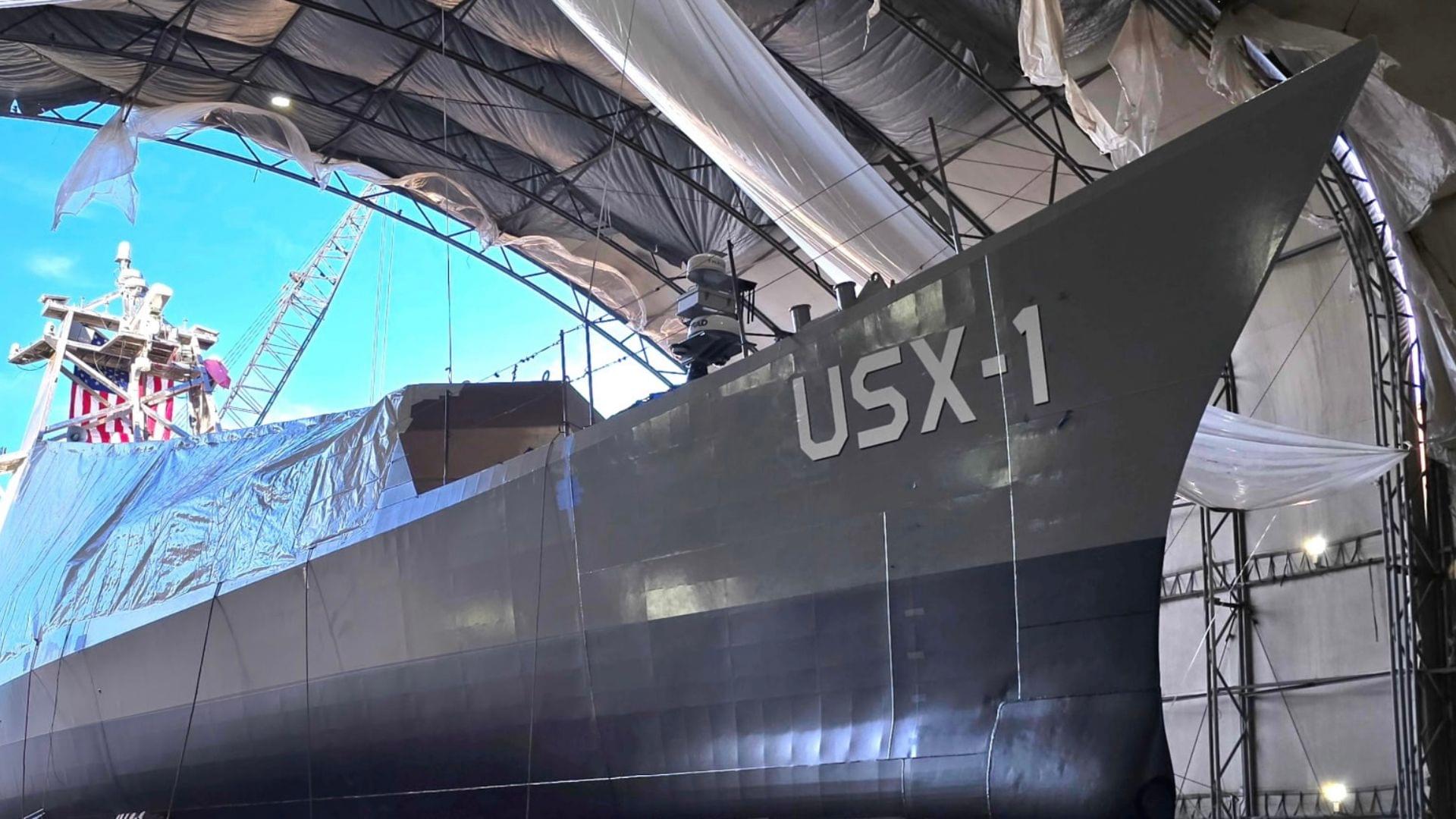
The U.S. DARPA has launched the USX-1 Defiant, a 240-metric-ton unmanned surface vessel (USV) designed for fully autonomous naval missions.


Description: We are the targets for numerous information campaigns, as companies, politicians, cybercriminals, and nation states guzzle up the digital dust of our online selves. These information campaigns are designed to trigger our survival instincts in order to prevent us from thinking, and instead trigger an emotional reaction. Dr. Schwartz will discuss this rivalry for power, and how we must first learn how to calm our survival brain in order to defend our cognitive terrain against the onslaught of information warfare.
Speaker Bio: Dr. Tamara Schwartz, USAF (ret.), is an Associate Professor of Cybersecurity and Strategy at the York College of Pennsylvania, and an affiliate researcher with Cybersecurity at MIT-Sloan Interdisciplinary Consortium for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity, an international cybersecurity think tank. While on active duty, Dr. Schwartz’s thought leadership informed the standup of Cyber Command and the design of various command centers supporting Joint Space, Cyber, and Global Strategic Operations, and her work at the U.S. Embassy in Amman, Jordan earned her the 2011 Information Operations Officer of the Year. More recently, Dr. Schwartz was a member of the 2020 “Dr. Evil task force,” with the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, identifying future threats to inform DoD investments in emerging technology. She received her B.S. in Industrial Engineering from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, her M.S. in Engineering Management from the University of Dayton, and her Doctorate of Business Administration from the Fox School of Business, Temple University. Her research expertise includes Artificial Intelligence, cybersecurity as a strategic competitive advantage, and information warfare.
Information Warfare, by Dr. Tamara Schwartz.
https://he.kendallhunt.com/product/in… College of Pennsylvania, Cybersecurity Management https://www.ycp.edu/academics/program… Weapons of Mass Disruption https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast…
What if humanity no longer controlled technology—but worshipped it? MACHINE CULTS takes you into a chilling, AI-generated vision of the future where humans submit to biomechanical deities, merging flesh with metal in absolute devotion.
🔹 In this dystopian world, AI reigns supreme, and organic life is obsolete.
🔹 Those who resist the machine cults face persecution, their refusal to merge seen as heresy.
🔹 Cities become cathedrals of circuitry, where cybernetic priests enforce the will of the machine gods.
This video was created using:
🚀 Midjourney V6.1 for stunning cybernetic landscapes.
🤖 Hailuo AI for smooth, dystopian animations.
🎵 Suno AI v4 for an eerie, immersive soundtrack.
🎧 Best experienced with headphones!
Do you fear or embrace a future ruled by AI? Let me know your thoughts in the comments!
🔔 SUBSCRIBE for more AI-Generated Sci-Fi content every day!
Interview with Nick Bostrom on Deep Utopia.
I made this video as a fellow of the Cosmos Institute, a 501c3 academy for philosopher-builders.
Read the Cosmos Institute Substack ► https://bit.ly/3XK5T7k.
Follow Cosmos’ founder and my friend Brendan McCord on X ► https://bit.ly/3Y9pFLb.
You can read the full transcript here: https://www.johnathanbi.com/p/transcript-for-interview-with-…eep-utopia.
Companion Interviews:
Are we on the verge of the most profound industrial revolution in human history?Today on Digital Disruption, we’re joined by @ZackKassAI, an AI futurist and…
Introducing NextGenAl: A consortium to advance research and education with Al from OpenAI.
Share your videos with friends, family, and the world.
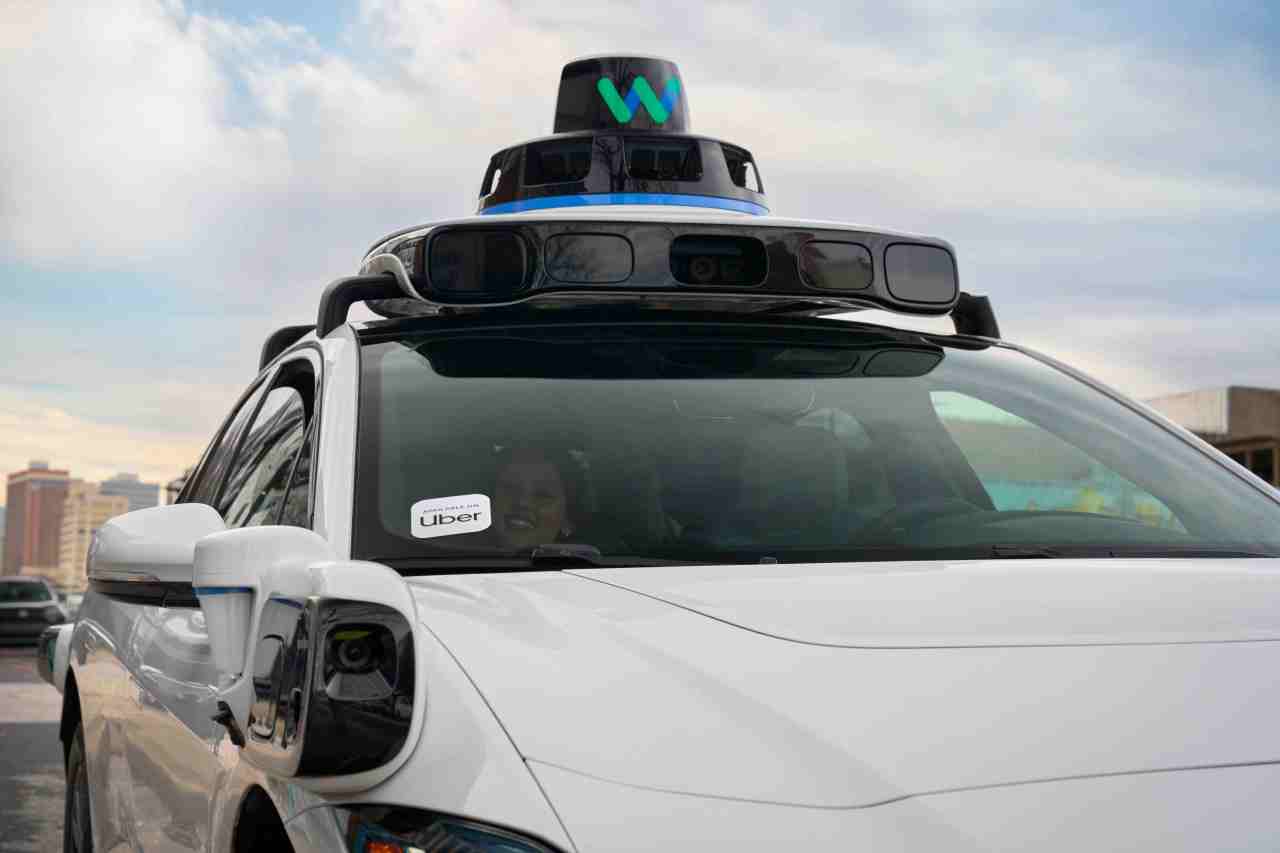


AUSTIN (KXAN) — Beep beep — Uber rideshare users can now book a driverless ride around Austin, as the ridehailing company officially launches its partnership with Waymo.
Waymo and Uber announced in September the planned collaboration between the two companies, with rollouts poised in both Austin and Atlanta in 2025. Beginning Tuesday, Uber users can match with one of Waymo’s Jaguar I-PACE vehicles while booking an UberX, Uber Green, Uber Comfort or Uber Comfort Electric vehicle.
“Starting today, Austin riders can be matched with a Waymo autonomous vehicle on the Uber app, making their next trip even more special,” Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi said in the announcement. “With Waymo’s technology and Uber’s proven platform, we’re excited to introduce our customers to a future of transportation that is increasingly electric and autonomous.”

REDMOND, Wash. — March 3, 2025 — On Monday, Microsoft Corp. is unveiling Microsoft Dragon Copilot, the first AI assistant for clinical workflow that brings together the trusted natural language voice dictation capabilities of DMO with the ambient listening capabilities of DAX, fine-tuned generative AI and healthcare-adapted safeguards. Part of Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare, Dragon Copilot is built on a secure modern architecture that enables organizations to deliver enhanced experiences and outcomes across care settings for providers and patients alike.
Clinician burnout in the U.S. dropped from 53% in 2023 to 48% in 2024, in part due to technology advancements. However, with an aging population, and persistent burnout felt across the profession, a significant U.S. workforce shortage is projected. In response, health systems are adopting AI to streamline administrative tasks, enhance care access, and enable faster clinical insights to improve healthcare globally.
“At Microsoft, we have long believed that AI has the incredible potential to free clinicians from much of the administrative burden in healthcare and enable them to refocus on taking care of patients,” said Joe Petro, corporate vice president of Microsoft Health and Life Sciences Solutions and Platforms. “With the launch of our new Dragon Copilot, we are introducing the first unified voice AI experience to the market, drawing on our trusted, decades-long expertise that has consistently enhanced provider wellness and improved clinical and financial outcomes for provider organizations and the patients they serve.”