Robotic hand manipulates thousands of objects with ease: bit.ly/3bI367h
At just one year old, a baby is more dexterous than a robot. Sure, machines can do more than just pick up and put down objects, but we’re not quite there as far as replicating a natural pull towards exploratory or sophisticated dexterous manipulation goes.
OpenAI gave it a try with “Dactyl” (meaning “finger” from the Greek word daktylos), using their humanoid robot hand to solve a Rubik’s cube with software that’s a step towards more general AI, and a step away from the common single-task mentality. DeepMind created “ RGB-Stacking ‚” a vision-based system that challenges a robot to learn how to grab items and stack them.
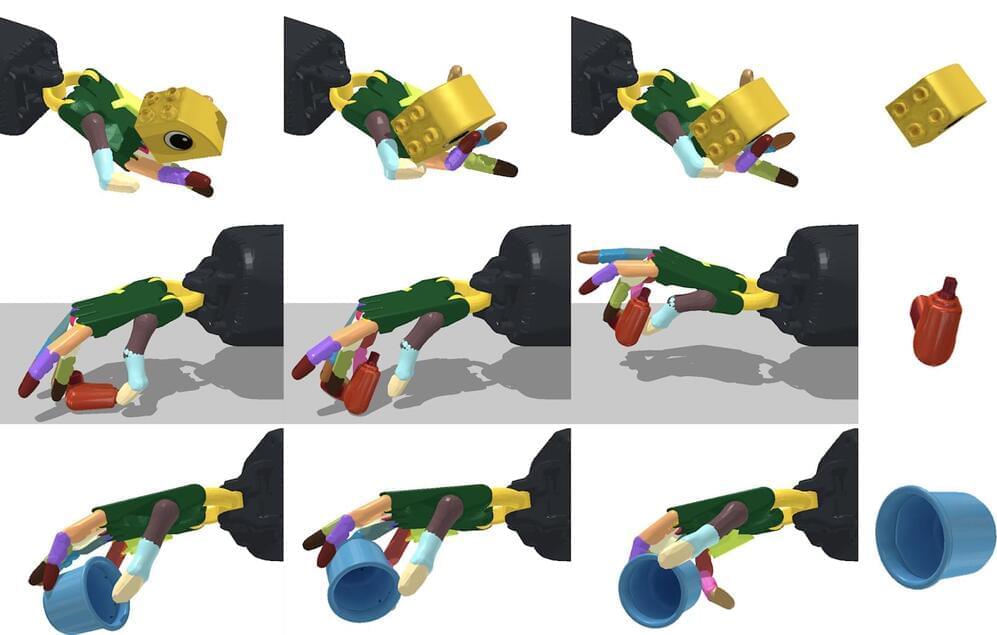
Scientists from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL), in the ever-present quest to get machines to replicate human abilities, created a framework that’s more scaled up: a system that can reorient over two thousand different objects, with the robotic hand facing both upwards and downwards. This ability to manipulate anything from a cup to a tuna can, and a Cheez-It box, could help the hand quickly pick-and-place objects in specific ways and locations — and even generalize to unseen objects.