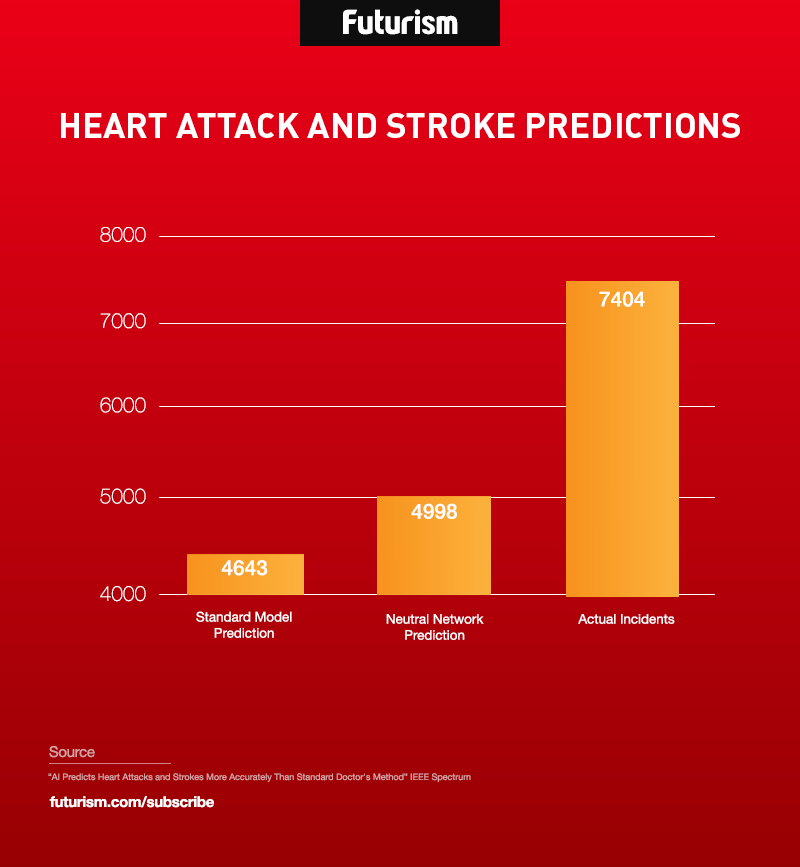
University of Nottingham researchers created an AI system that scanned routine medical data to predict which patients would have strokes or heart attacks within 10 years. The AI system beat the standard method of prediction, correctly making calls in 355 more cases than traditional means. Predicting cardiovascular events like strokes and heart attacks is a notoriously challenging task. In fact, the researchers note in their recent paper that around half of all strokes and heart attacks occur in patients who were never identified as being “at risk.”
The records included a decade of health outcomes, lab data, drug information, hospital records, and demographic information. The team identified the distinguishing characteristics of patients who experienced strokes and heart attacks using 75 percent of the records. They then tested their models against the standard guidelines using the remaining 25 percent of the records. The standard guidelines scored 0.728 out of 1.0, with the latter signifying 100 percent accuracy. The machine models scored between 0.745 to 0.764, with the neural network making 355 more accurate predictions than the standard guidelines, therefore earning the best score. Had those predictions been made in real time, the patients could have been provided with preventative care.