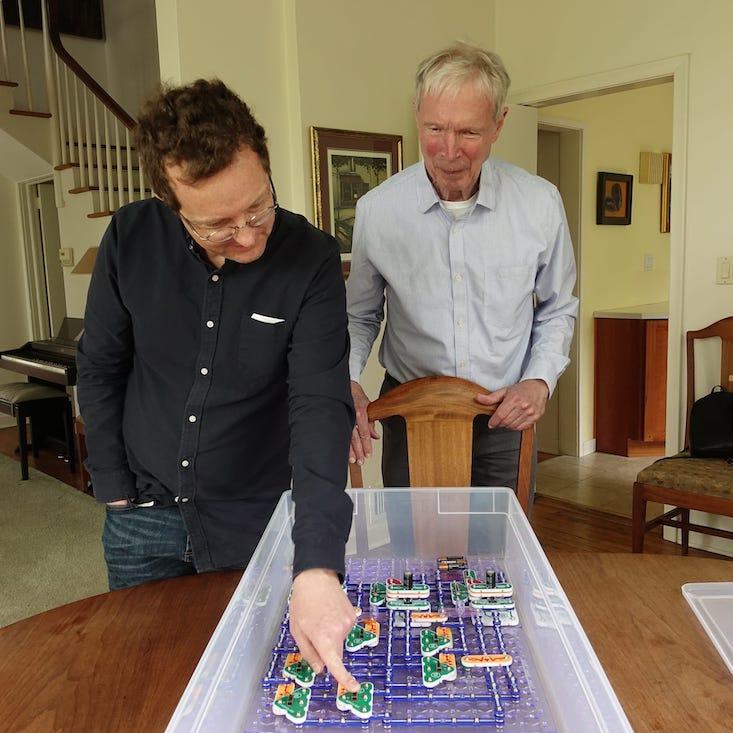
The first artificial neural networks weren’t abstractions inside a computer, but actual physical systems made of whirring motors and big bundles of wire. Here I’ll describe how you can build one for yourself using SnapCircuits, a kid’s electronics kit. I’ll also muse about how to build a network that works optically using a webcam. And I’ll recount what I learned talking to the artist Ralf Baecker, who built a network using strings, levers, and lead weights.
I showed the SnapCircuits network last year to John Hopfield, a Princeton University physicist who pioneered neural networks in the 1980s, and he quickly got absorbed in tweaking the system to see what he could get it to do. I was a visitor at the Institute for Advanced Study and spent hours interviewing Hopfield for my forthcoming book on physics and the mind.
The type of network that Hopfield became famous for is a bit different from the deep networks that power image recognition and other A.I. systems today. It still consists of basic computing units—“neurons”—that are wired together, so that each responds to what the others are doing. But the neurons are not arrayed into layers: There is no dedicated input, output, or intermediate stages. Instead the network is a big tangle of signals that can loop back on themselves, forming a highly dynamic system.