In “A World Without Work,” the economist Daniel Susskind argues that, unlike during past technological shifts, machines really are becoming smart enough to take over our jobs.


Artificial Intelligence can now detect over 50 eyes diseases as accurately as doctors!
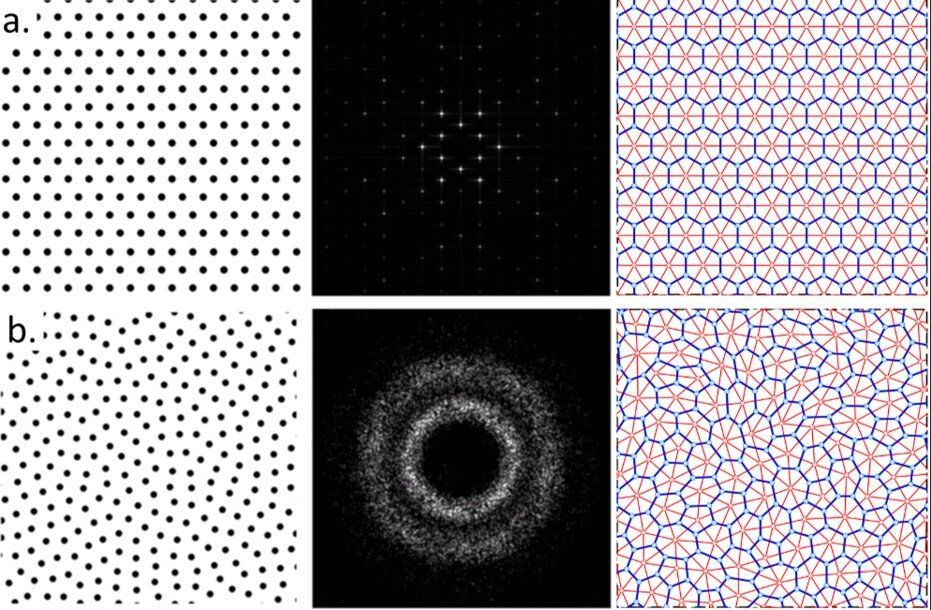
In a new report published on Scientific Reports, Milan M. Milošević and an international research team at the Zepler Institute for Photonics and Nanoelectronics, Etaphase Incorporated and the Departments of Chemistry, Physics and Astronomy, in the U.S. and the U.K. Introduced a hyperuniform-disordered platform to realize near-infrared (NIR) photonic devices to create, detect and manipulate light. They built the device on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) platform to demonstrate the functionality of the structures in a flexible, silicon-integrated circuit unconstrained by crystalline symmetries. The scientists reported results for passive device elements, including waveguides and resonators seamlessly integrated with conventional silicon-on-insulator strip waveguides and vertical couplers. The hyperuniform-disordered platform improved compactness and enhanced energy efficiency as well as temperature stability, compared to silicon photonic devices fabricated on rib and strip waveguides.
Academic and commercial efforts worldwide in the field of silicon photonics have led to engineer optical data communications at the Terabit-scale at increasingly lower costs to meet the rapidly growing demand in data centers. Explosive growth in cloud computing and entertainment-on-demand pose increasingly challenging costs and energy requirements for data transmission, processing and storage. Optical interconnects can replace traditional copper-based solutions to offer steadily increasing potential to minimize latency and power consumption, while maximizing the bandwidth and reliability of the devices. Silicon photonics also leverage large-scale, complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) manufacturing processes to produce high-performance optical transceivers with high yield at low-cost. The properties allow applications of optical transceivers (fiber optical technology to send and receive data) to be increasingly compelling across shorter distances.
More than three decades ago, physicist Richard Soref identified silicon as a promising material for photonic integration. Leading to the present-day steady development and rapid production of increasingly complex photonic integrated circuits (PICs). Researchers can integrate large numbers of massively-parallel compact energy-efficient optical components on a single chip for cloud computing applications from deep learning to artificial intelligence and the internet of things. Compared to the limited scope of commercial silicon photonic systems, photonic crystal (PhC) architectures promise smaller device sizes, although they are withheld by layout constraints imposed by waveguide requirements along the photonic crystal’s axis. Until recently, photonic band gap (PBG) structures that efficiently guide light were limited to photonic crystal platforms. Now, newer classes of PBG structures include photonic quasicrystals, hyperuniform disordered solids (HUDs) and local self-uniform structures.
Brain cancer remains challenging to diagnose, due to nonspecific symptoms and a lack of cost-effective tests. A new blood test that uses attenuated total reflection (ATR)-Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in conjunction with machine learning technology, may help advance the detection of brain cancer.
The patented technology, developed by a team at the University of Strathclyde, uses infrared light to produce a “bio-signature” of a blood sample and applies artificial intelligence to check for the signs of cancer.
The research is published in Nature Communications in a paper titled, “Development of high-throughput ATR-FTIR technology for rapid triage of brain cancer.”
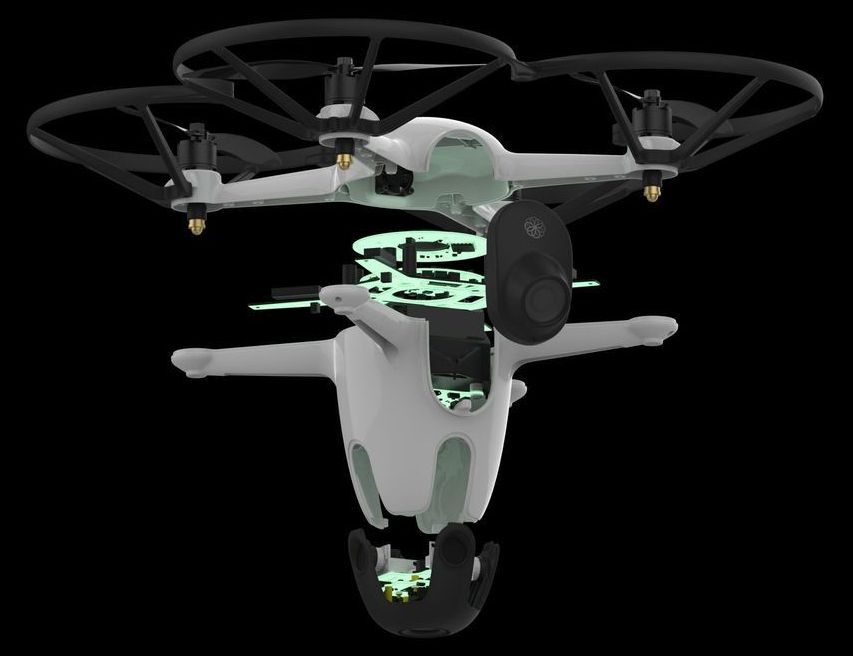

One of the new products unveiled at CES this year is a new kind of home security system — one that includes drones to patrol your property, along with sensors designed to mimic garden light and a central processor to bring it all together.
Sunflower Labs debuted their new Sunflower Home Awareness System, which includes the eponymous Sunflowers (motion and vibration sensors that look like simple garden lights but can populate a map to show you cars, people and animals on or near your property in real time); the Bee (a fully autonomous drone that deploys and flies on its own, with cameras on board to live-stream video); and the Hive (a charging station for the Bee, which also houses the brains of the operation for crunching all the data gathered by the component parts).
Roving aerial robots keeping tabs on your property might seem a tad dystopian, and perhaps even unnecessary, when you could maybe equip your estate with multiple fixed cameras and sensors for less money and with less complexity. But Sunflower Labs thinks its security system is an evolution of more standard fare because it “learns and reacts to its surroundings,” improving over time.
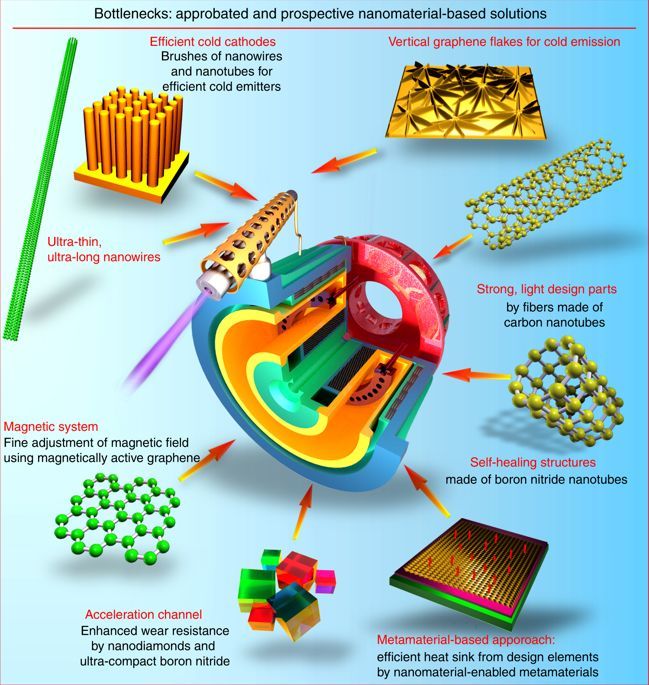
Drastic miniaturization of electronics and ingression of next-generation nanomaterials into space technology have provoked a renaissance in interplanetary flights and near-Earth space exploration using small unmanned satellites and systems. As the next stage, the NASA’s 2015 Nanotechnology Roadmap initiative called for new design paradigms that integrate nanotechnology and conceptually new materials to build advanced, deep-space-capable, adaptive spacecraft. This review examines the cutting edge and discusses the opportunities for integration of nanomaterials into the most advanced types of electric propulsion devices that take advantage of their unique features and boost their efficiency and service life. Finally, we propose a concept of an adaptive thruster.
Recent AI lecture by Stanford University.
What do web search, speech recognition, face recognition, machine translation, autonomous driving, and automatic scheduling have in common? These are all complex real-world problems, and the goal of artificial intelligence (AI) is to tackle these with rigorous mathematical tools.
In this course, you will learn the foundational principles that drive these applications and practice implementing some of these systems. Specific topics include machine learning, search, game playing, Markov decision processes, constraint satisfaction, graphical models, and logic. The main goal of the course is to equip you with the tools to tackle new AI problems you might encounter in life.
Instructors:
Tesla vehicles are apparently going to talk to people not only inside the car but also outside. CEO Elon Musk even released a quick preview video.
It’s no secret that Tesla wants to use more artificial intelligence in its business.
Two years ago, Tesla hired Andrej Karpathy to lead its computer vision and AI team and they have been expanding their team since then.