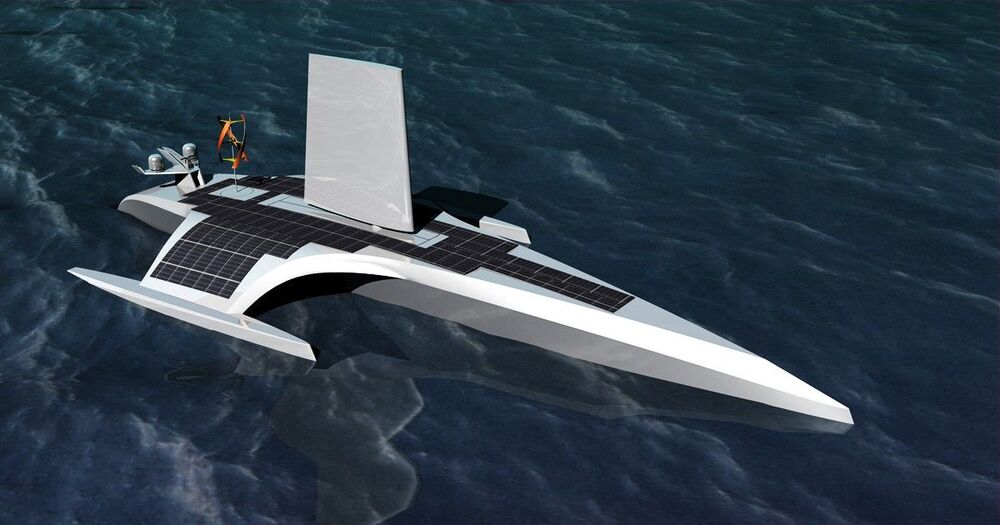
The new Mayflower, set to traverse the Atlantic in 2021, won’t bear any pilgrims. It’s a robot boat, sailing sailor-free.



One of my favorite science fiction authors is/was Isaac Asimov (should we use the past tense since he is no longer with us, or the present tense because we still enjoy his writings?). In many ways Asimov was a futurist, but — like all who attempt to foretell what is to come — he occasionally managed to miss the mark.
Take his classic Foundation Trilogy, for example (before he added the two prequels and two sequels). On the one hand we have a Galactic Empire that spans the Milky Way with millions of inhabited worlds and quadrillions of people. Also, we have mighty space vessels equipped with hyperdrives that can convey people from one side of the galaxy to the other while they are still young enough to enjoy the experience.
On the other hand, in Foundation and Empire, when a message arrives at a spaceship via hyperwave for the attention of General Bel Riose, it’s transcribed onto a metal spool that’s placed in a message capsule that will open only to his thumbprint. Asimov simply never conceived of things like today’s wireless networks and tablet computers and suchlike.
Nanobots, tiny nano-sized robots and vehicles that can navigate through blood vessels to reach the site of a disease could be used to deliver drugs to tumours that are otherwise difficult to treat.
Once injected or swallowed, most drugs rely upon the movement of body fluids to find their way around the body. It means that some types of disease can be difficult to treat effectively in this way.
One aggressive type of brain tumour known as glioblastoma, for example, kills hundreds of thousands of people a year. But because it produces finger-like projections into a patient’s brain tissue that damage the blood vessels around them, it is hard for drugs to reach the tumour site.
It’s been over for human fighter pilots, it will come down to who has the best AI fighter aircraft. AI will also take over ground combat vehicles (tanks), ships, and last will be armed humanoid robot combat soldiers.
The reported testing of AI against Chinese fighter pilots mirrors US military efforts and underscores China’s major investments in this technology.
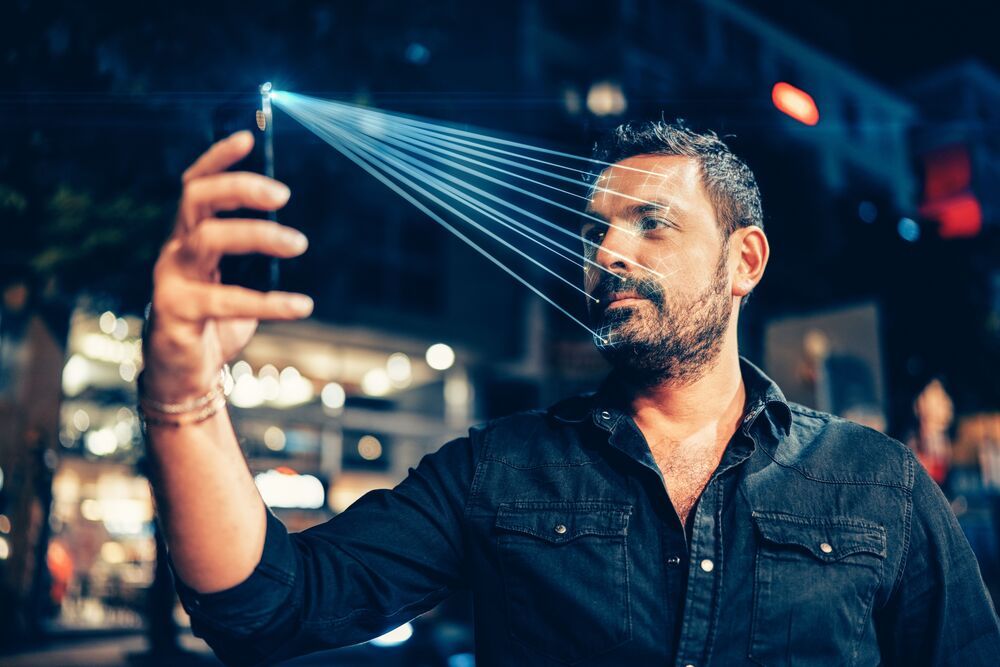

A recent string of problems suggests facial recognition’s reliability issues are hurting people in a moment of need. Motherboard reports that there are ongoing complaints about the ID.me facial recognition system at least 21 states use to verify people seeking unemployment benefits. People have gone weeks or months without benefits when the Face Match system doesn’t verify their identities, and have sometimes had no luck getting help through a video chat system meant to solve these problems.
ID.me chief Blake Hall blamed the problems on users rather than the technology. Face Match algorithms have “99.9% efficacy,” he said, and there was “no relationship” between skin tone and recognition failures. Hall instead suggested that people weren’t sharing selfies properly or otherwise weren’t following instructions.
Motherboard noted that at least some people have three attempts to pass the facial recognition check, though. The outlet also pointed out that the company’s claims of national unemployment fraud costs have ballooned rapidly in just the past few months, from a reported $100 billion to $400 billion. While Hall attributed that to expanding “data points,” he didn’t say just how his firm calculated the damage. It’s not clear just what the real fraud threat is, in other words.


We may have progressed beyond drinking mercury to try to prolong life. Instead, by a British government estimate, we have what may be called the ‘immortality industrial research complex’ – using genomics, artificial intelligence and other advanced sciences, and supported worldwide by governments, big business, academics and billionaires – that’s worth US$110 billion today and US$610 billion by 2025.
We are living longer than at any time in human history. And while the search is on for increased longevity if not immortality, new research suggests biological constraints will ultimately determine when you die.
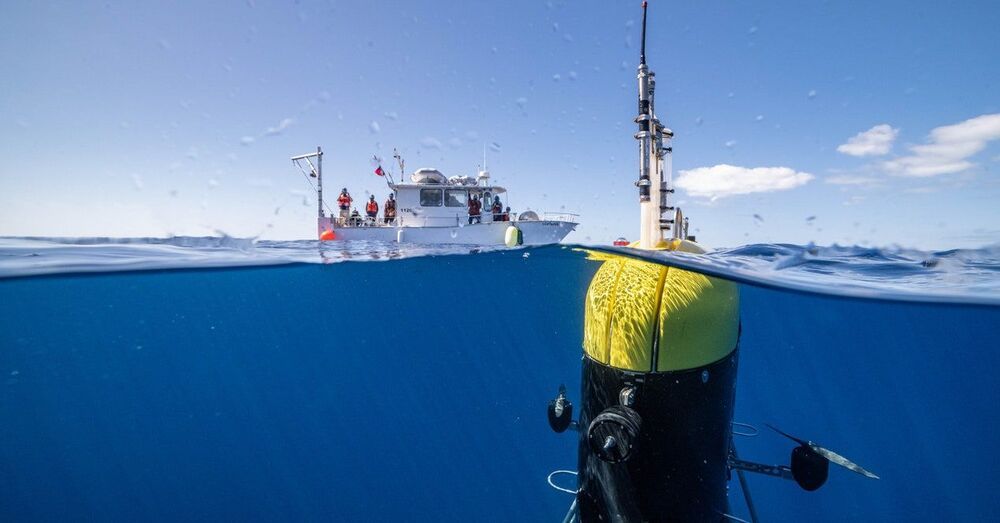

But now a spy swims among them: Mesobot. Today in the journal Science Robotics, a team of engineers and oceanographers describes how they got a new autonomous underwater vehicle to lock onto movements of organisms and follow them around the ocean’s “twilight zone,” a chronically understudied band between 650 feet and 3200 feet deep, which scientists also refer to as mid-water. Thanks to some clever engineering, the researchers did so without flustering these highly sensitive animals, making Mesobot a groundbreaking new tool for oceanographers.
“It’s super cool from an engineering standpoint,” says Northeastern University roboticist Hanumant Singh, who develops ocean robots but wasn’t involved in this research. “It’s really an amazing piece of work, in terms of looking at an area that’s unexplored in the ocean.”
Mesobot looks like a giant yellow-and-black AirPods case, only it’s rather more waterproof and weighs 550 pounds. It can operate with a fiber-optic tether attached to a research vessel at the surface, or it can swim around freely.