Preprogrammed AI definitely won’t.


Anarchy AI ✌️😆
There’s a big new feature for iPhone experts this year: It’s an app called Shortcuts, and with a little bit of logic and know-how, you can stitch together several apps and create a script that can be activated by pressing a button or using Siri.
Some early uses are predictable, like saving Instagram photos, sharing the song you’re listening to, or creating a morning routine that activates your lights and plays a song.
But Robert Petersen of Arizona has developed a more serious shortcut: It’s called Police, and it monitors police interactions so you have a record of what happened.

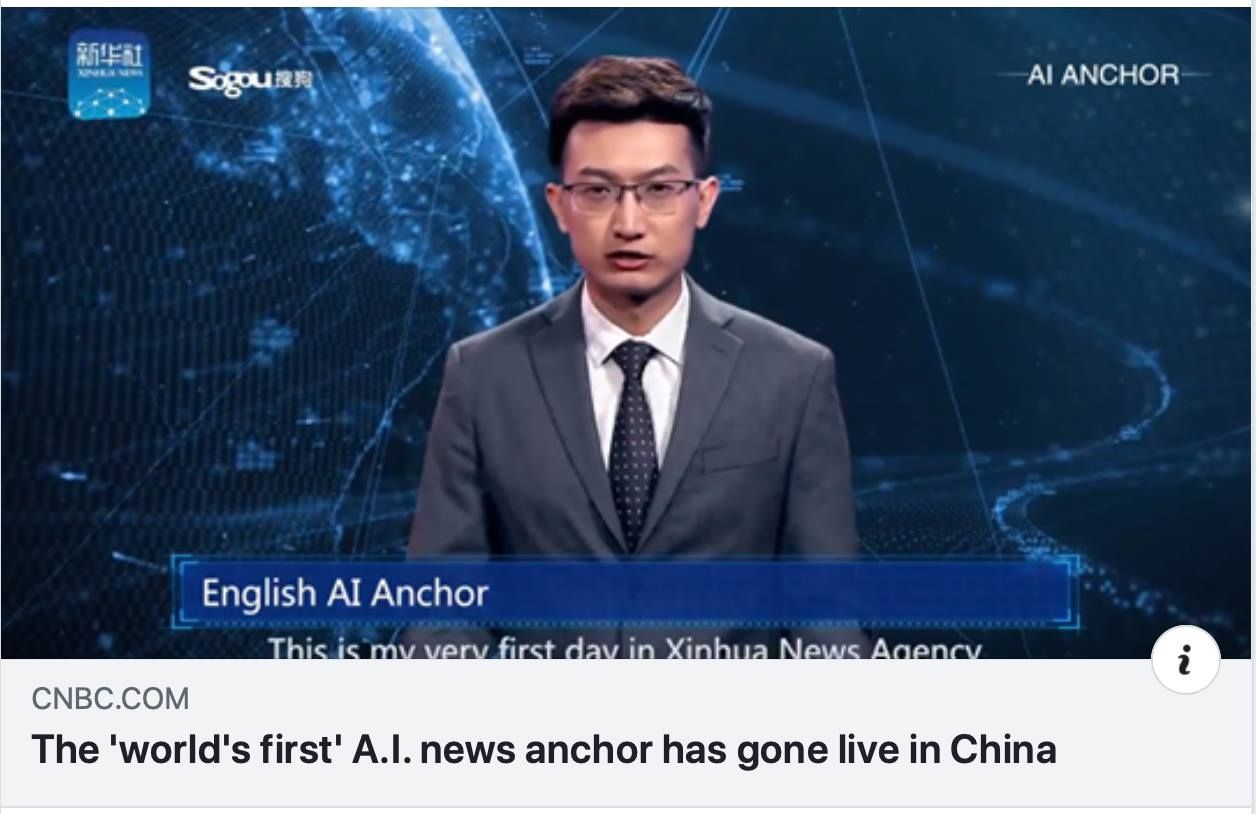
China’s state-run press agency Xinhua has unveiled what it claims are the world’s first AI-generated news anchors.
Xinhua revealed the anchors at the World Internet Conference on Thursday. Modeled on two real presenters, the agency showcased two AI-generated anchors, one who speaks Chinese and another who speaks English.

But the agency’s new host isn’t any more sophisticated than a CGI puppet.
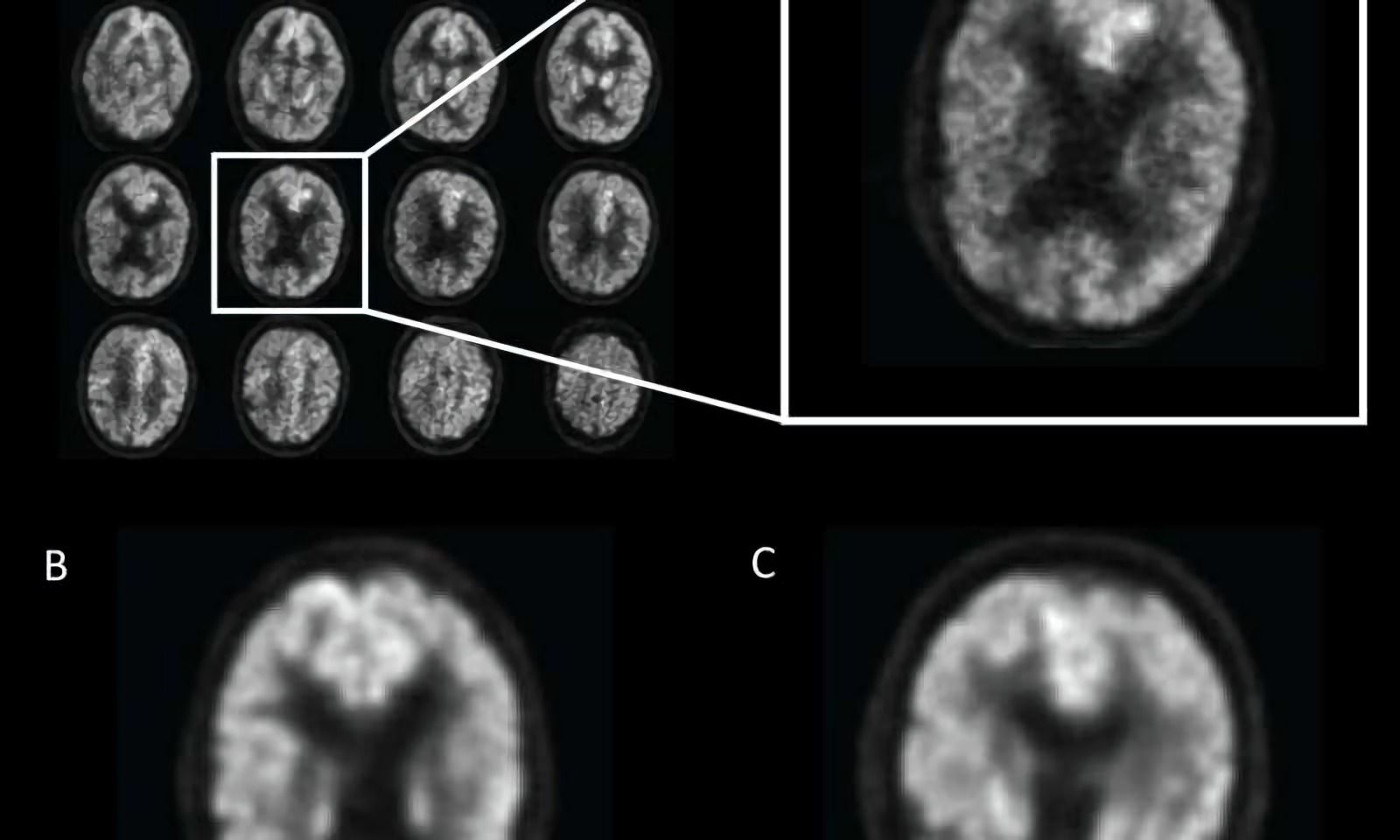
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have recently developed a new model that enables fast and accurate object detection in high-resolution 4K and 8K video footage using GPUs. Their attention pipeline method carries out a two-stage evaluation of every image or video frame under rough and refined resolution, limiting the total number of evaluations necessary.
In recent years, machine learning has attained remarkable results in computer vision tasks, including object detection. However, most object recognition models typically perform best on images with a relatively low resolution. As the resolution of recording devices is rapidly improving, there is a rising need for tools that can process high-resolution data.
“We were interested in finding and overcoming the limitations of current approaches,” Vít Růžička, one of the researchers who carried out the study told TechXplore. “While plenty of data sources record in high resolution, current state-of-the-art object detection models, such as YOLO, Faster RCNN, SSD, etc., work with images that have a relatively low resolution of approximately 608 × 608 px. Our main objective was to scale the object detection task to 4K-8K videos (up to 7680 × 4320 px) while maintaining high processing speed. We also wanted to understand if and by how much we can benefit from high resolution compared to using low-resolution images, in terms of accuracy of the models.”
#ParkerSolarProbe
Parker Solar Probe is alive and well after skimming by the Sun at just 15 million miles from our star’s surface. This is far closer than any spacecraft has ever gone — the previous record was set by Helios B in 1976 and broken by Parker on Oct. 29 — and this maneuver has exposed the spacecraft to intense heat and solar radiation in a complex solar wind environment.
“Parker Solar Probe was designed to take care of itself and its precious payload during this close approach, with no control from us on Earth — and now we know it succeeded,” said Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at the agency headquarters in Washington. “Parker is the culmination of six decades of scientific progress. Now, we have realized humanity’s first close visit to our star, which will have implications not just here on Earth, but for a deeper understanding of our universe.”
Mission controllers at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab received the status beacon from the spacecraft at 4:46 p.m. EST on Nov. 7, 2018. The beacon indicates status “A” — the best of all four possible status signals, meaning that Parker Solar Probe is operating well with all instruments running and collecting science data and, if there were any minor issues, they were resolved autonomously by the spacecraft.
Scientist use magnetic field to drive spiral nanobots.