A new crop of artificial-intelligence models allows users to create, manipulate and learn about biology using ordinary language.

Make sure to watch this next video about Type 1 to Type 4 Civilizations: https://youtu.be/5fTNGvuPTMU.
💡 Future Business Tech explores AI, emerging technologies, and future technologies.
SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/3geLDGO
This video explores the Kardashev scale and the type 1 to type 7 civilizations. Related terms: ai, future business tech, future technology, future tech, future business technologies, future technologies, artificial intelligence, kardashev scale, type 7 civilization, type 6 civilization, type 5 civilization, type 4 civilization, type 3 civilization, type 2 civilization, type 1 civilization, etc.
ℹ️ Some links are affiliate links. They cost you nothing extra but help support the channel so I can create more videos like this.
#technology #ai

Researchers from the University of Innsbruck have unveiled a novel method to prepare quantum operations on a given quantum computer, using a machine learning generative model to find the appropriate sequence of quantum gates to execute a quantum operation.
The study, recently published in Nature Machine Intelligence, marks a significant step forward in realizing the full extent of quantum computing.
Generative models like diffusion models are one of the most important recent developments in machine learning (ML), with models such as Stable Diffusion and DALL·E revolutionizing the field of image generation. These models are able to produce high quality images based on text description.

Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei believes today’s AI models hallucinate, or make things up and present them as if they’re true, at a lower rate than humans do, he said during a press briefing at Anthropic’s first developer event, Code with Claude, in San Francisco on Thursday.
Amodei said all this in the midst of a larger point he was making: that AI hallucinations are not a limitation on Anthropic’s path to AGI — AI systems with human-level intelligence or better.
“It really depends how you measure it, but I suspect that AI models probably hallucinate less than humans, but they hallucinate in more surprising ways,” Amodei said, responding to TechCrunch’s question.
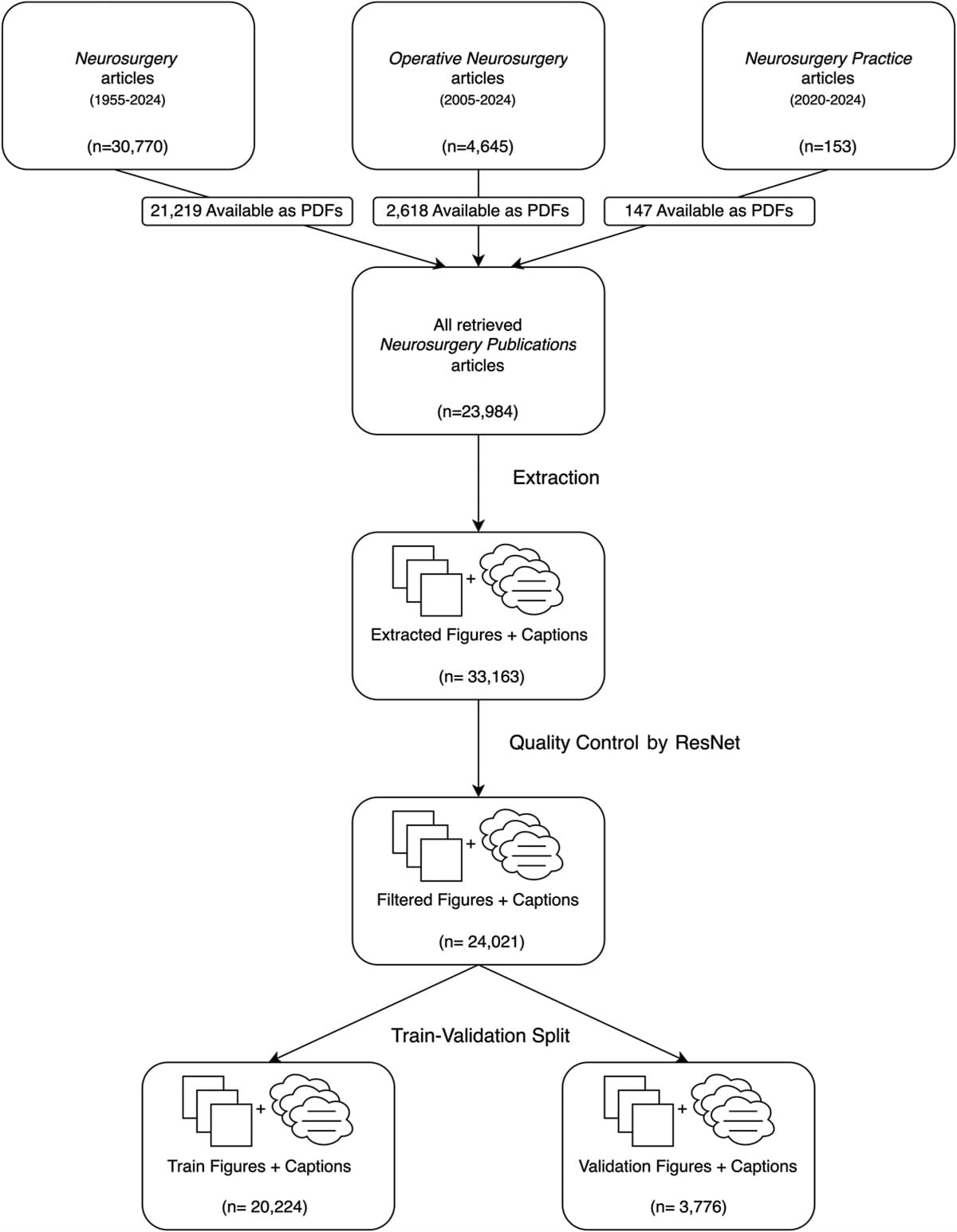
Classical biomedical data science models are trained on a single modality and aimed at one specific task. However, the exponential increase in the size and capabilities of the foundation models inside and outside medicine shows a shift toward task-agnostic models using large-scale, often internet-based, data. Recent research into smaller foundation models trained on specific literature, such as programming textbooks, demonstrated that they can display capabilities similar to or superior to large generalist models, suggesting a potential middle ground between small task-specific and large foundation models. This study attempts to introduce a domain-specific multimodal model, Congress of Neurological Surgeons (CNS)-Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP), developed for neurosurgical applications, leveraging data exclusively from Neurosurgery Publications.
METHODS:
We constructed a multimodal data set of articles from Neurosurgery Publications through PDF data collection and figure-caption extraction using an artificial intelligence pipeline for quality control. Our final data set included 24 021 figure-caption pairs. We then developed a fine-tuning protocol for the OpenAI CLIP model. The model was evaluated on tasks including neurosurgical information retrieval, computed tomography imaging classification, and zero-shot ImageNet classification.

Self-driving cars which eliminate traffic jams, getting a health care diagnosis instantly without leaving your home, or feeling the touch of loved ones based across the continent may sound like the stuff of science fiction.
But new research, led by the University of Bristol and published in the journal Nature Electronics, could make all this and more a step closer to reality thanks to a radical breakthrough in semiconductor technology.
The futuristic concepts rely on the ability to communicate and transfer vast volumes of data much faster than existing networks. So physicists have developed an innovative way to accelerate this process between scores of users, potentially across the globe.