A new wave of startups are using deep learning to build synthetic voice actors for digital assistants, video-game characters, and corporate videos.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 1,969
Dating AI Robots, with Elon Musk & Boston Dynamics
A Dangerous AI and Robot Dance, with Elon Musk, Tom Scott & Pissbot (aka Boston Dynamics’ Spot).
We’re new to youtube, so comments and subs are really helpful.
Tom Scott’s video about grocery store robots: https://youtu.be/ssZ_8cqfBlE
Michael Reeves teaches Boston Dynamics’ robot dog spot to pee beer: https://youtu.be/tqsy9Wtr1qE
Microscopic robots, Itai Cohen, Cornell University: https://youtu.be/Wl6uw8dRrPA
Robot chair dance, Mattias Lindström (Swebounce): https://youtu.be/m7NxnPbOZFE

Harnessing AI to Discover New Drugs: Rewriting the Rulebook for Pharmaceutical Research
Artificial intelligence (AI) is able to recognize the biological activity of natural products in a targeted manner, as researchers at ETH Zurich have demonstrated. Moreover, AI helps to find molecules that have the same effect as a natural substance but are easier to manufacture. This opens up huge possibilities for drug discovery, which also has potential to rewrite the rulebook for pharmaceutical research.
Nature has a vast store of medicinal substances. “Over 50 percent of all drugs today are inspired by nature,” says Gisbert Schneider, Professor of Computer-Assisted Drug Design at ETH Zurich. Nevertheless, he is convinced that we have tapped only a fraction of the potential of natural products. Together with his team, he has successfully demonstrated how artificial intelligence (AI) methods can be used in a targeted manner to find new pharmaceutical applications for natural products. Furthermore, AI methods are capable of helping to find alternatives to these compounds that have the same effect but are much easier and therefore cheaper to manufacture.
And so the ETH researchers are paving the way for an important medical advance: we currently have only about 4000 basically different medicines in total. In contrast, estimates of the number of human proteins reach up to 400000, each of which could be a target for a drug. There are good reasons for Schneider’s focus on nature in the search for new pharmaceutical agents. “Most natural products are by definition potential active ingredients that have been selected via evolutionary mechanisms,” he says.
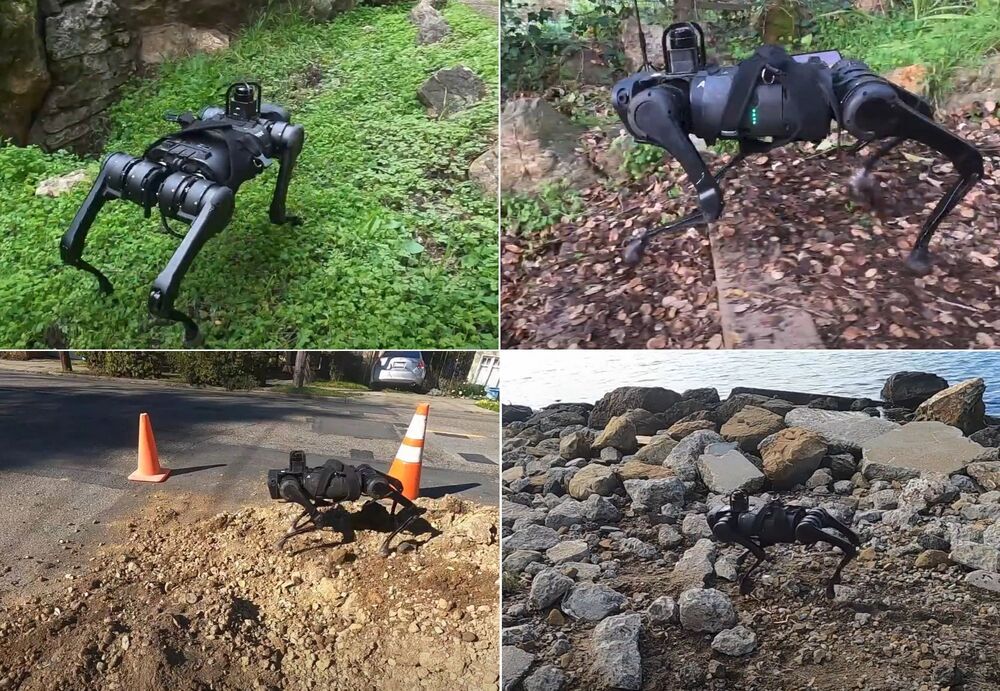

Stumble-proof robot adapts to challenging terrain in real time
Robots have a hard time improvising, and encountering an unusual surface or obstacle usually means an abrupt stop or hard fall. But researchers have created a new model for robotic locomotion that adapts in real time to any terrain it encounters, changing its gait on the fly to keep trucking when it hits sand, rocks, stairs and other sudden changes.
Although robotic movement can be versatile and exact, and robots can “learn” to climb steps, cross broken terrain and so on, these behaviors are more like individual trained skills that the robot switches between. Although robots like Spot famously can spring back from being pushed or kicked, the system is really just working to correct a physical anomaly while pursuing an unchanged policy of walking. There are some adaptive movement models, but some are very specific (for instance this one based on real insect movements) and others take long enough to work that the robot will certainly have fallen by the time they take effect.
The team, from Facebook AI, UC Berkeley and Carnegie Mellon University, call it Rapid Motor Adaptation. It came from the fact that humans and other animals are able to quickly, effectively and unconsciously change the way they walk to fit different circumstances.
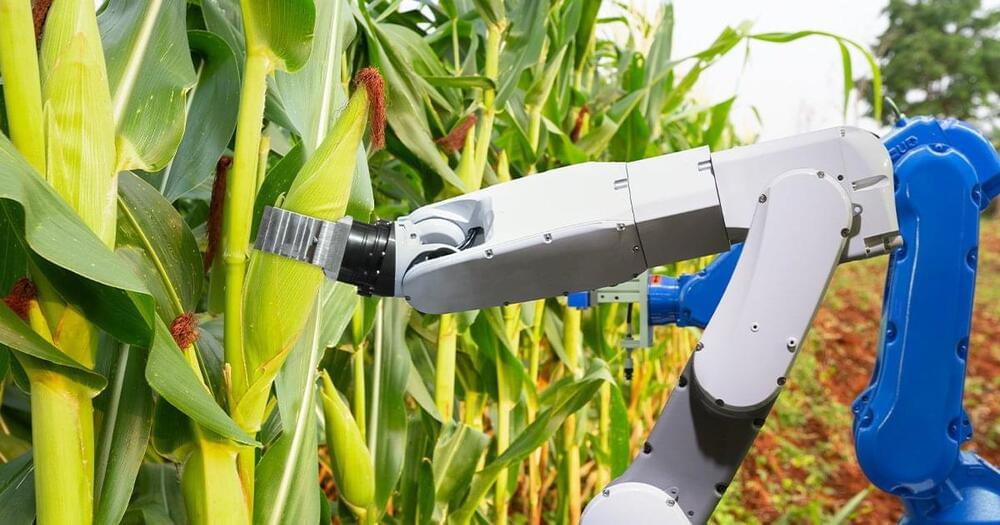

Australia’s First Fully Automated Smart Farm Will Use Only Robots For Field Work
The smart farm: To show just how much these technologies could help farmers, CSU and Food Agility have partnered to create the Global Digital Farm (GDF).
The smart farm will be built at CSU’s Wagga Wagga campus, and it will feature autonomous tractors, harvesters, and other farming robots, as well as AI programs designed to help with farm management and more.
Teachable moments: The plan isn’t for the GDF to simply demonstrate what a smart farm can look like — CSU and Food Agility want to use it to teach Australia’s farmers how to take advantage of all the tech that will be on display.
Facebook teaches AI-powered robot to adapt while walking
Researchers tested a four-legged robot on sand, oil, rocks and other tricky surfaces.

DARPA FENCE seeks to develop smart camera tech that mimics human brain
The US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has selected three teams of researchers led by Raytheon, BAE Systems, and Northrop Grumman to develop event-based infrared (IR) camera technologies under the Fast Event-based Neuromorphic Camera and Electronics (FENCE) program. It is designed to make computer vision cameras more efficient by mimicking how the human brain processes information. DARPA’s FENCE program aims to develop a new class of low-latency, low-power, event-based infrared focal plane array (FPA) and digital signal processing (DSP) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. The development of these neuromorphic camera technologies will enable intelligent sensors that can handle more dynamic scenes and aid future military applications.
New intelligent event-based — or neuromorphic — cameras can handle more dynamic scenes.
Meet PetBot, a DIY robot that turns plastic bottles into filaments
A new DIY robot called PetBot is a unique development that will help to recycle ordinary plastic bottles. The process is not yet fully automated, and the device does not claim to be used for commercial purposes, but the benefits of its operation are obvious. Built by JRT3D, the PetBot automates the plastic recycling process by cutting PET bottles into the tape and then turning them into filament. The robot combines several mechanics, each of which performs its part of the task. It carries out the two separate processes at the same time using the same stepper motor.
The machine automates the plastic recycling process by cutting PET bottles and turning them into filament.

This TikTok Lawsuit Is Highlighting How AI Is Screwing Over Voice Actors
AI taking over voice acting is just the beginning. Why cant the AI render and generate the game world all by itself. Why cant it generate the models, and actors for the game from scratch; and then use deepfake type animation to animate characters. And, then write an original script for the story. These things are all possible now. Only a matter of time before someone has the idea to put it all together.
Voice actors are rallying behind Bev Standing, who is alleging that TikTok acquired and replicated her voice using AI without her knowledge.