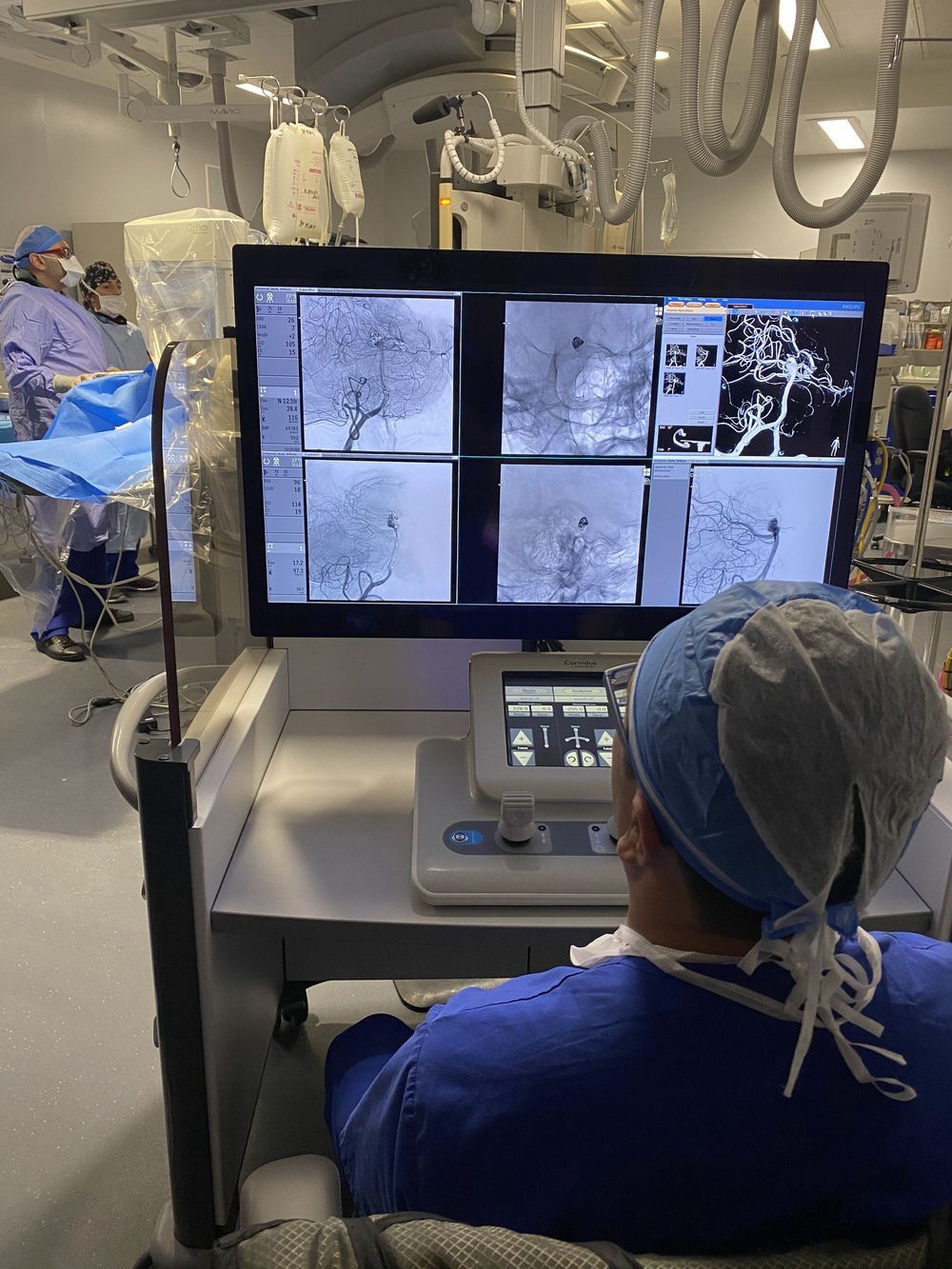
Using a robot to treat brain aneurysms is feasible and could allow for improved precision when placing stents, coils and other devices, according to late breaking science presented today at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2020.
Robotic technology is used in surgery and cardiology, but not for brain vascular procedures. In this study, Canadian researchers report the results of the first robotic brain vascular procedures. They used a robotic system specifically adapted for neurovascular procedures. Software and hardware adaptations enable it to accommodate microcatheters, guidewires and the other devices used for endovascular procedures in the brain. These modifications also provide the operator additional precise fine-motor control compared to previous system models.
“This experience is the first step towards achieving our vision of remote neurovascular procedures,” said lead researcher Vitor Mendes Pereira, M.D., M.Sc., a neurosurgeon and neuroradiologist at the Toronto Western Hospital, and professor of medical imaging and surgery at the University of Toronto in Canada. “The ability to robotically perform intracranial aneurysm treatment is a major step forward in neuro-endovascular intervention.”