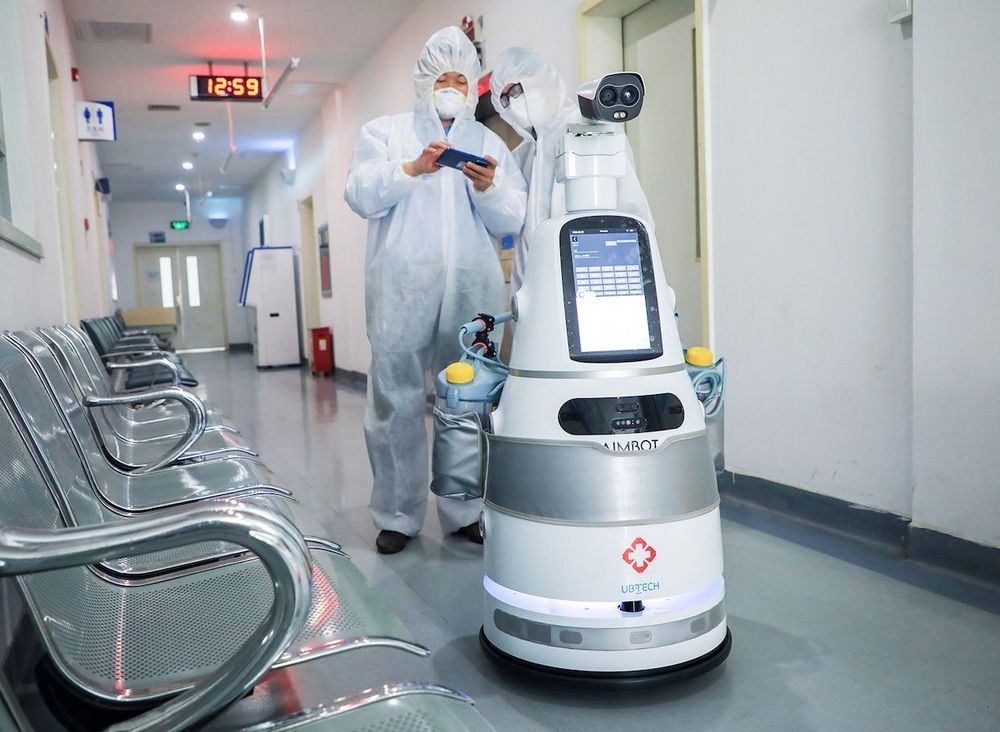
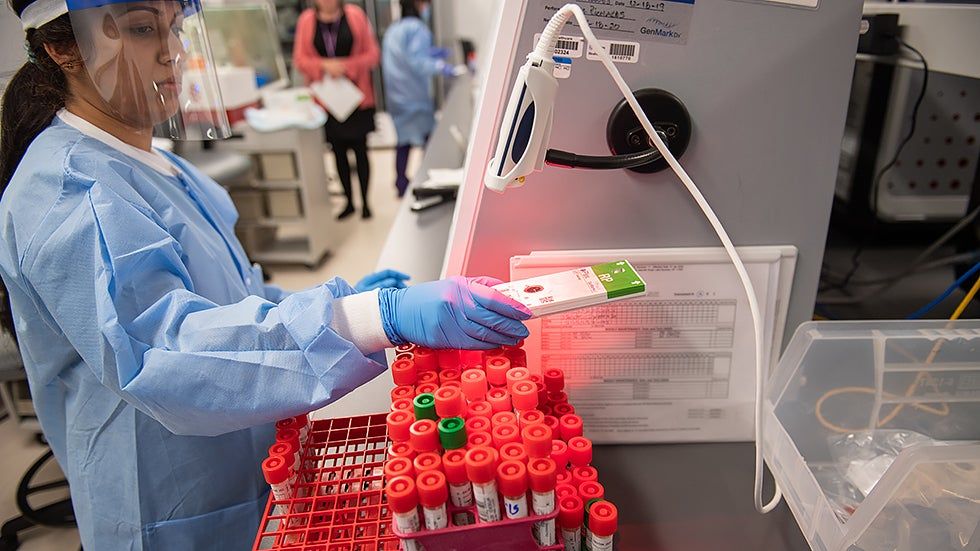
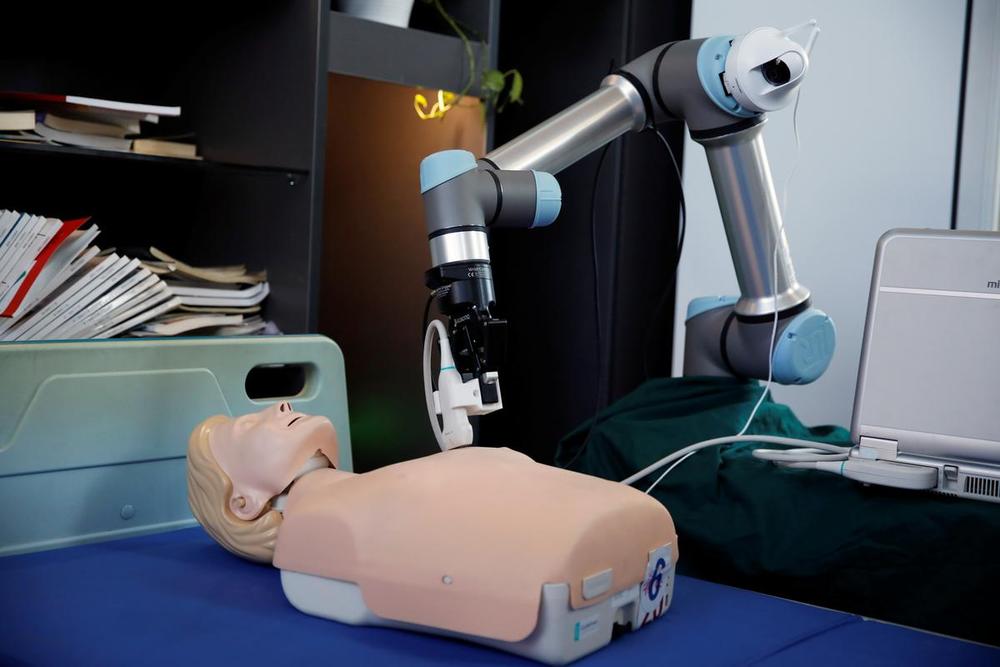
This movement towards a more automated society has some positives: it will help us stay healthy during times like the present, it will drive down the cost of goods and services, and it will grow our GDP in the long run. But by leaning into automation, will we be enabling a future that keeps us more physically, psychologically, and emotionally distant from each other?
We’re in a crisis, and desperate times call for desperate measures. We’re sheltering in place, practicing social distancing, and trying not to touch each other. And for most of us, this is really unpleasant and difficult. We can’t wait for it to be over.
For better or worse, this pandemic will likely make us pick up the pace on our path to automation, across many sectors and processes. The solutions people implement during this crisis won’t disappear when things go back to normal (and, depending who you talk to, they may never really do so).