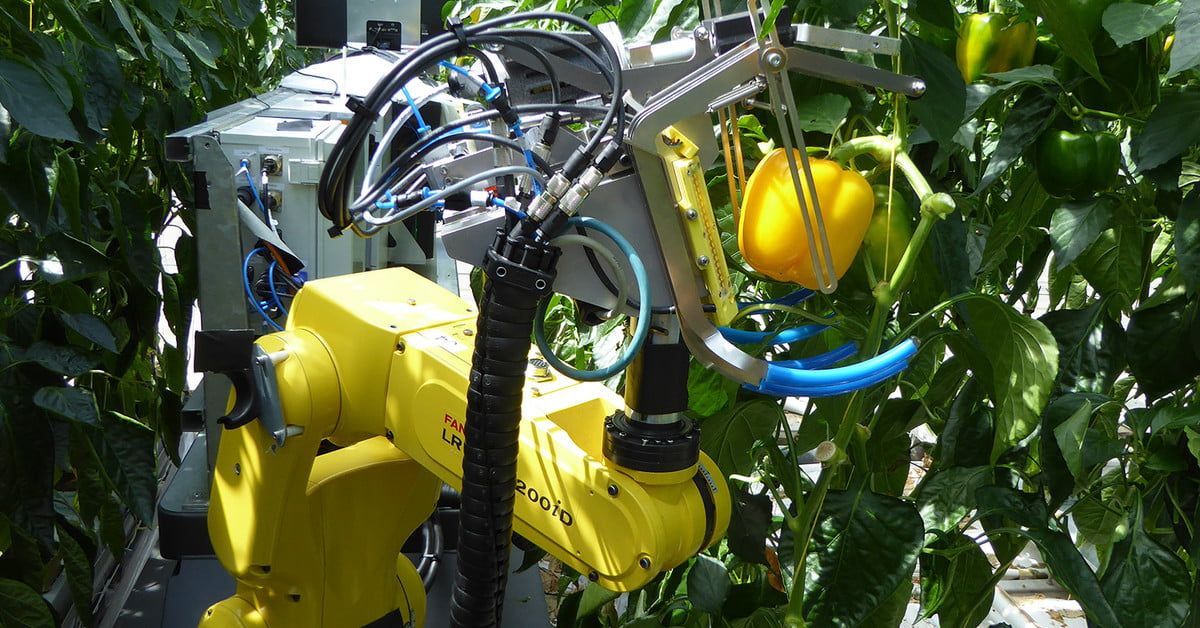
Supply chain and sales and marketing are the first big opportunities.


Not long ago, getting a virus was about the worst thing computer users could expect in terms of system vulnerability. But in our current age of hyper-connectedness and the emerging Internet of Things, that’s no longer the case. With connectivity, a new principle has emerged, one of universal concern to those who work in the area of systems control, like João Hespanha, a professor in the departments of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Mechanical Engineering at UC Santa Barbara. That law says, essentially, that the more complex and connected a system is, the more susceptible it is to disruptive cyber-attacks.
“It is about something much different than your regular computer virus,” Hespanha said. “It is more about cyber physical systems—systems in which computers are connected to physical elements. That could be robots, drones, smart appliances, or infrastructure systems such as those used to distribute energy and water.”
In a paper titled “Distributed Estimation of Power System Oscillation Modes under Attacks on GPS Clocks,” published this month in the journal IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, Hespanha and co-author Yongqiang Wang (a former UCSB postdoctoral research and now a faculty member at Clemson University) suggest a new method for protecting the increasingly complex and connected power grid from attack.


Nicholas Papernot discusses “Making Machine Learning Robust Against Adversarial Inputs” (cacm.acm.org/magazines/2018/7/229030), a Contributed Article in the July 2018 CACM.
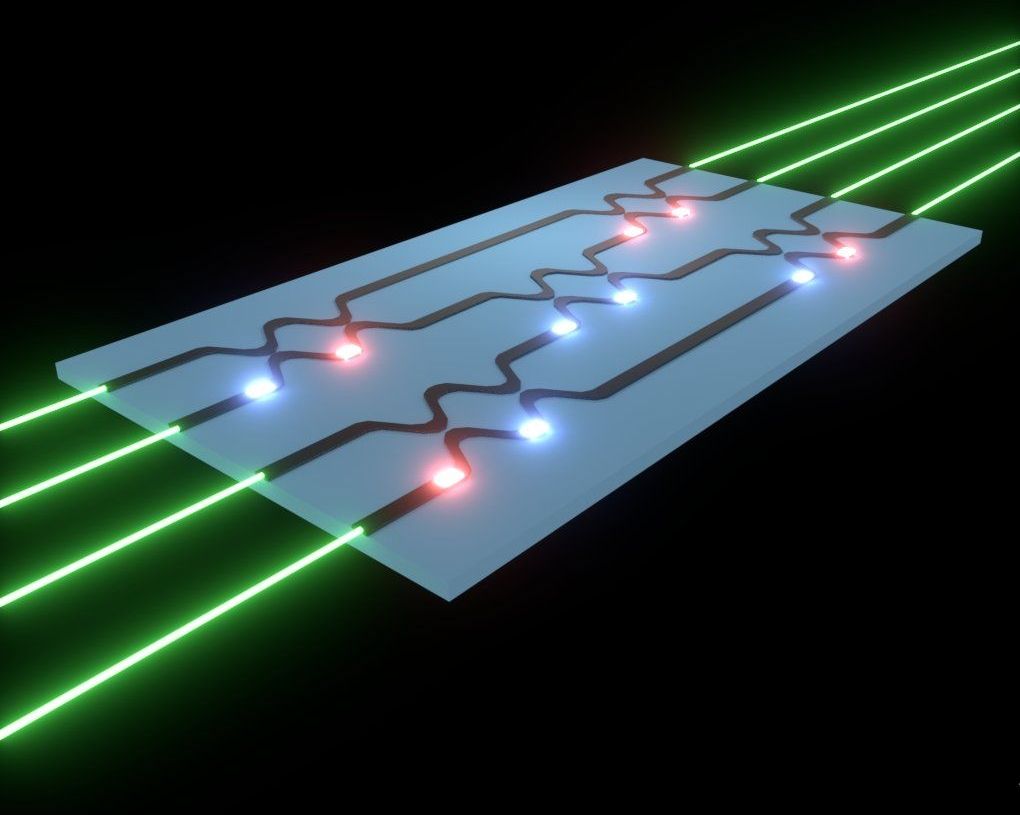
Researchers have shown that it is possible to train artificial neural networks directly on an optical chip. The significant breakthrough demonstrates that an optical circuit can perform a critical function of an electronics-based artificial neural network and could lead to less expensive, faster and more energy efficient ways to perform complex tasks such as speech or image recognition.
“Using an optical chip to perform neural network computations more efficiently than is possible with digital computers could allow more complex problems to be solved,” said research team leader Shanhui Fan of Stanford University. “This would enhance the capability of artificial neural networks to perform tasks required for self-driving cars or to formulate an appropriate response to a spoken question, for example. It could also improve our lives in ways we can’t imagine now.”
An artificial neural network is a type of artificial intelligence that uses connected units to process information in a manner similar to the way the brain processes information. Using these networks to perform a complex task, for instance voice recognition, requires the critical step of training the algorithms to categorize inputs, such as different words.


But even though money is necessary, it’s not sufficient to provide human beings a sense of satisfaction, Obama cautioned. As more and more tasks and services become automated with the rise of artificial intelligence, “that’s going to make the job of giving everybody work that is meaningful tougher, and we’re going to have to be more imaginative, and the pace of change is going to require us to do more fundamental re-imagining of our social and political arrangements, to protect the economic security and the dignity that comes with a job.”
The former president says “we’re going to have to consider new ways of thinking” as technology threatens current labor markets.
Our Fast Lightweight Autonomy program recently completed Phase 2 flight tests, demonstrating advanced algorithms designed to turn small air and ground systems into team members that can autonomously perform tasks dangerous for humans — such as pre-mission reconnaissance in a hostile urban setting or searching damaged structures for survivors following an earthquake.

“Will machines replace humans?” This question is on the mind of anyone with a job to lose. Daniel Susskind confronts this question and three misconceptions we have about our automated future, suggesting we ask something else: How will we distribute wealth in a world when there will be less — or even no — work?
