Now that AI is invading classrooms and homework assignment, students need to learn reasoning more than ever


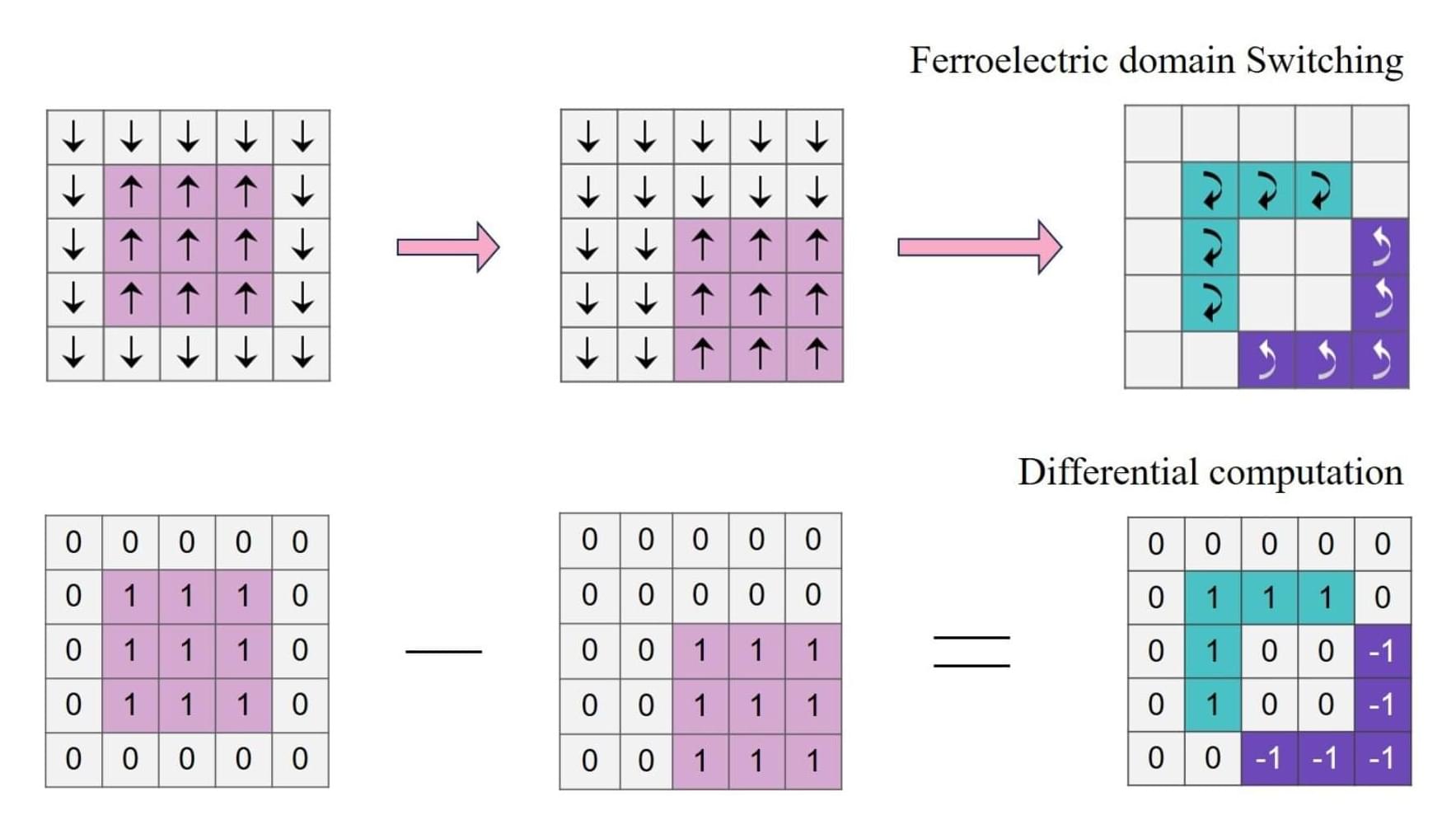
In a new Nature Communications study, researchers have developed an in-memory ferroelectric differentiator capable of performing calculations directly in the memory without requiring a separate processor.
The proposed differentiator promises energy efficiency, especially for edge devices like smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and security cameras.
Traditional approaches to tasks like image processing and motion detection involve multi-step energy-intensive processes. This begins with recording data, which is transmitted to a memory unit, which further transmits the data to a microcontroller unit to perform differential operations.


Andreessen Horowitz’s Anjney Midha argues that the US has no choice in terms of how it approaches the artificial intelligence race with China: “We must win.”
Speaking with Semafor’s Reed Albergotti at Semafor’s World Economy Summit on Wednesday, Midha, who is a general partner at the Silicon Valley venture capital firm, said that US AI companies should double down on driving growth rather than stifle innovation over concerns of potentially harmful use cases. People all over the world will choose to use American AI tools, so long as they’re the best available.
“This is why a billion people in India still use WhatsApp. It was invented in Silicon Valley,” Midha said.
Essential for many industries ranging from Hollywood computer-generated imagery to product design, 3D modeling tools often use text or image prompts to dictate different aspects of visual appearance, like color and form. As much as this makes sense as a first point of contact, these systems are still limited in their realism due to their neglect of something central to the human experience: touch.
Fundamental to the uniqueness of physical objects are their tactile properties, such as roughness, bumpiness, or the feel of materials like wood or stone. Existing modeling methods often require advanced computer-aided design expertise and rarely support tactile feedback that can be crucial for how we perceive and interact with the physical world.
With that in mind, researchers at MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) have created a new system for stylizing 3D models using image prompts, effectively replicating both visual appearance and tactile properties. Their research is published on the arXiv preprint server.

Cybersecurity researchers have revealed that Russian military personnel are the target of a new malicious campaign that distributes Android spyware under the guise of the Alpine Quest mapping software.
“The attackers hide this trojan inside modified Alpine Quest mapping software and distribute it in various ways, including through one of the Russian Android app catalogs,” Doctor Web said in an analysis.
The trojan has been found embedded in older versions of the software and propagated as a freely available variant of Alpine Quest Pro, a paid offering that removes advertising and analytics features.
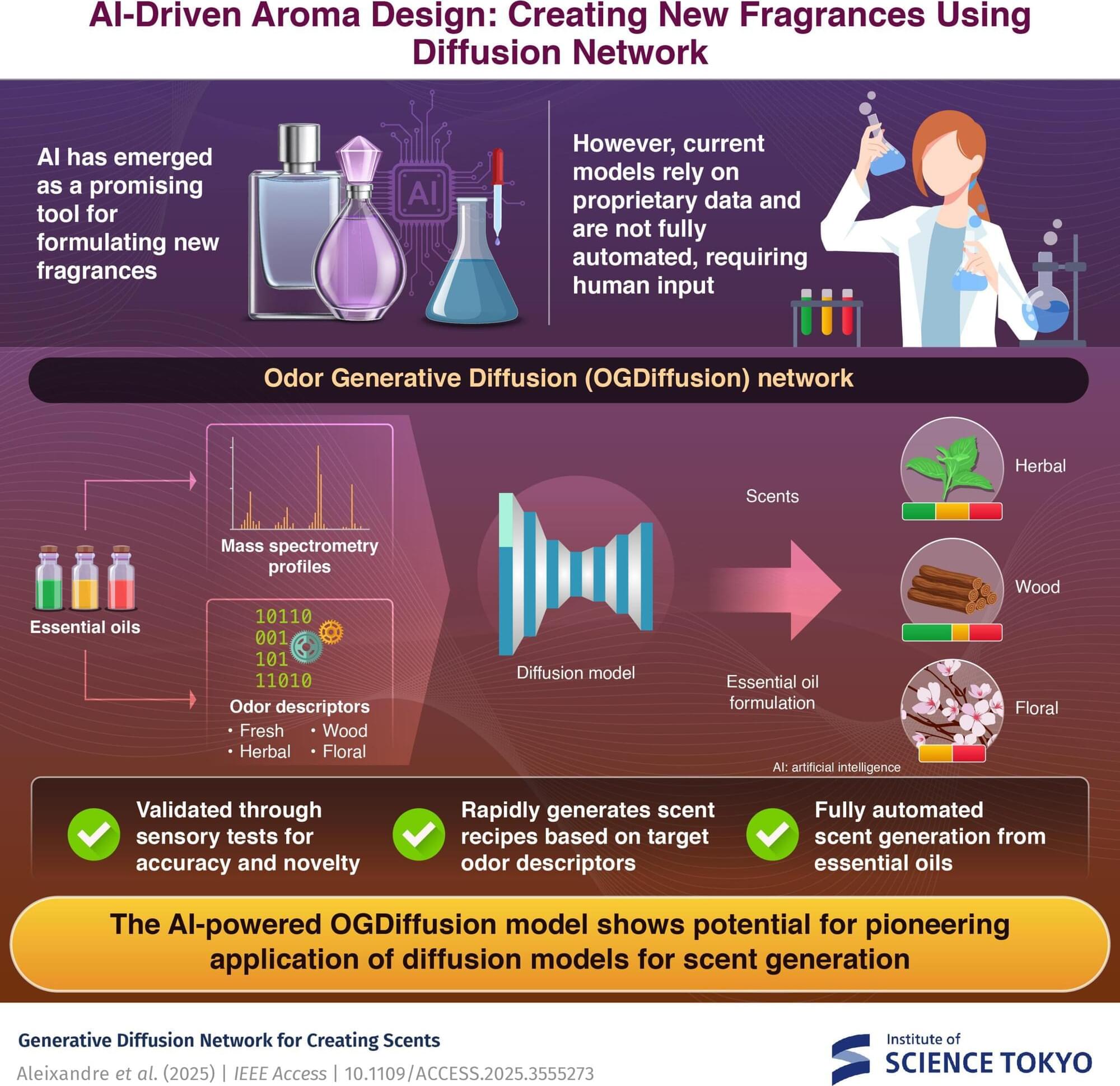
Addressing the challenges of fragrance design, researchers at the Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) have developed an AI model that can automate the creation of new fragrances based on user-defined scent descriptors. The model uses mass spectrometry profiles of essential oils and corresponding odor descriptors to generate essential oil blends for new scents.
This advance could be a game-changer for the fragrance industry, moving beyond trial-and-error to enable rapid and scalable fragrance production. The findings are published in IEEE Access.
Designing new fragrances is crucial in industries like perfumery, food, and home products, where scent significantly influences the overall experience of these products. However, traditional fragrance creation can be time-consuming and often depends on the skill and expertise of specialized perfumers. The process is typically challenging and labor-intensive, requiring numerous trial-and-error attempts to achieve the desired scent.
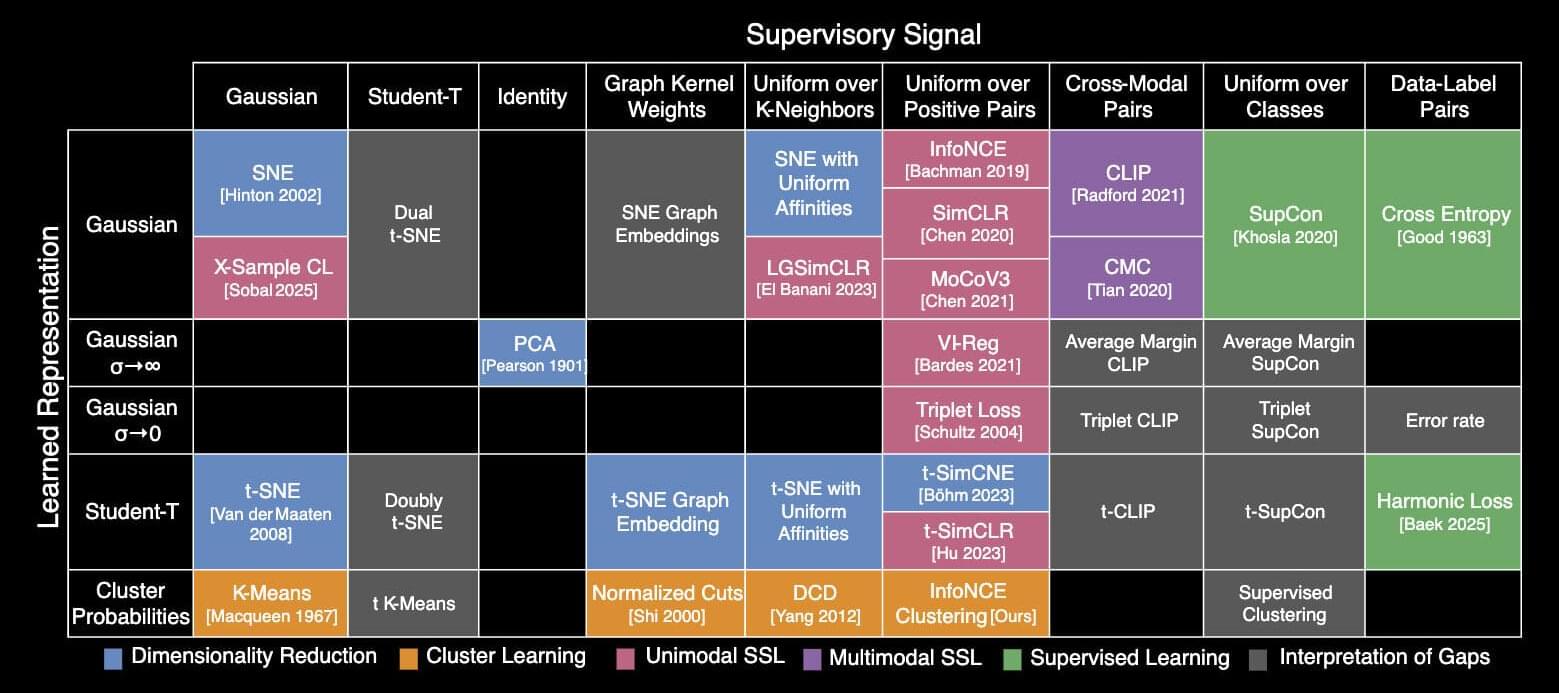
MIT researchers have created a periodic table that shows how more than 20 classical machine-learning algorithms are connected. The new framework sheds light on how scientists could fuse strategies from different methods to improve existing AI models or come up with new ones.
For instance, the researchers used their framework to combine elements of two different algorithms to create a new image-classification algorithm that performed 8% better than current state-of-the-art approaches.
The periodic table stems from one key idea: All these algorithms learn a specific kind of relationship between data points. While each algorithm may accomplish that in a slightly different way, the core mathematics behind each approach is the same.
ICLR 2025
Shaden Alshammari, John Hershey, Axel Feldmann, William T. Freeman, Mark Hamilton.
MIT, Microsoft, Google.
[ https://openreview.net/forum?id=WfaQrKCr4X](https://openreview.net/forum?id=WfaQrKCr4X
[ https://github.com/mhamilton723/STEGO](https://github.com/mhamilton723/STEGO
Genome editing has advanced at a rapid pace with promising results for treating genetic conditions—but there is always room for improvement. A new paper by investigators from Mass General Brigham showcases the power of scalable protein engineering combined with machine learning to boost progress in the field of gene and cell therapy.
In their study, the authors developed a machine learning algorithm—known as PAMmla—that can predict the properties of approximately 64 million genome-editing enzymes. The work could help reduce off-target effects and improve editing safety, enhance editing efficiency, and enable researchers to predict customized enzymes for new therapeutic targets. The results are published in Nature.
“Our study is a first step in dramatically expanding our repertoire of effective and safe CRISPR-Cas9 enzymes. In our manuscript, we demonstrate the utility of these PAMmla-predicted enzymes to precisely edit disease-causing sequences in primary human cells and in mice,” said corresponding author Ben Kleinstiver, Ph.D., Kayden-Lambert MGH Research Scholar associate investigator at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH).