SpaceX launches Crew-3, Tesla crashes, Elon Musk considers selling… again?
SpaceX launches Crew-3 and Starlink, Tesla’s Full Self-Driving potentially causes a crash, angered by Bernie Sanders, Elon Musk considers selling stock… again?
SpaceX launches Crew-3, Tesla crashes, Elon Musk considers selling… again?
SpaceX launches Crew-3 and Starlink, Tesla’s Full Self-Driving potentially causes a crash, angered by Bernie Sanders, Elon Musk considers selling stock… again?
Dr. Ben Goertzel with Philip K. Dick at the Web Summit in Lisbon 2019.
Ben showcases the use of OpenCog within the SingularityNET enviroment which is powering the AI of the Philip K. Dick Robot.
We apologise for the poor audio quality.
SingularityNET is a decentralized marketplace for artificial intelligence. We aim to create the world’s global brain with a full-stack AI solution powered by a decentralized protocol.
We gathered the leading minds in machine learning and blockchain to democratize access to AI technology. Now anyone can take advantage of a global network of AI algorithms, services, and agents.
Website: https://singularitynet.io.
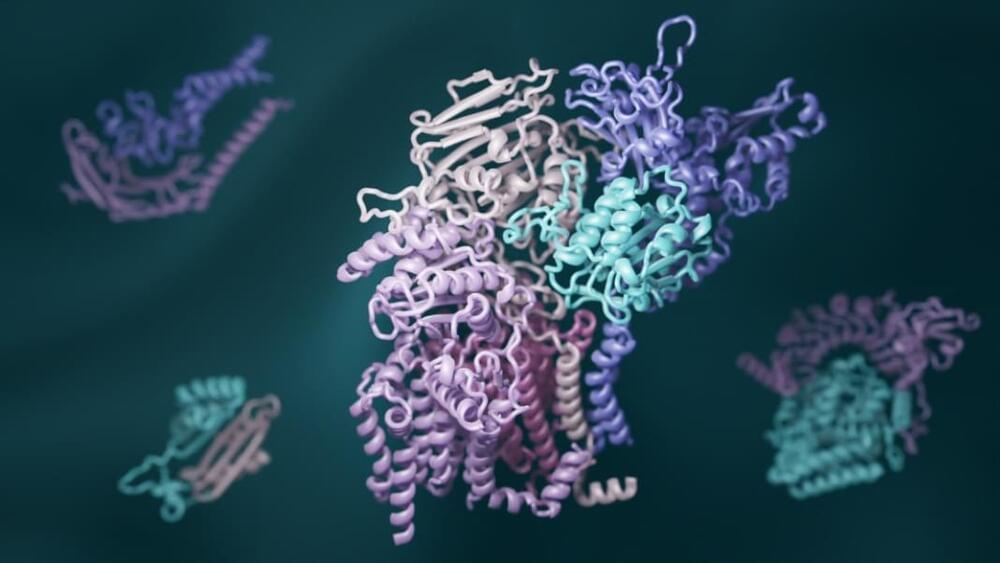
This month, the UW team upped their game.
Tapping into both AlphaFold and RoseTTAFold, they tweaked the programs to predict which proteins are likely to tag-team and sketched up the resulting complexes into a 3D models.
Using AI, the team predicted hundreds of complexes—many of which are entirely new—that regulate DNA repair, govern the cell’s digestive system, and perform other critical biological functions. These under-the-hood insights could impact the next generation of DNA editors and spur new treatments for neurodegenerative disorders or anti-aging therapies.

The year is almost at an end, and so it is once again time for the obligatory trends articles (Trends for 2022). We already know that AI is impacting every industry. In past articles I have covered “The tipping point”, the fact that AI is already immersed in our daily lives and with no end in sight. Here I outline seven areas where we can expect a greater involvement of AI in the lives of all of us, in 2022.
Data marketplaces.
AI thrives on data, and the rise and ubiquity of AI has placed a yet greater emphasis on the value of data as both a competitive advantage and a core asset to companies and countries alike. This in turn has risen to privacy laws and efforts to educate the public on how their data can be used. These efforts are geared towards giving individuals agency in exercising their data rights. The confluence of these factors is already leading to data marketplaces. Data marketplaces are online venues where individuals and corporations can buy and sell data. Data marketplaces have the potential to combine democratized access, privacy controls and monetization models to enable data owners to benefit from data use.
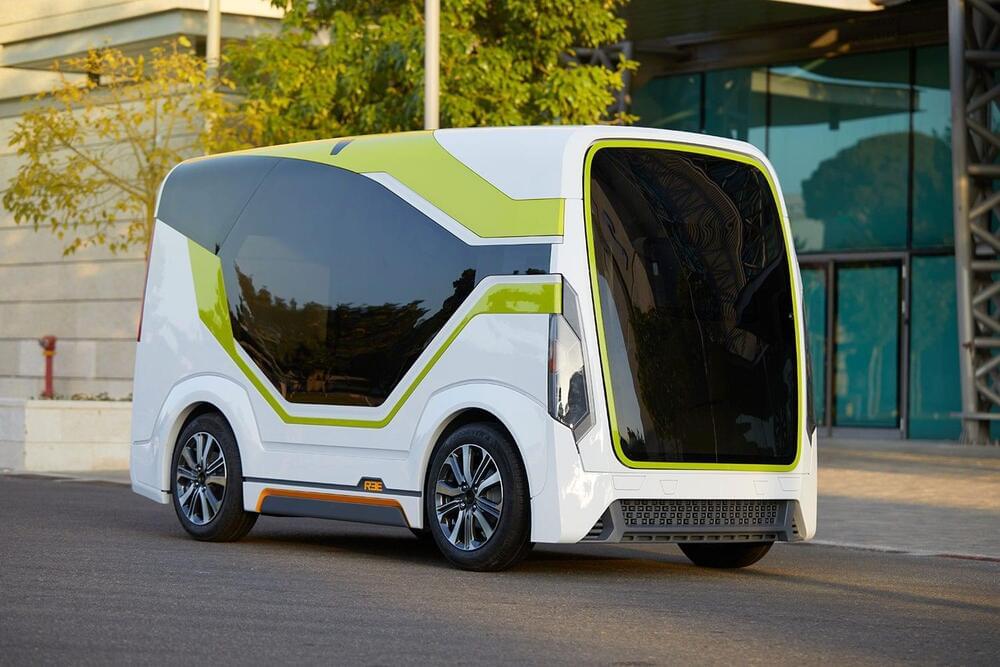

REE Automotive has revealed Leopard, its autonomous concept vehicle based on a brand new ultra-modular EV platform design. The full-scale concept is intended for customers, including last-mile autonomous and electric delivery companies, delivery fleet operators, e-retailers, and technology companies seeking to build fully autonomous solutions.
Developed with leading global delivery and technology companies focused on autonomous delivery and Mobility as a Service (MaaS) fleets, the Leopard concept vehicle measures 3.4 meters in length and just 1.4 meters in width. It is built on a home-brewed platform that contains the batteries, along with REEcorner units, front-wheel-steer, rear-wheel-drive, steering, suspension, motor, gearbox, and braking components.
Leopard is powered by a 50 kWh battery of unspecified range and an undisclosed type of electric motor that provides a top speed of 60 mph (96 km/h). It has a cargo capacity of 180 cubic feet (5 cubic meters) and a gross vehicle weight rating of 2 tonnes (2.2 tons). The vehicle is also designed to carry significantly more cargo due to REE’s low, flat floor.

Qualcomm is diversifying from mobile phones, to supplying chips for BMW’s self-driving cars.
#News #Reuters #BMW #Qualcomm #SelfDriving.
Subscribe: http://smarturl.it/reuterssubscribe.
Reuters brings you the latest business, finance and breaking news video from around the globe. Our reputation for accuracy and impartiality is unparalleled.
Get the latest news on: http://reuters.com/
Follow Reuters on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Reuters.
Follow Reuters on Twitter: https://twitter.com/Reuters.
Follow Reuters on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/reuters/?hl=en
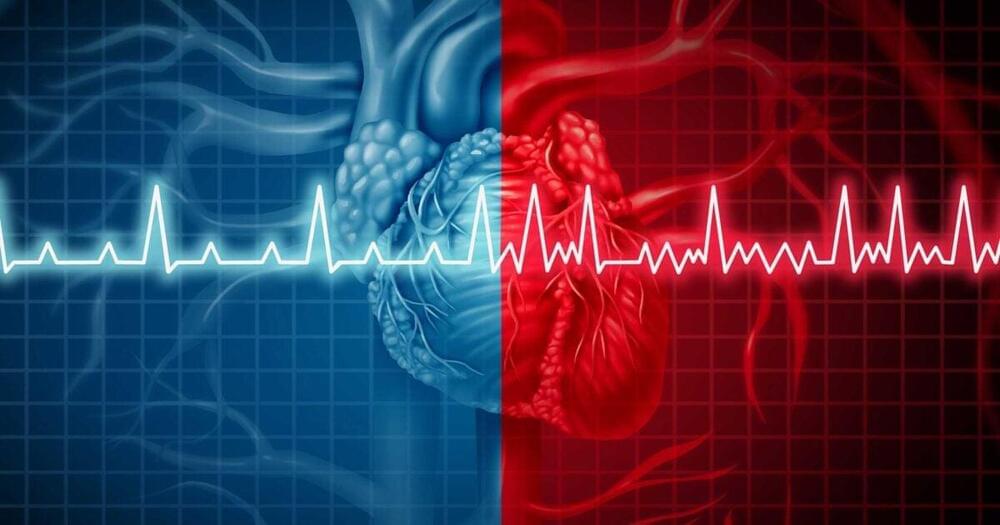
An artificial intelligence-based method for identifying patients who are at risk for atrial fibrillation has been developed by a team led by researchers at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard.
Atrial fibrillation — an irregular and often rapid heart rate — is a common condition that often leads to the formation of clots in the heart that can travel to the brain to cause a stroke. The study was published in Circulation.
The investigators developed the artificial intelligence-based method to predict the risk of atrial fibrillation within the next five years based on results from electrocardiograms (noninvasive tests that record the electrical signals of the heart) in 45,770 patients receiving primary care at MGH.
Ad Astra School is the experimental school that Elon Musk started in one of SpaceX’s factories to give an education to his own children and selected children of SpaceX employees. The future of work will require a set of skills that are not taught in schools today. The future of work will involve robots and Artificial Intelligence collaborating with humans. The Astra Nova School’s pillars include caring about community, focusing on student experiences, and sharing the work they do with the world.
Here students learn about simulations, case studies, fabrication and design projects, labs, and corporate collaboration. In general, school systems are rigid. They are more system-centric than student-centric. Astra Nova is changing that by creating a philosophy of student centricity, a value for individual abilities, praising curiosity, and encouraging problem-solving and critical thinking.
💰 Get Free Bitcoin on CoinBase: https://rb.gy/dhms0s.
💰 Earn Free Crypto: https://rb.gy/jf0q9n.
💰Get Free Stocks: https://rb.gy/2fy0a3My Favorite Editing Software:
▶ Adobe Premier Pro: https://rb.gy/qzfnsgMy Favorite Royalty Free Music Site:
▶ Epidemic Sounds: https://rb.gy/wssm4kFor more by Smart Sense subscribe now: https://bit.ly/36lGHuU
For the best videos be sure to subscribe and turn on the post notifications so you don’t miss any videos and once you’ve subscribed comment something nice for a shoutout.

SVT Robotics, a provider of software that orchestrates robots in warehouses and factories, has raised $25 million in series A funding led by Tiger Global with participation from Prologis Ventures, the company announced this morning. SVT says that it’ll use the new capital to bolster its product R&D and expand its customer outreach efforts.
According to cofounder and CEO A.K. Schultz, SVT’s platform helps customers to solve the growing “interoperability problem” in industrial automation. The industry is severely limited by its capacity to execute, he says. Integrations are typically custom-coded, translating to long, complex development cycles. A recent piece in Industry Today finds that factors ranking among the top concerns of manufacturers adopting automation include a lack of experienced workers to operate the machines, high transition expenses, and safety concerns.
“It’s expensive, and companies wait as much as a year or more for new automation to go live,” Schultz said in a statement. “Solving that problem with [SVT’s platform] empowers the market to grow at its full potential.”