Circa 2016
From driverless buses to an AI council worker called Amelia, municipal services are becoming increasingly automated. But what does that mean for the future of our cities – and the jobs market?


Most computer systems are designed to store and manipulate information, such as documents, images, audio files and other data. While conventional computers are programmed to perform specific operations on structured data, emerging neuro-inspired systems can learn to solve tasks more adaptively, without having to be engineered to carry out a set type of operations.
Researchers at University of Pennsylvania and University of California recently trained a recurrent neural network (RNN) to adapt its representation of complex information based only on local data examples. In a paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence, they introduced this RNN and outlined the key learning mechanism underpinning its functioning.
“Every day, we manipulate information about the world to make predictions,” Jason Kim, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “How much longer can I cook this pasta before it becomes soggy? How much later can I leave for work before rush hour? Such information representation and computation broadly fall into the category of working memory. While we can program a computer to build models of pasta texture or commute times, our primary objective was to understand how a neural network learns to build models and make predictions only by observing examples.”


Welcome to the rapidly advancing world of autonomous weapons — the cheap, highly effective systems that are revolutionizing militaries around the world. These new unmanned platforms can make U.S. forces much safer, at far lower cost than aircraft carriers and fighter jets. But beware: They’re being deployed by our potential adversaries faster than the Pentagon can keep up, and they increase the risk of conflict by making it easier and less bloody for the attacker.
Artificial intelligence and drones are transforming the battlefield into something that looks more like a video game than hand-to-hand combat. It could save lives — but also increase the risk of combat.

“The Russian military is more technologically advanced than the U.S. realized and is quickly developing artificial intelligence capabilities to gain battlefield information advantage, an expansive new report commissioned by the Pentagon warned.”
Need more money for AI research.
A new report written for the Pentagon warns of more technologically advanced Russian force that’s focused on winning information advantage over the United States.
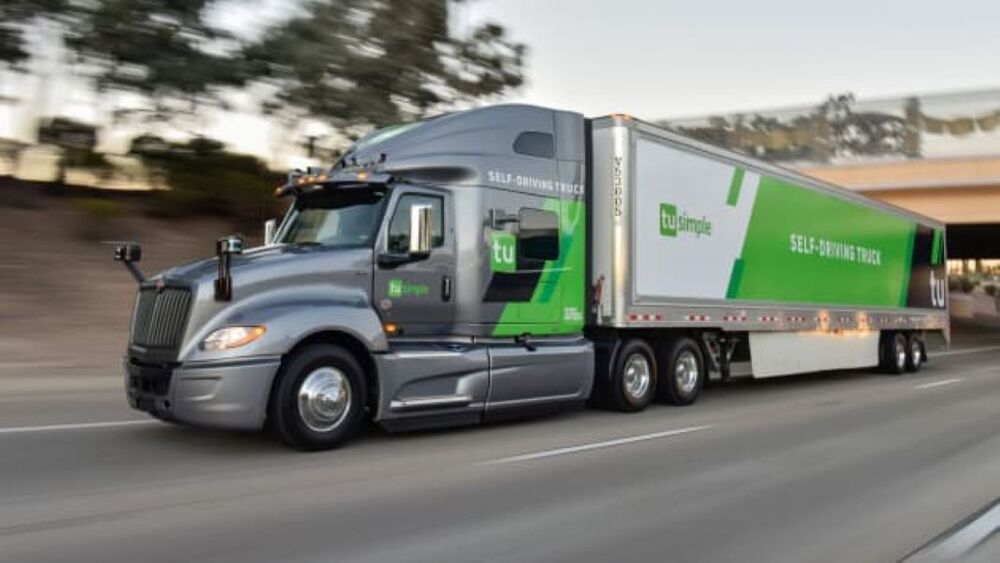

Self-driving cars are taking longer to come to market than many expected. In fact, it’s looking like they may be outpaced by pilotless planes and driverless trucks. A truck isn’t much different than a car, but self-driving technology is already coming in handy on long-haul trucking routes, as a recent cross-country trip showed.
Last month TuSimple, a transportation company focused on self-driving technology for heavy-duty trucks, shipped a truckload of watermelons from Arizona to Oklahoma using the truck’s autonomous system for over 80 percent of the journey. The starting point was Nogales, at Arizon’s southern end right on the border with Mexico. A human driver took the wheel for the first 60 miles or so, from Nogales to Tucson—but from there the truck went on auto-pilot, and not just for a little while. It drove itself all the way to Dallas, 950 miles to the east (there was a human safety driver on board the whole time, but not controlling the truck).
If you look at the most direct route, it’s pretty straightforward: there’s one fork where I-10 splits off and merges with I-20, but other than that, it’s straight on through ‘til morning. Literally, in this case; the truck drove the route in 14 hours and 6 minutes, as compared to the given estimate of the average time it takes a human to drive the same route—24 hours and 6 minutes.

😀
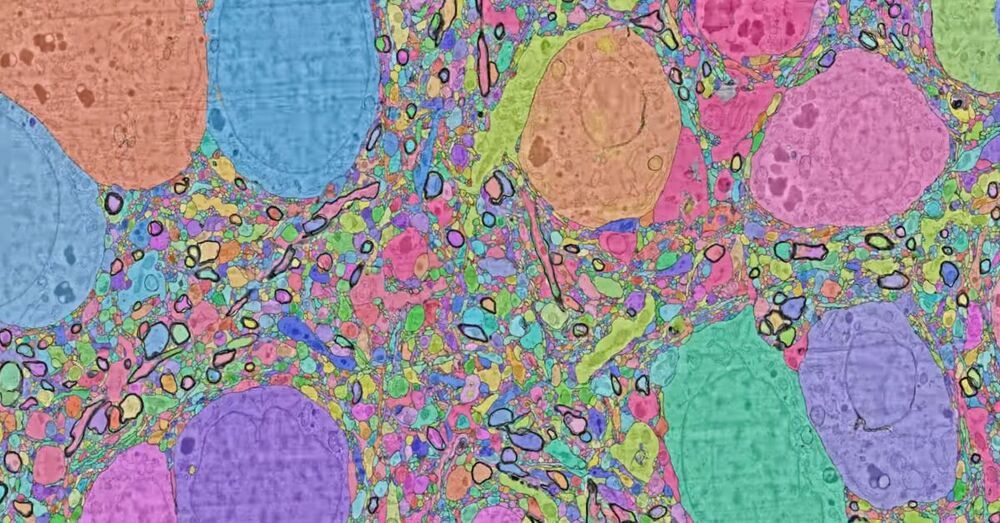
This sample tissue was anonymously donated from patients that have undergone surgery to treat epilepsy at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston (MGH). It was then given to researchers at Harvard’s Lichtman laboratory.
The Harvard researchers cut the tissue into ~5300 individual 30 nanometer sections using an automated tape collecting ultra-microtome, mounted those sections onto silicon wafers, and then imaged the brain tissue at 4 nm resolution in a customized 61-beam parallelized scanning electron microscope for rapid image acquisition.
The end result was 225 million individual 2D images that Google then computationally stitched and aligned into a 3D volume with thousands of Google Cloud TPUs were leveraged in the process. This human brain map is now accessible through Google’s web-based Neuroglancer visualization tool.
Satellite images showing the expansion of large detention camps in Xinjiang, China, between 2016 and 2018 provided some of the strongest evidence of a government crackdown on more than a million Muslims, triggering international condemnation and sanctions.
Other aerial images—of nuclear installations in Iran and missile sites in North Korea, for example—have had a similar impact on world events. Now, image-manipulation tools made possible by artificial intelligence may make it harder to accept such images at face value.
In a paper published online last month, University of Washington professor Bo Zhao employed AI techniques similar to those used to create so-called deepfakes to alter satellite images of several cities. Zhao and colleagues swapped features between images of Seattle and Beijing to show buildings where there are none in Seattle and to remove structures and replace them with greenery in Beijing.