SpaceX now employs robotic dogs, each costing $75000!
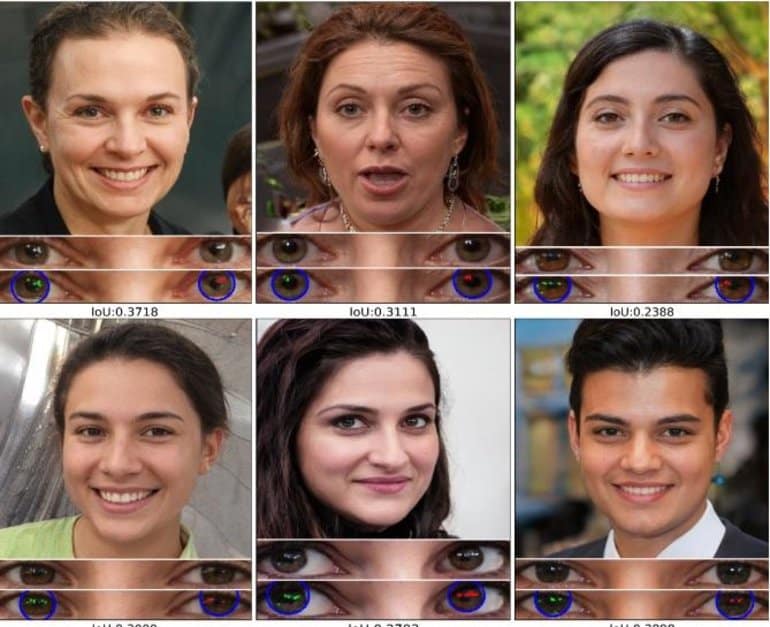



Summary: A newly developed AI tool can identify “deepfakes” of faces by examining the light reflection in the eyes of the images. The system is 94% accurate at detecting deepfakes.
Source: University ay Buffalo.
University at Buffalo computer scientists have developed a tool that automatically identifies deepfake photos by analyzing light reflections in the eyes.
Technology paves way for intelligent solar cells, other highly efficient devices programmed at the macro and nano scale.
Researchers at Tufts University School of Engineering have created light-activated composite devices able to execute precise, visible movements and form complex three-dimensional shapes without the need for wires or other actuating materials or energy sources. The design combines programmable photonic crystals with an elastomeric composite that can be engineered at the macro and nano scale to respond to illumination.
The research provides new avenues for the development of smart light-driven systems such as high-efficiency, self-aligning solar cells that automatically follow the sun’s direction and angle of light, light-actuated microfluidic valves or soft robots that move with light on demand. A “photonic sunflower,” whose petals curl towards and away from illumination and which tracks the path and angle of the light, demonstrates the technology in a paper that appears today (March 12th, 2021) in Nature Communications.
Facebook has announced a new AI project called Learn From Video, which will use public Facebook videos to train its machine learning models. The company is vague about future applications, but it says such models could be used to improve captions, search functions, and much more.
P.e.a.c.e!nc. is proud to announce the conclusion as finalists in the $500k Pandemic Response Challenge sponsored by Cognizant with Landmark AI Experiment.

Space roboticist Vandi Verma, who operates the Perseverance—the most advanced astrobiology lab ever sent to another world—as it roams Mars looking for signs of ancient microbial life, said unconscious bias was also a factor in shaping aspirations. “Don’t make assumptions about what a child may be interested in because of their gender or race,” she said. “Don’t buy the Lego just for the boy.”

AI And Robots For Law And Order — Irakli Beridze — Head, Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, UNICRI – United Nations Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute.
Irakli Beridze is the Head of the Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics at The United Nations Interregional Crime and Justice Research Institute (UNICRI).
With a Master’s Degree in International Relations and National Security Studies, and a law degree, Mr. Beridze has more than 20 years of experience in leading multilateral negotiations, developing stakeholder engagement programs with governments, UN agencies, international organizations, private industry and corporations, think tanks, civil society, foundations, academia, and other partners on an international level.
Mr. Beridze advises governments and international organizations on numerous issues related to international security, scientific and technological developments, emerging technologies, innovation and disruptive potential of new technologies, particularly on the issue on crime prevention, criminal justice and security, and is now actively focused on supporting government’s worldwide on the strategies, action plans, roadmaps and policy papers on Artificial Intelligence.
Since 2014, Mr. Beridze has initiated and managed one of the first United Nations Programs on AI, initiating and organizing a number of high-level events at the United Nations General Assembly, and other international organizations, finding synergies with traditional threats and risks, as well as identifying solutions that AI can contribute to the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
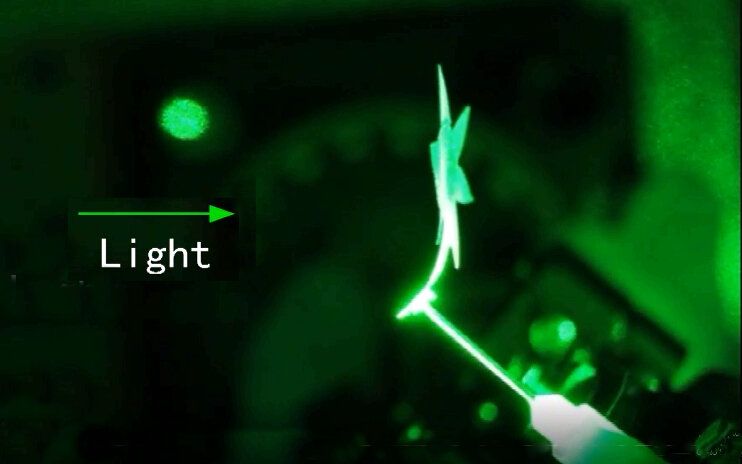
Researchers at Tufts University School of Engineering have created light-activated composite devices able to execute precise, visible movements and form complex three-dimensional shapes without the need for wires or other actuating materials or energy sources. The design combines programmable photonic crystals with an elastomeric composite that can be engineered at the macro and nano scale to respond to illumination.
The research provides new avenues for the development of smart light-driven systems such as high-efficiency, self-aligning solar cells that automatically follow the sun’s direction and angle of light, light-actuated microfluidic valves or soft robots that move with light on demand. A “photonic sunflower,” whose petals curl towards and away from illumination and which tracks the path and angle of the light, demonstrates the technology in a paper that appears March 12th, 2021 in Nature Communications.
Color results from the absorption and reflection of light. Behind every flash of an iridescent butterfly wing or opal gemstone lie complex interactions in which natural photonic crystals embedded in the wing or stone absorb light of specific frequencies and reflect others. The angle at which the light meets the crystalline surface can affect which wavelengths are absorbed and the heat that is generated from that absorbed energy.