AI marketing…
By leveraging artificial intelligence, business leaders can better understand opportunities for customer experience improvement — AI-powered analytics platform, InMoment, expects to lead the charge.


And yet, as impressive and powerful as these new technologies and machines are—and they’re becoming more so all the time—I believe they’re an opportunity to be embraced by accountants.
Computers and software have evolved to a point where they can populate spreadsheets, crunch numbers, and generate financial statements and earnings reports more quickly and accurately than any human accountant. In fact, machines are already taking on many of an accountant’s old, routine, administrative chores—on-line tax returns, and book-keeping software, are great examples of routine work that accountants no longer have to do.
This is a good thing. It is already allowing for human accountants to be more sophisticated advisors and planners. In this way, technology can be best used as a tool that gives humans more space to focus on analysis, interpretation, and strategy. In other words, computers have enormous potential to empower—rather than displace—accountants.
We’ve created the world’s first Spam-detecting AI trained entirely in simulation and deployed on a physical robot.
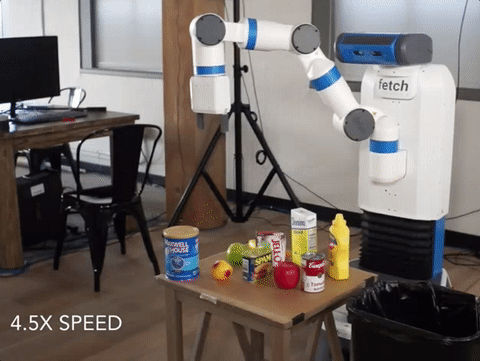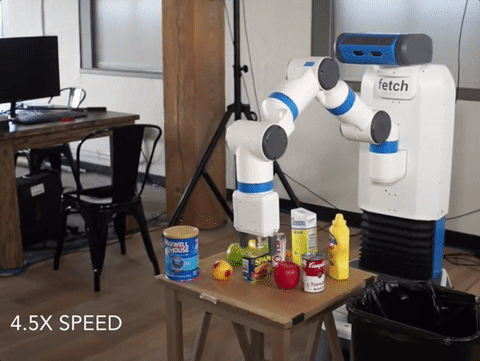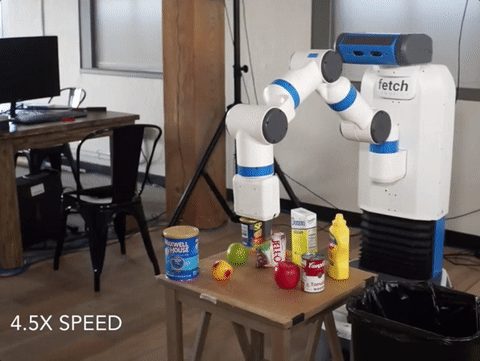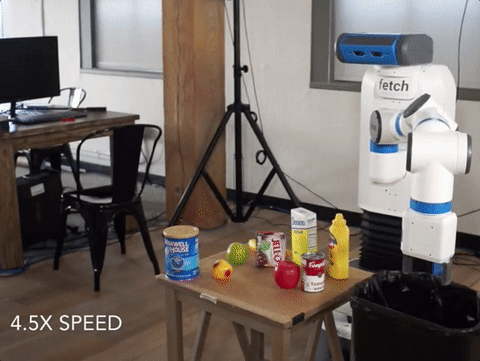
Our vision system successfully flagging a can of Spam for removal. The vision system is trained entirely in simulation, while the movement policy for grasping and removing the Spam is hard-coded. Our detector is able to avoid other objects, including healthy ones such as fruit and vegetables, which it never saw during training.
Deep learning-driven robotic systems are bottlenecked by data collection: it’s extremely costly to obtain the hundreds of thousands of images needed to train the perception system alone. It’s cheap to generate simulated data, but simulations diverge enough from reality that people typically retrain models from scratch when moving to the physical world.

Before each job interview, Alex Ren offers the following advice to his clients to ensure their success: “Be humble and appreciate the opportunity to fully demonstrate your strength and what you can offer”.
The advice is not for potential employees. Rather, it is for Chinese technology companies trying to hire top-tier Silicon Valley talent in artificial intelligence (AI) in competition with the likes of Alphabet, Uber Technologies and Facebook.
“Chinese companies are obsessed with hiring Silicon Valley talent because winning talent here is like reaching the commanding heights of the AI battlefield,” said Ren, founder of TalentSeer, a San Francisco-based headhunting company focused on AI expert recruitment.

By Paula Klein
Is work becoming obsolete? Will Americans learn to love their leisure time? As the spotlight focuses on AI and its various implementations, former Harvard Professor Jeffrey Sachs, now at Columbia University and a special adviser to the United Nations, has some strong and diverse opinions about the macroeconomic impact of robots on the role of work in the future.
At a Mar. 24 seminar hosted by MIT IDE — the same day Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin amazed the tech community by saying AI wasn’t even on his radar — Sachs described AI developments as a “huge” with implications as vast as any previous seismic technology wave. “We are in the midst of a major transformation” that will fundamentally change civilization from the past, he said.
Brick Laying Robot
This construction robot can lay bricks 6 times faster than you.

Your job isn’t safe. Nearly half of the jobs in America today may soon be done by robots.
Robots will begin delivering Domino’s pizza starting this summer. The small, six-wheeled devices go 4 miles per hour and will drop the pizzas off within a one-mile radius of its stores in the Netherlands and Germany.
It’s part of a the robotification of American jobs. Indeed, almost half of the jobs in America are at risk of being done by robots on computers in the next two decades, a study by researchers at Oxford University found.
Late for work? Imagine skipping the subway and instead heading to your local “vertiport,” where you can hop into an aircraft the size of an SUV that runs on electricity and works pretty much like an elevator.
Get in, punch in your destination, and off you go. Alone.
It may sound like an episode of “The Jetsons,” but electric air taxis are a form of transportation that is coming to Dubai in just a few months. And investors hope American cities aren’t much far behind.

Wednesday, March 1st Baltimore, MD — In March 2016 Insilico Medicine initiated a research collaboration with Life Extension to apply advanced bioinformatic methods and deep learning algorithms to screen for naturally occurring compounds that may slow down or even reverse the cellular and molecular mechanisms of aging. Today Life Extension (LE) launched a new line of nutraceuticals called GEROPROTECTTM, and the first product in the series called Ageless CellTM combines some of the natural compounds that were shortlisted by Insilico Medicine’s algorithms and are generally recognized as safe (GRAS).
The first research results on human biomarkers of aging and the product will be presented at the Re-Work Deep Learning in Healthcare Summit in London 28.02−01.03, 2017, one of the popular multidisciplinary conferences focusing on the emerging area of deep learning and machine intelligence.
“We salute Life Extension on the launch of GEROPROTECTTM: Ageless Cell, the first combination of nutraceuticals developed using our artificial intelligence algorithms. We share the common passion for extending human productive longevity and investing every quantum of our energy and resources to identify novel ways to prevent age-related decline and diseases. Partnering with Life Extension has multiple advantages. LE has spent the past 37 years educating consumers on the latest in nutritional therapies for optimal health and anti-aging and is an industry leader and a premium brand in the supplement industry. Also, LE also has a unique mail order blood test service that allows US customers to perform comprehensive blood tests to help identify potential health concerns and to track the effects of the nutraceutical products,” said Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, CEO of Insilico Medicine, Inc.