Opinion: Progress in deep learning research will come from the convergence of engineering and neuroscience.



While it might be nice to use a $4,000 oscilloscope in a lab at a university or well-funded corporate environment, a good portion of us won’t have access to that kind of equipment in our own home shops. There are a few ways of getting a working oscilloscope without breaking the bank, though. One option is to find old CRT-based unit for maybe $50 on craigslist which might still have 60% of its original 1970s-era equipment still operational. A more reliable, and similarly-priced, way of getting an oscilloscope is to just convert a device you already have.
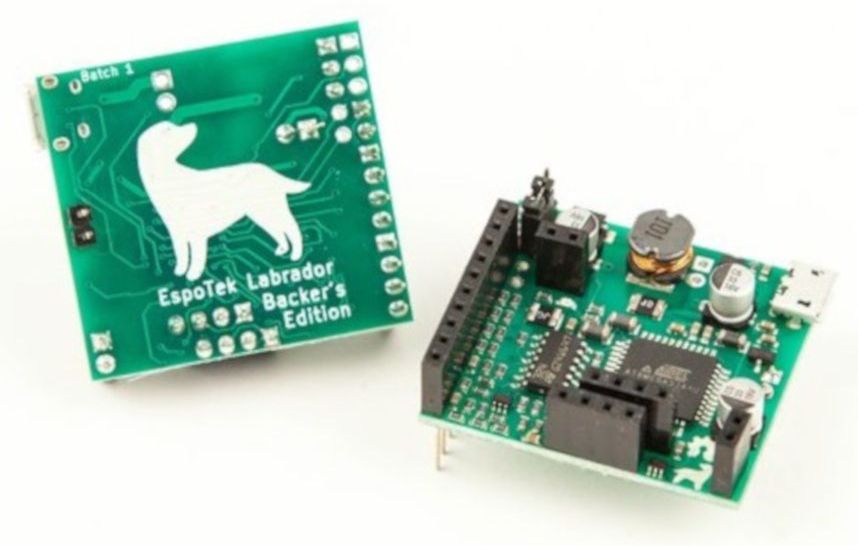
The EspoTek Labrador is an open-source way of converting a Raspberry Pi, Android device, or even a regular run-of-the-mill computer into a working oscilloscope. It’s a small USB device with about a two square inch PCB footprint that includes some other features as well like a signal generator and logic analyzer. It’s based on an ATxmega which is your standard Arduino-style AVR microcontroller but geared for low power usage. It looks as though it is pretty simple to use as well, and the only requirements are that you can install the software needed for the device on whatever computing platform you decide to use.
While the Labrador is available for sale at their website, it is definitely a bonus when companies offer products like this but also release the hardware and software as open source. That’s certainly a good way to get our attention, at least. You can build your own if you’d like, but if you’d rather save the time you have pre-built options. And it doesn’t hurt that most of the reviews of this product seem to be very favorable (although we haven’t tried one out ourselves). If you’d prefer an option without a company backing it, though, we have you covered there too.

A group of researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have developed a tool that can cross-train standard convolutional neural networks (CNN) to a spiking neural model that can be used on neuromorphic processors. The researchers claim that the conversion will enable deep learning applications to take advantage of the much better energy efficiency of neuromorphic hardware, which are designed to mimic the way the biological neurons work.
The tool, known as Whetstone, works by adjusting artificial neuron behavior during the training phase to only activate when it reaches an appropriate threshold. As a result, neuron activation become a binary choice – either it spikes or it doesn’t. By doing so, Whetstone converts an artificial neural network into a spiking neural network. The tool does this by using an incremental “sharpening process” (hence Whetstone) through each network layer until the activation becomes discrete.
According to Whetstone researcher Brad Aimone, this discrete activation greatly minimizes communication costs between the layers, and thus energy consumption, but with only minimal loss of accuracy. “We continue to be impressed that without dramatically changing what the networks look like, we can get very close to a standard neural net [in accuracy],” he says. “We’re usually within a percent or so on performance.”
Neuromorphic systems carry out robust and efficient neural computation using hardware implementations that operate in physical time. Typically they are event- or data-driven, they employ low-power, massively parallel hybrid analog/digital VLSI circuits, and they operate using the same physics of computation used by the nervous system. Although there are several forums for presenting research achievements in neuromorphic engineering, none are exclusively dedicated to this increasingly large research community. Either because they are dedicated to single disciplines, such as electrical engineering or computer science, or because they serve research communities which focus on analogous areas (such as biomedical engineering or computational neuroscience), but with fundamentally different goals and objectives. The mission of Neuromorphic Engineering is to provide a publication medium dedicated exclusively and specifically to this field. Topics covered by this publication include: Analog and hybrid analog/digital electronic circuits for implementing neural processes, such as conductances, neurons, synapses, plasticity mechanisms, photoreceptors, cochleae, etc. Neuromorphic circuits and systems for implementing real-time event-based neural processing architectures. Hardware models of neural and sensorimotor processing systems, such as selective attention systems, coordinate transformation systems, auditory and/or visual processing systems, sensory fusion systems, etc. Implementations of neural computational systems found in insects, birds, mammals, etc. Embedded neuromorphic systems, including actuated or robotic platforms which process sensory signals and interact with the environment using event-based sensors and circuits. To ensure high quality and state-of-the-art material, publications should demonstrate experimental results, using physical implementations of neuromorphic systems, and possibly show the links between the artificial system and the neural/biological one they model.

A new photonic chip could run optical neural networks 10 million times more efficiently than conventional chips.
The classical physical limit for computing energy is the Landauer limit that sets a lower bound to the minimum heat dissipated per bit erasing operation. Performance below the thermodynamic (Landauer) limit for digital irreversible computation is theoretically possible in this device. The proposed accelerator can implement both fully connected and convolutional networks.
Previous photonic chips had bulky optical components that limited their use to relatively small neural networks. MIT researchers have a new photonic accelerator that uses more compact optical components and optical signal-processing techniques, to drastically reduce both power consumption and chip area. That allows the chip to scale to neural networks several orders of magnitude larger than its counterparts.